
School Entrance Age:
Primary school - Age 6
Duration and Official Ages for School Cycle:
Primary : 7 years - Ages 6 - 12
Lower secondary : 3 years - Ages 13 - 15
Upper secondary : 2 years - Ages 16 - 17
Academic Calendar:
Starting month : January
Ending month : October
Mozambique
In Mozambique, the academic year begins in January and ends in October, and the official primary school entrance age is 6. The system is structured so that the primary school cycle lasts 7 years, lower
secondary lasts 3 years, and upper secondary lasts 2 years. Mozambique has a total of 7,355,000 pupils enrolled in primary and secondary education. Of these pupils, about 6,139,000 (83%) are enrolled
in primary education. Figure 3 shows the highest level of education reached by youth ages 15-24 in Mozambique. Although youth in this age group may still be in school and working towards their
educational goals, it is notable that approximately 12% of youth have no formal education and 48% of youth have attained at most incomplete primary education, meaning that in total 59% of 15-24 year
olds have not completed primary education in Mozambique.
SCHOOL PARTICIPATION AND EFFICIENCY
OVERVIEW
Region: Sub-Saharan Africa
Income Group: Low Income
Source for region and income groupings: World Bank 2018
National Education Profile
2018 Update
The percentage of out of school children in a country shows what proportion of children are not currently participating in the education system and who are, therefore, missing out on the benefits of
school. Figure 5 looks at the percentage of youth of secondary school ages who are out of school in Mozambique. Nearly 44% of female youth of secondary school age are out of school compared to 32%
of male youth of the same age. For youth of secondary school age, the biggest disparity can be seen between the poorest and the richest youth.
Primary
6,139
Lower
Secondary
811
Upper
Secondary
405
Data Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics 2017
FIG 2. NUMBER OF PUPILS BY SCHOOL LEVEL
(IN 1000S)
25
#N/A
14
29
5
37
24
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Male Female Urban Rural Richest
Quintile
