
Pre-Installation Guide 2
Table of Contents
1 Pre-installation 5
2 Windows updates 6
3 Required certificates for Relativity 7
3.1 Microsoft Storage Sense 8
3.2 Creating a self-signed certificate in PowerShell 8
3.2.1 Certificate requirements for message broker 9
3.3 Certificate requirements for Service Bus for Windows Server 9
4 User and group accounts 16
4.1 Relativity service account 16
5 Database server setup 17
5.1 Required software 17
5.2 Enable Microsoft DTC 17
5.3 Assign admin permissions to the Relativity service account 19
5.4 Create SQL Server login 19
5.5 Set authentication mode 19
5.6 Create BCP share 20
5.6.1 Update the permissions on the BCPPath file share 21
5.7 Optionally configure an authentication token-signing certificate 22
5.7.1 Pre-installation steps for a token-signing certificate 23
5.8 Optionally restrict account permissions for third party applications 23
6 Web server setup 25
6.1 Setting IIS options 25
6.1.1 HTTP Strict Transport Security 25
6.2 IIS role service configuration 26
6.2.1 IIS roles on Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows Server 2016 26
6.3 Enabling the WebSocket protocol 29
6.4 Configuring log file options 29
6.4.1 Log file options for Windows Server 2012 R2 29
6.5 Configuring SSL on a web server 33
6.5.1 Obtaining a certificate for your web server 33

Pre-Installation Guide 3
6.5.2 Installing a certificate on your web server 33
6.5.3 Configuring HTTPS site bindings 33
6.5.4 Updating the SSL setting on the IIS 34
6.5.5 Setting up HTTPS for Service Host Manager 35
7 Agent server setup 36
7.1 Enabling Microsoft DTC 36
7.2 Enabling HTTP activation 36
7.3 Message broker options 37
7.3.1 RabbitMQ 38
7.3.2 Service Bus for Windows Server 51
8 File (document) share or server 66
8.1 Create share 66
9 Cache location server 68
10 Analytics server setup 69
10.0.1 Required software 69
10.1 CAAT 4.5.0 and above 69
10.1.1 Create installation index directory 69
10.1.2 Assign permissions to the analytics directories 69
10.1.3 Required setup 70
10.2 Elasticsearch server setup 73
10.2.1 Required software 73
11 Index share - dtSearch repository 74
11.1 Create share 74
12 SMTP server setup 75
13 Environment modification for processing or native imaging 76
14 Database server for processing or native imaging 77
14.1 Required software 77
14.2 Relativity Service Account 77
14.3 Create Invariant worker network file path share 78
15 Worker server for processing or native imaging 79
15.1 Required software 79
15.2 Required Microsoft Visual C++ redistributables 80

Pre-Installation Guide 4
15.3 Relativity Service Account 80
16 Obtaining applications for native imaging and processing 81
17 Default log file location 82
18 Post-installation considerations 83
18.1 User group for uploading documents 83
18.2 Relativity service account information 83
18.3 Post-installation steps for a token-signing certificate 83
18.4 Logo customization 85
18.5 Resource groups 85
18.6 License keys 86
18.7 Relativity instance name 86

Pre-Installation Guide 5
1 Pre-installation
You must complete the pre-installation process to ensure that your environment is configured with the
software, user accounts, directories, and other prerequisites required for an initial installation of Relativity. In
addition, the Relativity service bus requires that you either install and configure Service Bus for Windows
Server or RabbitMQ.
As you set up your environment, use the Installation accounts and directories list to record information about
your environment configuration that the installation process requires. You can download this document from
Pre-Installation on the Relativity Server 2022 Documentation site.
For additional information, see the System Requirements and Environment Optimization guides.
Note: If you use a firewall, refer to the Ports Diagram in the Relativity Community to ensure that you
configure your firewall correctly with Relativity.
Note: Relativity plans to deprecate Windows Service Bus in Server 2023. We recommend that you begin
conversion to RabbitMQ beginning in Server 2022.

