
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
COVID - 19COVID - 19
RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONSRELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS
A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISMA GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
second report as of 28 April 2020second report as of 28 April 2020

Prepared by
UNWTO UNWTO
Sustainable Development of Tourism Department
COVID - 19COVID - 19
RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONSRELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS
A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISMA GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
second report as of 28 April 2020second report as of 28 April 2020

COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
AcknowledgmentsAcknowledgments
This second
report COVID-19 Related Travel Restrictions – A Global Review for Tourism
was developed by the
World Tourism Organization’s (UNWTO) Sustainable Development of Tourism Department. The report was
prepared under the supervision of Dr. Dirk Glaesser with lead contributions from Lorna Hartantyo, Marianna
Stori and Cordula Wohlmuther. Virginia Fernández-Trapa reviewed and provided feedback to the report.
Comments on the previous version of this report were provided by Sandra Carvao, Orianne Derrier, Hernán
Epstein, Harry Hwang, Beka Jakeli and Merjen Meretgulyyeva. Layout of the cover was provided by Alberto
G. Uceda and layout of the report by Javier P. Spuch.
We wish to thank Mrs Fiona Barron and Mr Rodolfo Losada from the World Food Programme for the
clarifications and support provided.

COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
1
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
Table of ContentsTable of Contents
1. Key Facts .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 2
2. Introduction ............................................................................................................................................................................................3
3. Overview on Global Travel Restrictions as of 20 April 2020 ..........................................................................................4
3.1 Volume and severity of travel restrictions under COVID-19 crisis .............................................................................. 4
3.2 Evolution of travel restrictions over time ..............................................................................................................................4
3.3 Categories of travel restrictions affecting tourists and travellers ..............................................................................6
3.4 Regional Breakdowns .......................................................................................................................................................................8
3.5 Lifting of travel restrictions ...........................................................................................................................................................8