Poorest
Quintile
Total
Gender Urbanicity Income Total
% of Children Out of School
Data source: EPDC extraction of DHS dataset 2011
FIG 4. PERCENTAGE OF CHILDREN OF PRIMARY SCHOOL AGE
(AGES 6-12) OUT OF SCHOOL
No Education
11%
Primary
Incomplete
48%
Primary Complete
14%
Secondary
Incomplete
24%
Secondary
Complete
2%
Post-
Secondary
1%
Data source: EPDC extraction of DHS dataset 2011
FIG 3. EDUCATIONAL ATTAINMENT, YOUTH
AGES 15-24
FIG 1. EDUCATION SYSTEM
Data source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics
32
44
23
47
15
57
38
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Male Female Urban Rural Richest
Quintile
Poorest
Quintile
Total
Gender Urbanicity Income Total
% of Children Out of School
Data source: EPDC extraction of DHS dataset 2011
FIG 5. PERCENTAGE OF CHILDREN OF SECONDARY SCHOOL AGE
(AGES 13-17) OUT OF SCHOOL
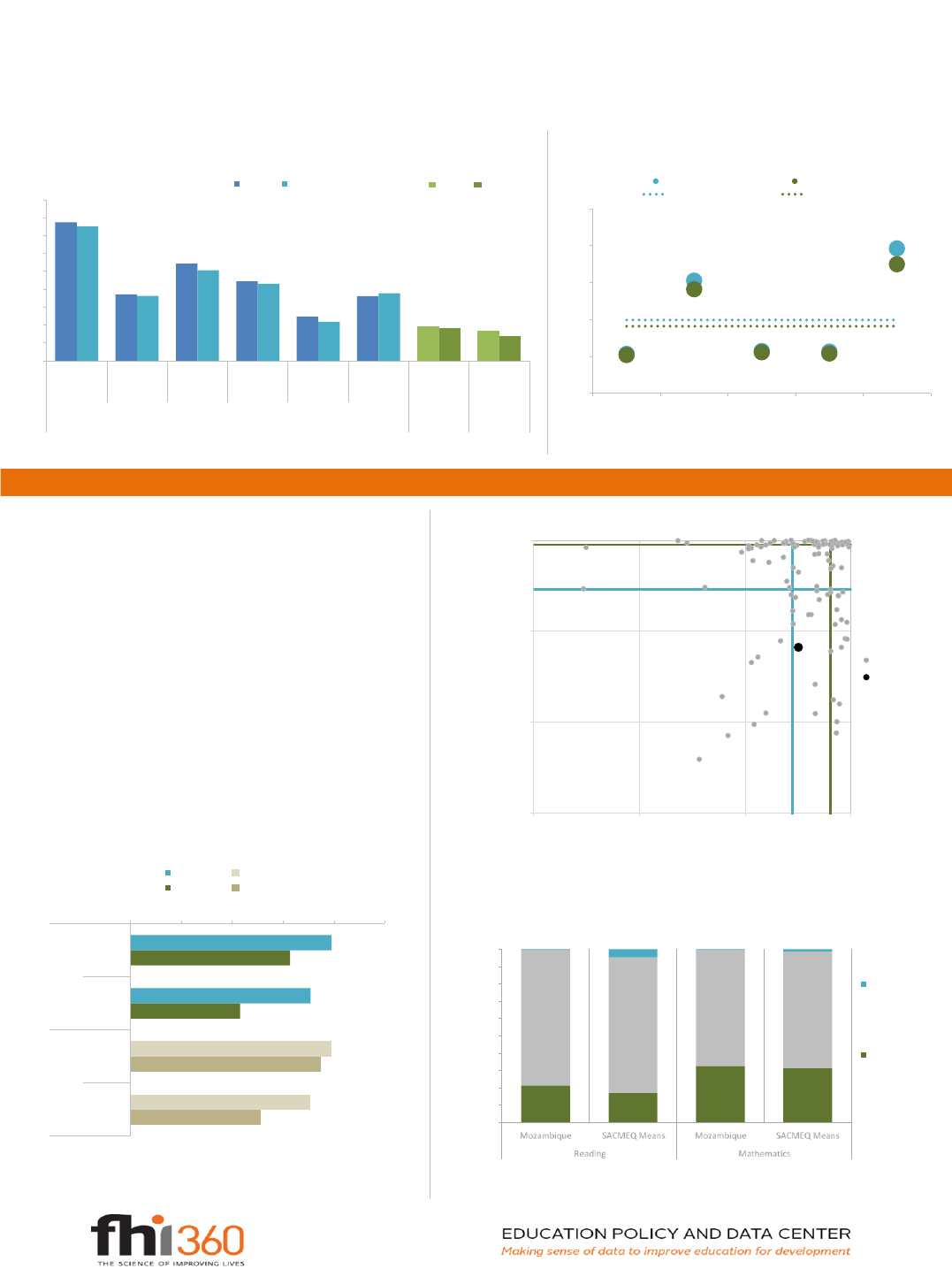
Figures 6 and 7 look at indicators of participation, completion, and progression in the education system. Figure 6 displays gross indicators (which include under- and over-age students) and net indicators
(which include only on-time students of official school age) for student intake, participation, and flows. In Mozambique, the gross enrollment rate in primary education is 105% for both girls and boys
combined. This decreases to 38% in lower secondary, with a student transition rate to secondary school of 74%. In Mozambique, the primary net enrollment rate is 88% and the primary completion rate
is 46%. Both of these indicators provide a sense of the progress a country is making towards universal primary education -- a key UN Millenium Development Goal -- and, for Mozambique, suggest that
the country has yet to achieve universal primary education. Figure 7 displays the repetition rate in primary education, showing the specific grades in which students are more likely to repeat. It suggests
that of the first 5 grades of primary in Mozambique, students are more likely to repeat grade 5. The repetition rate in grade 5 is 18.6% (for both males and females), which is 9.1 points higher than the
average repetition rate across primary grades of 9.5%.