Pre-Installation Guide 6
2 Windows updates
Install the latest Microsoft Windows Server Service Pack on all Relativity servers.
However, compatibility for higher .NET versions is not guaranteed and we do not recommend installing
higher .NET versions than what is listed as required by your Relativity version. Furthermore, install any
smaller security patches, Windows updates, and anything else at your own discretion. We only test major
service packs, not every Microsoft update. Deploy any patches to your test instance of Relativity first.
Ensure that a rollback plan is in place if you discover any issues during deployment.
Ensure you disable the option to Install updates automatically on all Relativity servers. Apply any required
updates during a planned maintenance window.
After installing Windows updates, reboot your machines before attempting to install Relativity. Complete this
step to ensure that all Relativity components are properly installed. Incomplete Windows updates lock
system files, which may cause silent failures and prevent the proper installation of Relativity components.
Note: You must enable Windows Network discovery on all machines.

Pre-Installation Guide 7
3 Required certificates for Relativity
Relativity verifies that all HTTPS services running in your environment have a trusted certificate. The
HTTPS services run on the following components of your Relativity installation, so they require that you
install valid certificates:
n
Analytics server
n
Components that connect to the Services API
n
Components that use HTTPS to connect to the REST API
n
Service Host Manager on all web and agent servers for running application-based Kepler services
n
Viewer
n
Web servers
Note: For more information about required certificates and their corresponding Relativity servers, see All
certificates used by Relativity servers on the Community site.
You need to add certificates to any server in your Relativity environment that is accessed by an HTTPS
service. By adding these certificates, you will not see warning messages and insecure-connection icons
displayed as you navigate to different components of your Relativity site. Use these guidelines for installing
certificates in your Relativity environment:
n
If your Relativity site is exposed to the internet, install a certificate on any server that users can
access with HTTPS services.
n
If Relativity users access your web server with different internal and external names, install a second
certificate for the internal name.
n
If you use different internal and external URLs bound to the same IP address on your servers, install a
second certificate on the server for the internal IP address. You may want to consider using Server
Name Indication (SNI), which is an extension to the Transport Layer Security (TLS). For more inform-
ation, see IIS 8.0 Server Name Indication (SNI): SSL Scalability on the Microsoft website
(http://www.iis.net/learn/get-started/whats-new-in-iis-8/iis-80-server-name-indication-sni-ssl-scalab-
ility).
Note: If you do not want to use SNI in your environment, then configure separate IP addresses on
your web servers for internal and external URLS. You might not be able to use SNI if your IIS or
web browser versions do not support it.
For information about generating certificates for servers in your Windows domain, see Public Key
Infrastructure Design Guidance on the Microsoft site,
http://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/2901.public-key-infrastructure-design-
guidance.aspx. We recommend that you use the Standalone offline root CA referenced in this article.
For information on setting up HTTPS for the Service Host Manager on web and agent servers, see Service
Host Manager on the Relativity Server 2022 Documentation site.
For information on enabling HTTPS for Invariant Kepler Services, see the Worker Manager Server
Installation Guide.

Pre-Installation Guide 8
3.1 Microsoft Storage Sense
The Microsoft Storage Sense feature that is built in to Windows Server 2019 and later has the potential to
cause instability in your Relativity Server instance by inadvertently clearing out Windows TEMP folders.
To mitigate this scenario, see the knowledge base article Temp folder inadvertent clean up by Windows on
the Community.
You must have valid Community credentials to access this content.
3.2 Creating a self-signed certificate in PowerShell
To create a self-signed certificate with PowerShell 4.0, perform the following steps:
1. Open PowerShell.
2. Ensure you are running PowerShell in administrator mode. Otherwise, you will receive an error when
attempting to create the certificate.
3. Import the PKI module into PowerShell via the following command:
Import-Module PKI
4. Create the certificate through the following commands, where "FQDN" is the fully-qualified domain
name.
Note: If you are performing these steps as part of enabling HTTPS for Invariant Kepler Services,
the fully-qualified domain name will be for the QueueManager. For details, see the Worker
Manager Server Installation Guide.
Set-Location Cert:\LocalMachine
New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName "FQDN" -CertStoreLocation Cer-
t:\LocalMachine\My
5. Confirm that you have created a certificate in the personal store. Your PowerShell display should
resemble the following image:
6. Create, or designate, a folder in your C drive to which you want to export the certificate, which you will
do through the final “Export-Certificate” prompt included below. You will receive an error if that file
path doesn’t exist.
7. Export the certificate through the following commands:

Pre-Installation Guide 9
Set-Location Cert:\LocalMachine\My
n
Doing this sets your location to the folder you just created the certificate in.
Get-ChildItem
n
This displays the thumbprint of all certificates in the folder you just created, including the one
you just added. Make sure to copy the signature of the certificate you created and paste it into
the following command.
Export-Certificate -Cert (Get-ChildItem –Path Cer-
t:\LocalMachine\My\CertificateSignature) -FilePath C:\Tem-
p\SelfSignedCert.cer -Type CERT
n
Make sure you pasted the certificate signature you copied after running the Get-ChildItem com-
mand into this command, specifically in place of "CertificateSignature" above.
8. Confirm that you successfully exported the certificate you created. Your PowerShell display and cor-
responding folder should resemble the following image:
3.2.1 Certificate requirements for message broker
The Relativity service bus requires the installation of one of the following message brokers as a
prerequisite. To facilitate secure communication, the message broker requires a certificate. Depending on
the message broker you decide to use, complete the following steps:
Service Bus for Windows Server
Certificate requirements for RabbitMQ
3.3 Certificate requirements for Service Bus for Windows Server
You can use one of the following options for obtaining a trusted certificate for Service Bus for Windows
Server:
n
Use an existing certificate—you may already have a certificate for externally facing web servers. If
the domain name for the certificate matches the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the service
bus server, you can use this same certificate for both the web server and the service bus.
Pre-Installation Guide 10
n
Issue a certificate with an internal certificate authority—if you have access to an internal CA,
issue a certificate with the internal FQDN of your service bus server. The certificate must include the
following information:
o
For any certificate, either the Subject Name, Subject Alternative Name, or both must be valid
for each host in the farm.
o
Private and public key.
o
Valid start date, end date, and trust chain.
o
AT_KeyExchange set.
o
Corresponding CRL list for the signing authority.
n
Auto-generate a certificate—you can use the Service Bus Configuration tool to auto-generate the
required certificate when you configure a new farm. If you use an auto-generated certificate, each
host must be on the same domain. For more information, see Configuring Service Bus for Windows
Server on page57.
The certificate must include the following information:
n
For any certificate, either the Subject Name, Subject Alternative Name, or both must be valid for the
Fully Qualified Domain name that will be configured in Relativity.
n
Private and public key.
n
Valid start date, end date, and trust chain.
n
Corresponding certificate for the authority that issued the certificate. A corresponding certificate is not
required if using a self-signed certificate.
n
Certificate itself, the private key, and the certificate for the authority must be in the PEM format. For
more information, see Convert certificates to PEM format.
You can use one of the following options for obtaining a trusted certificate for RabbitMQ:
n
Using a certificate authority—if using a certificate authority complete the following:
o
Request or generate a certificate with the required properties.
o
If you are using an internal certificate authority that is not capable of generating the key and cer-
tificate in PEM format directly, generate and convert the certificate, the certificate’s private key,
and the certificate authorities certificate to PEM format. For more information, see Convert cer-
tificates to PEM format.
o
Self-signed certificate—there are several ways to generate a self-signed certificate includ-
ing:
l
Powershell
l
OpenSSL—use the following script to directly generate the files in the PEM format. You
need to update the inputs for the following script for your environment.
Note: To run OpenSSL commands, you need to add the OpenSSL path to the
environmental variable or run a command prompt as an admin at that directory.