Annex 1 Overview on the different categories and applying destinations as of 20 April 2020 ......................... 9
Annex 2 Overview on COVID-19 and pandemic measures, including travel restrictions .......................................11
Table of FiguresTable of Figures
Figure 1 - Travel restrictions as of 20 April 2020 ........................................................................................................................4
Figure 2 - Number of confirmed cases and destinations with COVID-19-related travel restrictions ..............5
Figure 3 - Destinations with travel restrictions as of 20 April 2020 ................................................................................. 5
Figure 4 - Changes in type of travel restriction over time ....................................................................................................6
Figure 5 - Category of travel restrictions by destination with COVID-19 travel restrictions ................................7
Figure 6 - Regional breakdown of travel restrictions as of 20 April 2020 ..................................................................... 8
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
2
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
• As of today, 100% of destinationsAs of today, 100% of destinations worldwide
have COVID-19 related travel restrictions in
place. Never before in history has international
travel been restricted in such an extreme
manner.
• 180 destinations, i.e. 83% of all destinations
worldwide, have COVID-19 related travel
restrictions now in place for
more than four more than four
weeksweeks.
• Out of these, 107 destinations, i.e. 49% of all
destinations worldwide, have closed their
borders or suspended flights for more than 4
weeks.
• Currently,
four main categories four main categories of travel
restrictions are in use, with three of them
consisting of total or partial bans to the entry
of travellers.
•
Out of 217 destinations worldwideOut of 217 destinations worldwide,
o 97 destinations (45%) have totally or
partially closed their borders for tourists -
“Passengers are not allowed to enter”.
o 65 destinations (30%) have suspended
totally or partially international flights -
“All flights are suspended”.
o 39 destinations (18%) are implementing the
closing of borders in a more differentiated
manner by banning the entry for passengers
from specific countries of origin -
“Passengers who have transited or been in
x are not allowed to enter”.
o The remaining 16 destinations (7%) are
applying different measures, such as
quarantine or self-isolation for 14 days or
visa measures.
•
As of 20 April 2020, no destination has lifted a As of 20 April 2020, no destination has lifted a
travel restriction.travel restriction.
1. Key Facts1. Key Facts
Source: Data compiled by UNWTO as of 20 April 2020
1
.
1 The maps elaborated by UNWTO are for reference only and do not imply any judgement on the legal status of any territory, or any endorsement or acceptance of
such boundaries.
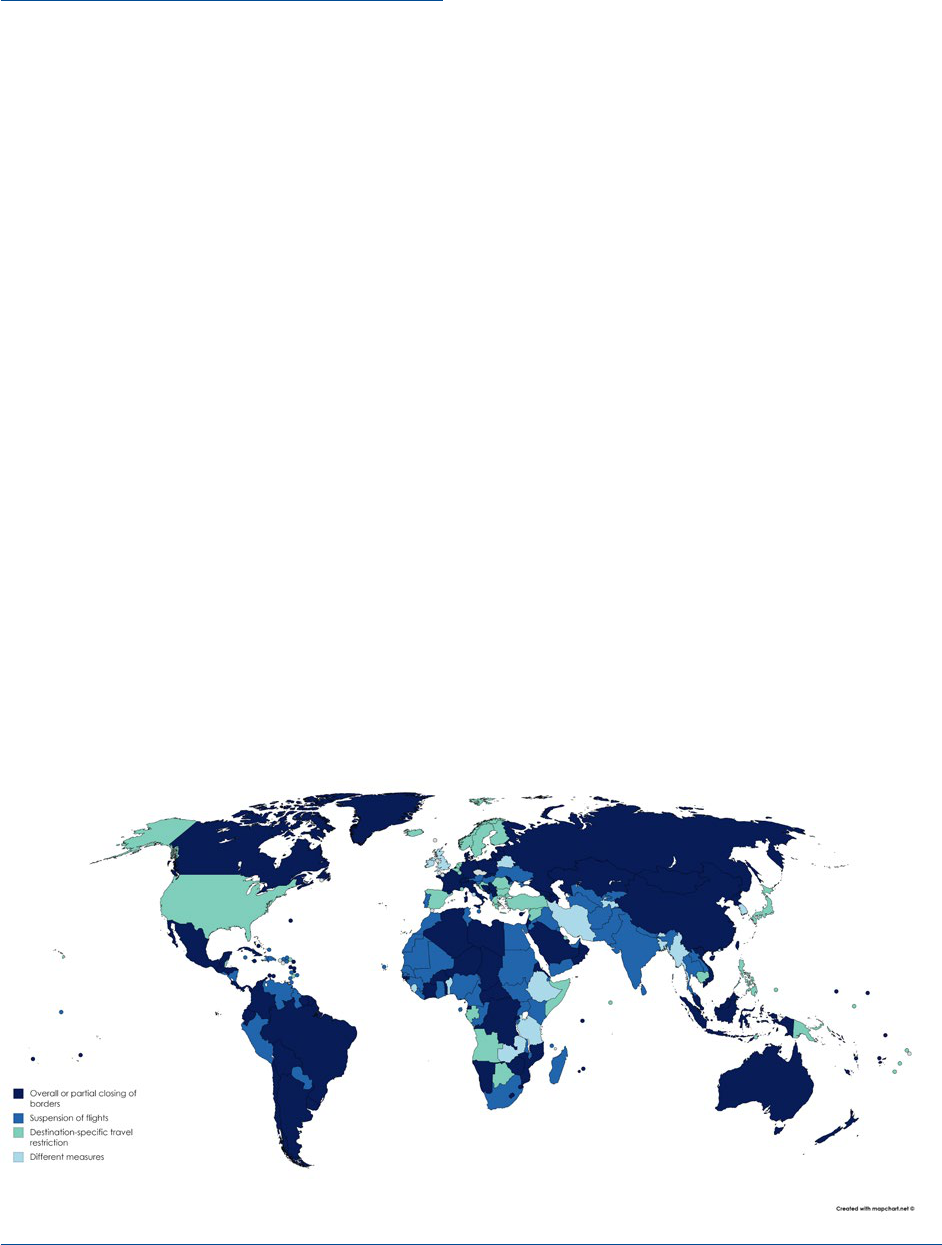
Figure A – Type of travel restriction by destination with COVID-19 travel restrictions

COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
2
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
3
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
This is the second issue of a series of reports on
COVID-19 Related Travel Restrictions – A Global
Review for Tourism, aimed at providing an overview
and analysis on the implementation of travel
restrictions by governments as one of the means
to address the global health crisis of COVID-19.
For the first time, UNWTO is reporting a historical
and unprecedented situation with 100% of
all destinations worldwide having introduced
COVID-19 related travel measures limiting or
interrupting entirely the access to their territories
for tourists.
The
UNWTO reports on COVID-19 Related Travel
Restrictions
are updated on a regular basis to
support mitigation and recovery efforts of the
tourism sector, providing a global overview of
the measures in place and analysing them from a
tourism perspective. With a view to supporting
the responsible and successful implementation
of exit strategies through which countries are
planning the gradual return to normality, the
report also aims at identifying critical issues and
best practices of COVID-19 related travel measures
and their implications on tourism.
The report is based on desk research carried out
from the end of January 2020 until 20 April 2020
and contains the results of monitoring all travel
restrictions that have been implemented during
this period. For this purpose, official websites
that provide such information, in particular the
International Air Transport Association (IATA)
Travel Centre
2
and the World Health Organization
(WHO) Extranet, as well as the International SOS
travel restrictions data contributing to the online
platform of the World Food Programme (WFP) on
global travel restrictions
3
, are reviewed on a regular
basis.
In addition, UNWTO contacted authorities
directly, when needed, to clarify the measures in
place.
The research includes the analysis of different
categories of travel restrictions, as well as their
respective evolution into more differentiated
and elaborated measures, and the timing of
their implementation and/or future lifting. The
monitoring of travel restrictions is carried out
from the standpoint of travel facilitation for
tourism purposes (i.e. focusing on temporary
visitors/tourists) and does not take into account
measures that are directed to residents, diplomats
and other categories of travellers. In addition, this
report does not consider travel advisories issued
by governments for their respective citizens/
residents.
This work is carried out by the World Tourism
Organization (UNWTO) Sustainable Development
of Tourism Department (SDT) that,
inter alia
,
monitors visa policies around the world since 2008
and produces the Visa Openness Reports, which
focus on entry requirements for tourism purposes.
4
2. Introduction2. Introduction
2 IATA Travel Centre, available online at: www.iatatravelcentre.com/.
3 International SOS is a medical and travel security services company, for more info on Travel restrictions, flight operations and screening see: https://pandemic.
internationalsos.com/2019-ncov/ncov-travel-restrictions-flight-operations-and-screening.
4 World Tourism Organization, Travel Facilitation reports, available online at: www.unwto.org/sustainable-development/travel-facilitation.

COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
4
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
3.1 Volume and severity of travel 3.1 Volume and severity of travel
restrictionsrestrictions
UNWTO has been monitoring travel restrictions
and facilitation measures for several years. The
regularly published UNWTO Visa Openness
reports
5
have shown a continuously growing
trend for more than a decade on the number of
destinations facilitating visa policies for temporary
visitors (tourists). When reporting last in 2018, the
world openness reached its highest level ever, with
an openness of 37 index points.
6
The current COVID-19 crisis has impacted on travel
like no other event before. For the first time in
history, all destinations worldwide have imposed
travel restrictions, including the full closure of
borders for travellers in many destinations (Figure 1).
3.2 Evolution of travel restrictions over 3.2 Evolution of travel restrictions over
timetime
When on 30 January 2020 the World Health
Organization declared COVID-19 a Public Health
Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC), 11
destinations had already implemented travel
restrictions directed at travellers coming from China
and prohibiting their entry into the destination. Six
days later, on 5 February 2020, this number had
grown four times and reached 40 destinations.
Within another 5 days, on 10 February 2020, the
number of destinations with travel restrictions had
grown to 56. By then, 24 destinations worldwide
had reported confirmed cases of COVID-19.
With the spread of COVID-19 cases in an increasing
number of countries, the number of travel
restrictions has also grown (Figure 2).
3. Overview on Global Travel 3. Overview on Global Travel
Restrictions as of 20 April 2020Restrictions as of 20 April 2020
Source: Data compiled by UNWTO as of 20 April 2020.
5 World Tourism Organization, Travel Facilitation reports, available online at: www.unwto.org/sustainable-development/travel-facilitation.
6 The Openness Index ranges from 0 – 100 and is calculated by summing the percentage of the world population affected by no visa weighted by 1, visa on arrival
weighted by 0.7, eVisa by 0.5 and traditional visa weighted by 0.
Figure 1 - Travel restrictions as of 20 April 2020

COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
4
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
5
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
On 11 March 2020, when WHO declared COVID-19
a pandemic, a total of 85 destinations had travel
restrictions already in place. The declaration of
the pandemic triggered a new wave of travel
restrictions, which included the beginning of the
implementation of such measures also in European
countries. As a result, between 9 and 16 March 2020,
an additional 38 destinations introduced travel
restrictions, out of which 20 were from Europe,
bringing the total to 119 destinations worldwide.
By 24 March 2020, the number of destinations
with restrictions more than doubled, from 85 to
181 destinations, an increase of 112%.
From 24 March to 20 April 2020, all remaining
destinations introduced travel restrictions bringing
the total to 217 destinations, representing 100% of
destinations worldwide (Figure 3).
As of today, 180 destinations, i.e. 83% of all
destinations worldwide have COVID-19 related
travel restrictions now in place for more than four
weeks. Out of these, 107 destinations, i.e. 49% of
all destinations globally have closed their borders
or suspended flights.
Figure 2 - Number of confirmed cases and destinations with COVID-19-related travel restrictions
Figure 3 - Destinations with travel restrictions as of 20 April 2020
Source: Data compiled by UNWTO as of 20 April 2020, based on desk research from IATA Travel Centre, WHO Extranet and International SOS.
Source: Data compiled by UNWTO as of 20 April 2020.

COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
6
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
3.3 Categories of travel restrictions 3.3 Categories of travel restrictions
affecting tourists and travellersaffecting tourists and travellers
At the beginning of the crisis two main categories
of travel restrictions were observed, one directed
at passengers coming from a country that had
confirmed COVID-19 cases and the other one
being the invalidation or suspension of visa.
Over time additional measures were observed,
such as the request for medical certificates upon
arrival at a destination or the request for self-
isolation or quarantine.
Once WHO declared COVID-19 a pandemic, two
new, more extreme categories of travel restrictions
started to be applied, namely the complete and
partial closure of borders and suspension of flights
by governments. These two categories are, at the
current date, used by the majority of destinations
(75%) (Figure 4).
The four broad categories of travel restrictions
under implementation in 217 destinations as of 20
April 2020 are as follows:
o 97 destinations (45%) have totally or partially
closed their borders for tourists - “Passengers
are not allowed to enter”.
Figure 4 - Changes in type of travel restriction over time
Source: Data compiled by UNWTO as of 20 April 2020.
Note: Different measures include:
Visa: includes the invalidation of visa, destinations are no longer visa-exempt or visa cannot be obtained upon arrival any longer
Regional: travel restriction directed at a region (sub-national) within a country, and not the whole country as such
Quarantine: quarantine or self-isolation requirement
Nationality: directed at a nationality

COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
6
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
7
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
o 65 countries (30%) have suspended totally or
partially international flights - “all flights are
suspended”.
o 39 destinations (18%) are implementing the
closing of borders in a more differentiated
manner by banning the entry for passengers
from specific countries of origin - “Passengers
who have transited or been in x are not allowed
to enter”.
o The remaining 16 destinations (7%) are applying
different measures, such as quarantine or self-
isolation for 14 days or visa measures.
Figure 5 - Category of travel restrictions by destination with COVID-19 travel restrictions
Source: Data compiled by UNWTO as of 20 April 2020.

COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
8
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
3.4 Regional analysis of travel restrictions 3.4 Regional analysis of travel restrictions
In the regions of the Middle East (54%) and Africa
(45%) the measure of suspending flights prevails
over other types of measures, while in the Americas
(51%), Europe (48%) and Asia and the Pacific (46%),
it is the closure of borders (total or partial) which
is more dominant.
With regard to measures focusing on differentiated
travel restrictions aimed at specific countries, it is
in Europe where more of these measures are under
implementation (28%) followed by Asia and the
Pacific (24%) (Figure 6).
3.5 Lifting of travel restrictions 3.5 Lifting of travel restrictions
As of 20 April 2020, no destination has lifted a
travel restriction introduced in the context of
COVID-19.
Figure 6 - Regional breakdown of travel restrictions as of 20 April 2020
Source: Data compiled by UNWTO as of 20 April 2020.

COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
8
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
9
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
Overview on the different Overview on the different
categories and applying categories and applying
destinations as of 20 April 20207destinations as of 20 April 20207
Total or partial closing of borders - Total or partial closing of borders -
“Passengers are not allowed to enter x”“Passengers are not allowed to enter x”
Applied by 97 destinations (45% of all destinations Applied by 97 destinations (45% of all destinations
worldwide).worldwide).
Algeria, Andorra, Argentina, Armenia, Aruba,
Australia, Azerbaijan, Bahamas, Bermuda, Bolivia,
Bosnia and Herzegovina, Brazil, Brunei Darussalam,
Burkina Faso, Canada, Central African Republic,
Chad, Chile, China, Colombia, Congo DR, Cook
Islands, Costa Rica, Cote D’Ivoire, Cuba, Curaçao,
Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Dominica, Ecuador,
Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Estonia, Eswatini, Fiji,
France, French Guiana, French Polynesia, Georgia,
Germany, Guadeloupe, Guatemala, Guinea Bissau,
Honduras, Hong Kong SAR, Indonesia, Israel, Italy,
Kazakhstan, Korea DPR, Latvia, Lesotho, Libya,
Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Malaysia, Marshall Islands,
Martinique, Mauritius, Mexico, Federated States
of Micronesia, Moldova, Mongolia, Montenegro,
Montserrat, Mozambique, Namibia, New Caledonia,
New Zealand, Niger, North Macedonia, Oman,
Panama, Poland, Qatar, Reunion, Russian Federation,
Rwanda, San Marino, Saudi Arabia, Serbia, Seychelles,
Singapore, Slovakia, Solomon Islands, St. Maarten,
Suriname, Switzerland, Taiwan Province of China,
Togo, Tuvalu, Uruguay, Vanuatu, Vietnam, Zimbabwe.
Suspension of Flights- partially or totally - Suspension of Flights- partially or totally -
“All flights are suspended”“All flights are suspended”
Applied by 65 destinations (30% of all destinations Applied by 65 destinations (30% of all destinations
worldwide).worldwide).
Afghanistan, Albania, Anguilla, Barbados, Burundi,
Cabo Verde, Cameroon, Cayman islands, Comoros
Islands, Congo, Djibouti, Dominican Republic, Egypt,
El Salvador, Gambia, Ghana, Grenada, Guinea (Rep.),
Guyana, Haiti, Hungary, India, Iraq, Jordan, Kenia,
Kiribati, Kuwait, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Lebanon, Liberia,
Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Malta, Mauritania,
Morocco, Nepal, Nicaragua, Nigeria, Pakistan,
Paraguay, Peru, Portugal, Sao Tomé and Principe,
Senegal, Slovenia, South Africa, South Sudan, Sri
Lanka, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Lucia, Sudan, Thailand,
Trinidad and Tobago, Tunisia, Turkmenistan, Turks
and Caicos Islands, Uganda, Ukraine, United Arab
Emirates, Uzbekistan, Venezuela, Virgin Islands
British, Yemen.
Destination-specific travel restrictions aimed Destination-specific travel restrictions aimed
at passengers from specific countries - at passengers from specific countries -
“Passengers who have transited or been in x “Passengers who have transited or been in x
are not allowed to enter x”are not allowed to enter x”
Applied by 39 destinations (18% of all destinations Applied by 39 destinations (18% of all destinations
worldwide).worldwide).
Angola, Antigua and Barbuda, Austria, Bahrain,
Belgium, Belize, Bonaire, Botswana, Bulgaria,
Cambodia, Croatia, Finland, Gabon, Greece, Iceland,
Japan, Luxembourg, Maldives, Monaco, Nauru,
Netherlands, Niue, Norway, Palau, Papua New
Guinea, Philippines, Romania, Saba, Samoa, Somalia,
Spain, St. Eustatius, St. Vincent and Grenadines,
Sweden, Syrian Arab Republic, Timor Leste, Tonga,
Turkey, United States of America.
Annex 1Annex 1
7 Some destinations apply more than one measure, in this case the measure affecting tourists most is used for the purpose of this analysis.
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
10
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
Quarantine or self-isolation related measures Quarantine or self-isolation related measures
Applied by 10 destinations (5% of all destinations Applied by 10 destinations (5% of all destinations
worldwide).worldwide).
Belarus, Benin, Ethiopia, Ireland, Puerto Rico, Sierra
Leone, Tajikistan, Tanzania, United Kingdom, Zambia.
Visa measures - Visa are invalidated or Visa measures - Visa are invalidated or
no longer visa exempt or visa cannot be no longer visa exempt or visa cannot be
obtained any longer upon arrival obtained any longer upon arrival
Applied by 5 destinations (2% of all destinations Applied by 5 destinations (2% of all destinations
worldwide). worldwide).
Bangladesh, Bhutan, Iran, Myanmar, Republic of
Korea.
Regional (sub-national) specific travel Regional (sub-national) specific travel
restriction within a country - “Passengers who restriction within a country - “Passengers who
reside or visitors who have been in region x reside or visitors who have been in region x
of a destination x in the past 14 days are not of a destination x in the past 14 days are not
allowed to enter destination x”allowed to enter destination x”
Applied by 1 destination.Applied by 1 destination.
Macao SAR.

COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
10
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
11
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
Overview on COVID-19 and pandemic Overview on COVID-19 and pandemic
measures, including travel restrictionsmeasures, including travel restrictions
On 31 December 2019, a pneumonia of unknown
cause was detected first in Wuhan, China and
reported to the local WHO office. Four weeks
later, on 30 January 2020 the WHO declared the
outbreak of this virus, initially named 2019-nCoV, a
Public Health Emergency of International Concern
(PHEIC). At that stage WHO referred to 83 cases in
18 countries
8
and did not recommend any travel or
trade restriction. In a joint statement by UNWTO and
WHO released on 26 February 2020, it was indicated
that “Tourism’s response needs to be measured
and consistent, proportionate to the public health
threat and based on local risk assessment, involving
every part of the tourism value chain”.
9
While from end of December 2019 until end of
February 2020 China reported the largest amount
of COVID-19 cases, by February 2020 the virus had
already spread almost all over the globe. When
WHO declared COVID-19 a pandemic on 11 March
2020, 114 countries had reported 118,000 cases with
Europe becoming the worst-affected region. As of
20 April 2020, there are worldwide reported 2 314
621 COVID-19 cases with 157 847 deaths.
10
Based on the WHO Pandemic Influenza Preparedness
and Response guidance document for governments
11
,
a variety of measures have been implemented
worldwide in order to reduce the spread of the
virus. These include individual measures, such as the
promotion of hand and respiratory hygiene, as well
as societal level measures, such as protocols related
to social distancing which include the suspension
Annex 2Annex 2
of school classes, adjusting work patterns, the
reduction of unnecessary travel and overcrowding of
mass transport systems as well as the development
of frameworks for cancellation/restriction of mass
gatherings.
12
Moreover, with regards to international
travel, measures to “develop capacities for emergency
public health actions at designated points of entry
in accordance with International Health Regulations
(IHR) (2005) Annex 1 B.2.”, which include relevant
control mechanisms for arriving and departing
travellers, have been implemented.
Furthermore, additional provisions of the IHR
13
have guided the introduction of measures. For
instance, under Chapter III on special provisions
for travellers, the treatment of suspected travellers
when entering a destination is outlined, ranging
from medical examination to providing the person
with food and water.
14
Also under IHR Article 43, it
is stated that additional health measures shall be
based on scientific principles, available scientific
evidence and available specific guidance of WHO.
In this context, the implementation of additional
health measures that significantly interfere with
international traffic, shall be reported to WHO
within 48 hours, including the public health rationale
and relevant scientific information. Significant
interference means “refusal of entry or departure of
international travellers, baggage, cargo, containers,
conveyances, good, and the like, or their delay, for
more than 24 hours”. The IHR stipulates that WHO
shall share this information with other governments
and request that the measure is reviewed within
three months. Furthermore, WHO may request a
government that implemented such measure to
reconsider its application.
15
8 World Health Organization (2020),
Statement on the second meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee regarding the outbreak
of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV),
30 January 2020, available online at: www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-meeting-of-the-
international-health-regulations-(2005)-emergency-committee-regarding-the-outbreak-of-novel-coronavirus-(2019-ncov).
9 World Tourism Organization, World Health Organization (2020),
Joint statement on tourism and covid-19: UNWTO and WHO call for responsibility and coordination,
26 February 2020, available online at: https://webunwto.s3.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/s3fs-public/2020-03/31012020%20Coronavirus_Feb_2020%20EN_3.pdf.
10 World Health Organization, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Situation report 91, available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/
situation-reports/20200420-sitrep-91-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=fcf0670b_4.
11 International Health Regulations (2005), Third Edition, WHO, pp. 40-42, available online at: www.who.int/ihr/publications/9789241580496/en.
12 International Health Regulations (2005).
13 International Health Regulations (2005).
14 International Health Regulations (2005), pp. 23-24.
15 International Health Regulations (2005), pp. 29.

COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
12
COVID-19 RELATED TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS – A GLOBAL REVIEW FOR TOURISM