LEARNING
This section provides information on indicators of learning, which lend insight into the
quality of educational provision. In this profile, learning is measured through literacy
rates, which are important because literacy is a foundational skill needed to attain
higher levels of learning, and national performance on learning assessments. Figure 8
demonstrates where Mozambique stands in comparison to other low and middle
income countries in access to education, measured as the primary school net enrollment
rate, and youth literacy. Compared to other countries, Mozambique ranks at the 40
percentile in access and at the 14 percentile in learning. Figure 9 compares youth and
adult literacy rates and shows that, in Mozambique, the literacy rate is 71% among the
youth population; this is lower than the average youth literacy rate in other low income
countries. Figure 10 looks at the most recent SACMEQ reading and SACMEQ math
assessment results for Mozambique in Grade 6, administered in 2007. It displays the
percentage of test takers that have fallen below the lowest performance levels and the
percentage of test takers that have exceeded the highest performance levels in these
assessments. Nearly 22% of test takers in Mozambique performed below the lowest
performance benchmark in reading, compared to an average of 17% for other countries
that took the same assessment. To learn about assessment data and what
competencies correspond with performance benchmarks, see www.epdc.org/data-
about-epdc-data/about-epdc-learning-outcomes-data.
25
50
75
100
25 50 75 100
Other countries
Mozambique
Literacy
(Youth)
Access
(Primary NER)
33rd percentile
33rd percentile
66 th percentile
66 th percentile
Data source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) (see Data Table for year)
FIG 8. COMPARISON OF ACCESS AND LITERACY
79
71
79
71
63
43
75
51
0 20 40 60 80 100
age 15-24
age 15+
age 15-24
age 15+
Mozambique
Low Income countries
(median)
%
Male
Female
Data source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) (see Data Table for year)
Male
Female
FIG 9. LITERACY RATE AMONG YOUTH AND ADULT
POPULATION
155
74
109
89
49
72
38
34
151
73
101
86
44
76
37
28
0.0
20.0
40.0
60.0
80.0
100.0
120.0
140.0
160.0
180.0
Gross Intake Net Intake Gross
Enrollment
Net Enrollment Completion Transition to
lower
secondary
Gross
Enrollment
Gross
Enrollment
Primary Lower
Secondary
Upper
Secondary
%
Male Female
Data sources: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS), EPDC calculation based on UIS data (see Data Table for year)
Male Female
FIG 6. STUDENT INTAKE AND FLOW FROM PRIMARY TO SECONDARY SCHOOLS
5.3
15.2
5.7
5.6
19.6
5.2
14.1
5.5
5.4
17.5
0.0
5.0
10.0
15.0
20.0
25.0
Prim G1 Prim G2 Prim G3 Prim G4 Prim G5
%
male by grade female by grade
male primary female primary
Data source: EPDC calculation based on UIS data (see Data Table for year)
FIG 7. STUDENT REPETITION BY GRADE AND LEVEL IN
PRIMARY SCHOOL
22
17
33
32
0
5
0
1
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
100%
Mozambique SACMEQ Means Mozambique SACMEQ Means
Reading Mathematics
Percent of Students
At the highest
performance
benchmark
Below the lowest
performance
benchmark
Data source: EPDC extraction of SACMEQ dataset 2007
FIG 10. PERFORMANCE ON LEARNING ASSESSMENTS
G
G
KEY
INDICATOR VALUE YEAR DATA SOURCE
43 2015 12% 36% 15% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
71 2015 16% 43% 21% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
63 2015 10% 32% 13% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
79 2015 14% 42% 17% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
151 2017 98% 92% 97% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
155 2017 97% 87% 95% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
73 2015 51% 81% 58% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
74 2015 53% 86% 59% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
101 2017 47% 46% 46% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
109 2017 76% 65% 69% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
37 2017 3% 15% 4% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
38 2017 3% 12% 4% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
28 2017 13% 51% 18% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
34 2017 13% 46% 18% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
86 2017 27% 60% 35% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
89 2017 31% 65% 40% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
19 2015 3% 14% 4% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
19 2015 2% 11% 3% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
9 2016 16% 45% 21% Education Policy and Data Center (EPDC)*
10 2016 18% 50% 24% Education Policy and Data Center (EPDC)*
68 2014 1% 3% 1% Education Policy and Data Center (EPDC)*
66 2014 1% 3% 1% Education Policy and Data Center (EPDC)*
48 2014 2% 7% 2% Education Policy and Data Center (EPDC)*
51 2014 2% 7% 3% Education Policy and Data Center (EPDC)*
44 2017 2% 7% 2% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
49 2017 1% 5% 1% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
76 2015 10% 35% 14% Education Policy and Data Center (EPDC)*
72 2015 6% 20% 9% Education Policy and Data Center (EPDC)*
52 2017 3% 10% 4% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
44 2013 3% 10% 4% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
36 2013 2% 4% 2% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
13 2013 39% 62% 47% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
44 2013 98% 96% 97% UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
37 2011 23% 49% 24% EPDC extraction of DHS dataset
57 2011 25% 38% 26% EPDC extraction of DHS dataset. Does not include Western Sahara.