Pre-Installation Guide 11
@echo off
REM IN YOUR OpenSSL FOLDER, SAVE THIS FILE AS:
makeCERT.bat
REM AT COMMAND LINE IN YOUR OpenSSL FOLDER, RUN: make-
cert
REM IT WILL CREATE THESE FILES: HOSTNAME.cnf,
HOSTNAMEKey.pem, HOSTNAMECert.pem, HOSTNAMEpfx.pfx
REM PLEASE UPDATE THE FOLLOWING VARIABLES FOR YOUR
NEEDS.
SET HOSTNAME=yourrabbitcluster
SET DOT=company.corp
SET COUNTRY=US
SET STATE=IL
SET CITY=Chicago
SET ORGANIZATION=PD
SET ORGANIZATION_UNIT=PD
SET EMAIL=admin@%HOSTNAME%.%DOT%
(
echo [req]
echo default_bits = 2048
echo prompt = no
echo default_md = sha256
echo x509_extensions = v3_req
echo distinguished_name = dn
echo:
echo [dn]
echo C = %COUNTRY%
echo ST = %STATE%
echo L = %CITY%
echo O = %ORGANIZATION%
echo OU = %ORGANIZATION_UNIT%
echo emailAddress = %EMAIL%
echo CN = %HOSTNAME%.%DOT%
echo:
echo [v3_req]
echo subjectAltName = @alt_names
echo:
echo [alt_names]
echo DNS.1 = *.%DOT%
echo DNS.2 = %HOSTNAME%.%DOT%
)>%HOSTNAME%.cnf
openssl req -new -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -sha256 -nodes
-keyout %HOSTNAME%Key.pem -days 3560 -out %HOSTNAME%Cert.pem -
config %HOSTNAME%.cnf
openssl pkcs12 -inkey %HOSTNAME%Key.pem -in