5 2011 36% 57% 37% EPDC extraction of DHS dataset
15 2011 36% 57% 37% EPDC extraction of DHS dataset
14 2011 25% 43% 25% EPDC extraction of DHS dataset
23 2011 34% 48% 35% EPDC extraction of DHS dataset
29 2011 20% 40% 20% EPDC extraction of DHS dataset
47 2011 21% 29% 21% EPDC extraction of DHS dataset
25 2011 14% 35% 17% EPDC extraction of DHS dataset
32 2011 28% 42% 29% EPDC extraction of DHS dataset
44 2011 22% 34% 22% EPDC extraction of DHS dataset
24 2011 17% 42% 20% EPDC extraction of DHS dataset
38 2011 24% 39% 24% EPDC extraction of DHS dataset
ˠ Lower data values indicate better performance on these indicators
Net enrollment rate, Primary, Male
Net enrollment rate, Secondary, Female
Low and
Middle
Income‡
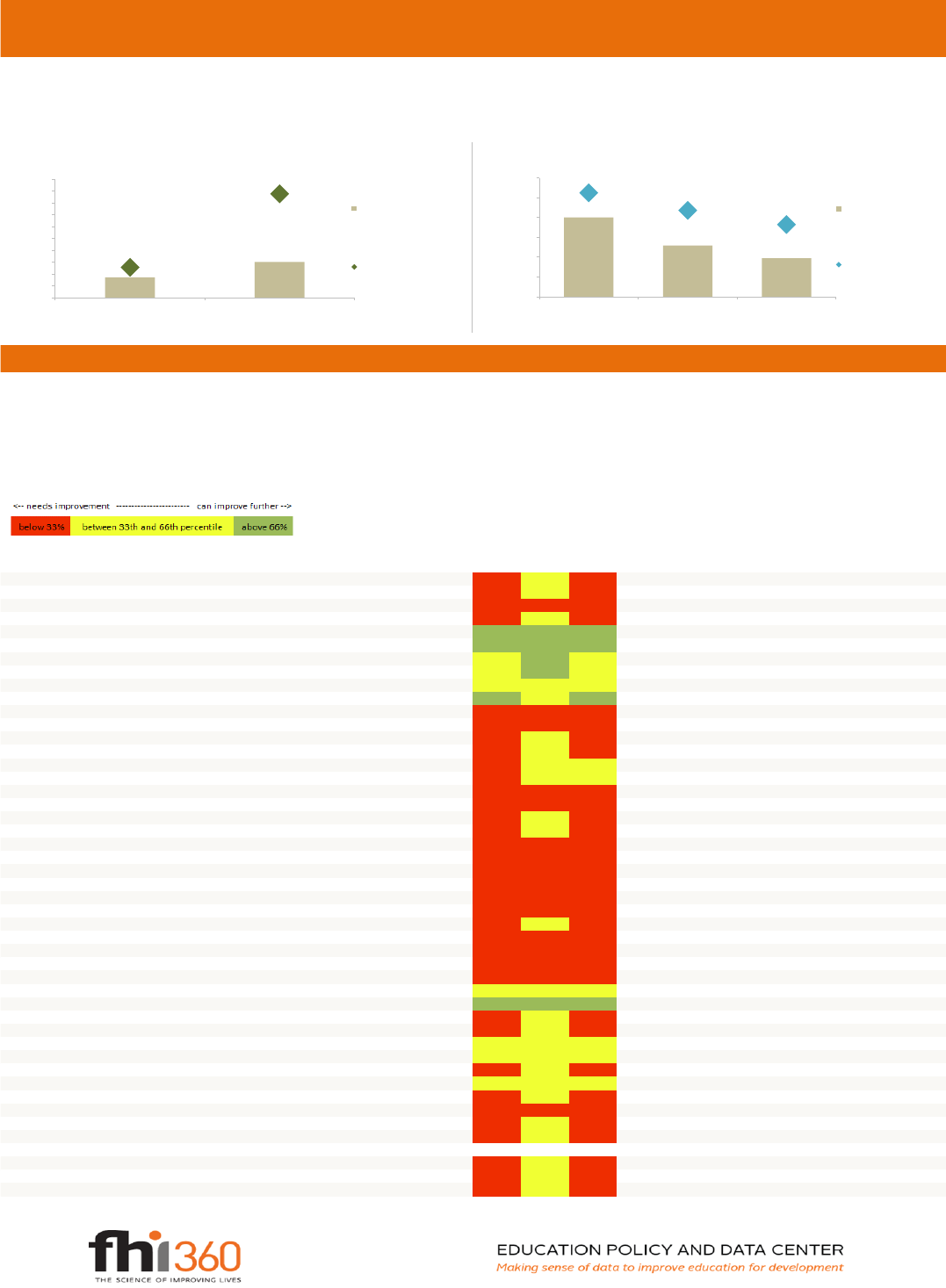
Figures 11 and 12 compare Mozambique's per pupil expenditure (PPE) and pupil teacher ratio (PTR), where data is available, to those of other low income countries. PPE indicates a country's
commitment to education at each school level. In Mozambique, PPE in primary education as a percentage of GDP per capita is 13%, higher than the median PPE in primary for low income countries,
which is 9%. In Mozambique, the PPE in primary is lower than the PPE in secondary. PTR is a proxy learning quality and resource availability indicator. In Mozambique, the PTR in primary education is
52.4, meaning that on average there is one teacher for every 52.4 primary school students. This is higher than the median PTR in primary for low income countries, which is 40. In Mozambique, the PTR
in primary is higher than the PTR in secondary.
All
Countries
Sub-
Saharan
Africa
PERCENTILE RANK
RELATIVE TO…
EDUCATION EXPENDITURE
Gross enrollment rate, Upper Secondary, Female
Gross enrollment rate, Upper Secondary, Male
Net enrollment rate, Primary, Female
Literacy rate, 15+, Female
Literacy rate, 15+, Male
Literacy rate, 15-24, Female
Literacy rate, 15-24, Male
Gross intake rate, Primary, Female
Gross intake rate, Primary, Male
Net intake rate, Primary, Female
Net intake rate, Primary, Male
Gross enrollment rate, Primary, Female
Gross enrollment rate, Primary, Male
Gross enrollment rate, Lower Secondary, Female
Gross enrollment rate, Lower Secondary, Male
* EPDC calculation based on UIS data
Public education expenditure per pupil (% of GDP per capita), Secondary
Dropout rate, Primary, Femaleˠ
Percentage of children out of school, Primary, Femaleˠ
Percentage of children out of school, Secondary, Femaleˠ
Percentage of children out of school, Primary, Totalˠ
Percentage of children out of school, Secondary, Totalˠ
‡ Includes World Bank classified low and middle income countries
Percentage of children out of school, Secondary, Urbanˠ
Percentage of children out of school, Primary, Ruralˠ
Percentage of children out of school, Secondary, Ruralˠ
Percentage of children out of school, Primary, Maleˠ
Percentage of children out of school, Secondary, Maleˠ
Completion rate, Primary, Female
Completion rate, Primary, Male
Survival rate, to Prim G5, Male
Transition rate, to Secondary, Female
Percentage of children out of school, Primary, Richest Quintileˠ
Percentage of children out of school, Primary, Poorest Quintileˠ
Percentage of children out of school, Secondary, Poorest Quintileˠ
Pupil teacher ratio, Lower Secondaryˠ
Pupil teacher ratio, Upper Secondaryˠ
Public education expenditure per pupil (% of GDP per capita), Primary
Percentage of children out of school, Secondary, Richest Quintileˠ
Percentage of children out of school, Primary, Urbanˠ
Pupil teacher ratio, Primaryˠ
DATA TABLE
Transition rate, to Secondary, Male
Net enrollment rate, Secondary, Male
Repetition rate, Primary, Femaleˠ
Repetition rate, Primary, Maleˠ
Dropout rate, Primary, Maleˠ
Survival rate, to Prim G5, Female
In this table, the values of different education indicators for Mozambique are compared to all countries, to Sub-Saharan Africa, and to low and middle income countries. The percentile rank that is given
indicates Mozambique's standing relative to these country groups. A higher percentile rank indicates better relative performance than a lower percentile rank. Percentile rankings above 66% are
considered high and colored in green, rankings between 33% and 66% are considered average and colored in yellow, and rankings below 33% are considered low and colored in red. For example, the
gross enrollment rate for females in primary education in Mozambique is 101%. For this indicator, Mozambique ranks in the 47 percentile relative to all countries, meaning that 47% of countries have
lower gross enrollment rates than Mozambique. As another example, the survival rate to grade 5 of primary school for males in Mozambique is 51%, and Mozambique ranks in the 2 percentile relative to
all countries, in the 7 percentile relative to Sub-Saharan Africa, and in the 3 percentile relative to low and middle income countries for this indicator.
40 26 20
52
44
36
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Primary Lower Secondary Upper Secondary
Pupil teacher ratio (PTR)
Low Income
countries (median)
Mozambique
Data source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) (see Data Table for year)
FIG 12. PUPIL TEACHER RATIO (PTR) BY SCHOOL LEVEL
9 15
13
44
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
Primary Secondary
% of GDP per capita
Low Income
countries (median)
Mozambique
Data source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) (see Data Table for year)
FIG 11. PER PUPIL EXPENDITURE (PPE) BY SCHOOL LEVEL (% OF
GDP PER CAPITA)

INDICATORS AND DEFINITIONS
Completion Rate
Dropout Rate
Educational Attainment
Gross Enrollment Rate (GER)
Gross Intake Ratio (GIR)
Literacy Rate
Net Enrollment Rate (NER)
Net Intake Rate (NIR)
Percentage of Children Out of School
Public Education Expenditure per Pupil (PPE)
Pupil Teacher Ratio (PTR)
Repetition Rate
Survival Rate
Transition Rate
Both
Poorest Quintile
Richest Quintile
DATA SOURCES AND LEARNING ASSESSMENTS
Demographic and Health Survey (DHS)
Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey (MICS)
UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS)
Analysis Programme of the CONFEMEN Education Systems
(PASEC)*
Progress in International Reading Literacy Study (PIRLS)*
Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS)*
Second Regional Comparative and Explanatory Study (SERCE)*
Southern and Eastern Africa Consortium for Monitoring
Educational Quality (SACMEQ)*
Highest Performance Benchmark*
Lowest Performance Benchmark*
* Learn more about assessment data and what competencies correspond with performance benchmarks at www.epdc.org/data-about-epdc-data/about-epdc-learning-outcomes-data.
The lowest test-specific performance or learning levels of an assessment. These benchmarks are different for each assessment
because each assessment uses different constructs, tools, and procedures. Additionally, assessments vary in the standards for
each learning achievement benchmark, the number of benchmarks according to which test-takers can be evaluated, and the
youth populations they test.
The highest level of education an individual has achieved.
Total number of pupils/Total education budget.
Proportion of children of a given age group who are not currently enrolled in any schooling.
GLOSSARY
The highest test-specific performance or learning levels of an assessment. These benchmarks are different for each assessment
because each assessment uses different constructs, tools, and procedures. Additionally, assessments vary in the standards for
each learning achievement benchmark, the number of benchmarks according to which test-takers can be evaluated, and the
youth populations they test.
Proportion of pupils from a cohort enrolled in a given grade at a given school-year who study in the same grade in the following
school-year.
Percentage of a cohort of pupils enrolled in the first grade level or cycle of education in a given school year who are expected to
survive through a certain grade regardless of repetition.
The number of pupils admitted to the first grade of a higher level of education in a given year, expressed as a percentage of the
number of pupils enrolled in the last grade of the lower level of education in the previous year.
The SACMEQ assessment is designed to assess student abilities in mathematics and reading English. SACMEQ reading and math
assessments have been carried out in countries in Anglophone East Africa in 1995, 2000, and 2007. SACMEQ is administered in
school to children in the 6th grade of formal school.
The SERCE assessment was administered in 16 countries in Latin America and the Caribbean by the Latin American Laboratory for
Assessment of the Quality of Education (LLECE) in 2006. SERCE was administered to children in the 3rd and 6th grades of formal
school. It measures student ability in the areas of reading, mathematics, and science.
Measures using "Both" in their title combine male and female rates.
Proportion of pupils who belong to the bottom 20% of a country's population, based on household wealth measured by an index
of household assets.
Proportion of pupils who belong to the top 20% of a country's population, based on household wealth measured by an index of
household assets.
The PIRLS reading assessment, which is carried out by the International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement
(IEA) is an assessment of reading comprehension skills. In most countries, PIRLS is administered in school to children in the 4th
grade of formal school, every five years since 2001. In a small number of countries, it may be administered at a different grade.
The TIMSS math assessment, which is carried out by the International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement
(IEA), assesses pupils knowledge and understanding of mathematical concepts. TIMMS has been administered to children in the
4th and 8th grades of formal schools every four years since 1995. In a small number of countries, it may be administered at
different grade levels.
PASEC has been administered in 13 countries in Francophone West Africa. PASEC is designed to assess student abilities in
mathematics and reading French. The program is managed by CONFEMEN (La Conférence des Ministres de l’Education des pays
ayant le français en partage) and has been in place since 1993. It is typically administered to students in 2nd and 5th grades.
Nationally-representative household surveys that provide data for a wide range of indicators in the areas of population, health,
and nutrition. They have large sample sizes (between 3,000 to 50,000 households) and are typically conducted about every 5 years
in developing countries. It is funded by USAID and implemented by ICF International.
Household surveys that produce internationally comparable estimates of a range of indicators in the areas of health, education,
child protection and HIV/AIDS. It is developed by UNICEF to provide statistically rigorous data on the situation
of children and women. Since the mid-1990s, there has been 4 rounds of the MICS survey, with the latest in 2009-2011.
Statistical office of UNESCO and the primary UN depository for cross-nationally comparable statistics on education, science and
technology, culture, and communication covering more than 200 countries and territories. It was established in 1999 and collects
data directly from the national statistics agencies of its members.
Average nationally of: Total number of pupils/Total number of teachers. Rates may vary significantly throughout the country.
Total number of new entrants in the first grade of primary education, regardless of age, expressed as a percentage of the
population at the official primary school-entrance age.
New entrants in the first grade of primary education who are of the official primary school entrance age, expressed as a
percentage of the population of the same age.
Total enrollment in a specific level of education, regardless of age, expressed as a percentage of the official school-age population
corresponding to the same level of education in a given school-year. Often higher than 100% because of repetition and overage
students.
The ability to read and write with understanding a simple statement related to one's daily life. Literacy often involves a continuum
of reading and writing skills.
Enrollment of the official age-group for a given level of education expressed as a percentage of the corresponding population.
Proportion of pupils from a cohort enrolled in a given grade at a given year who are no longer enrolled in the following school
year.
The total number of students completing (or graduating from) the final year of primary or secondary education, regardless of age,
expressed as a percentage of the population of the official primary or secondary graduation age.