Pre-Installation Guide 12
%HOSTNAME%Cert.pem -export -out %HOSTNAME%pfx.pfx
Note: After updating the inputs at the beginning of the script for your environment, this
script can be used to directly generate a self-signed certificate in the PEM format.
n
Existing Certificate from the Certificate Store—RabbitMQ service does not use the Windows Cer-
tificate Store. Instead, certificates have to be configured in the RabbitMQ advanced.config file. You
will need the certificate, private key, and CA certificate, or the same certificate for self-signed, all in
the PEM format. In order to export the certificates from the Window Certificate Store perform the fol-
lowing steps:
n
Open Run on your desktop, and enter MMC.exe.
n
Click OK.
n
In the Console window, click File > Add/Remove Snap-ins.
n
Select Certificates under Available Snap-ins.
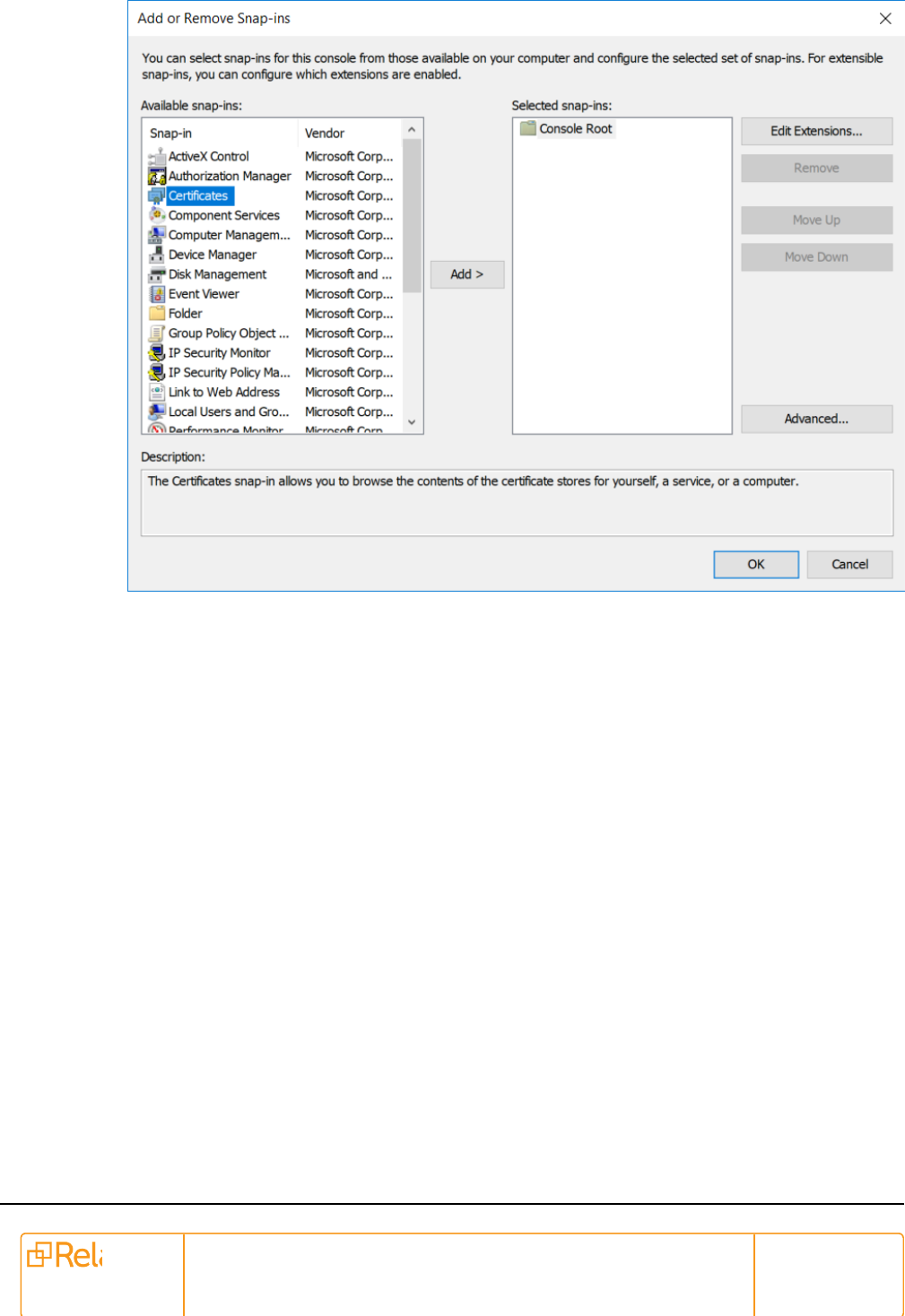
Pre-Installation Guide 13
n
Click Add.
n
Select Computer Account and click Next.
n
Select Local Computer and click Finish.
n
Click OK.
n
Right click the certificate you want to export and click All Tasks > Export.
n
On Export Private Key select Yes, export the private Key.
n
On Export File Format select Personal Information Exchange (.pfx).
n
Select Include all certificates in the certification path if possible.
n
Click Next.
n
On Security select Password.
n
Enter in a unique and secure password, you will need it for when converting the .pfx to a .pem.
n
Save the file in a secure location.
n
Using the Windows Certificate Manager store, export the .pfx certificate without the private
key, making sure to choose the .der (.cer) option.

Pre-Installation Guide 14
Convert certificates to PEM format
The certificates in RabbitMQ must be in PEM format. There are multiple ways to convert certificates to the
PEM format. The following an example conversion done using OpenSSL:
1. If applicable, export the certificates from the Window Certificate Store. For more information. see
Export existing certificates for conversion to PEM format.
2. Using OpenSSL, complete the following steps convert the certificate to PEMformat:
1.
Save the private key as a PEM file:
openssl pkcs12 -in <PathToPfx>.pfx -out <OutputPathForKey>.pem -
nodes -nocerts
2. Save the certificate as a PEM file:
openssl pkcs12 -in <PathToPfx>.pfx -out <OutputPathForCert>.pem -
nodes -nokeys
3. Save the CA certificate as a PEM file, this step is not required for self-signed certificates:
openssl x509 -inform der -in <PathToCACer>.cer -out <OutputPath>.pem
Note: For more information on using OpenSSL to convert the certificate to PEMformat, see
How to convert a certificate into the appropriate format.
3.3.0.1 (Optional) Running the RabbitMQCertificate utility
When configuring the RabbitMQ TLS setting, you have the option of running the RabbitMQCertificate utility
available on the Community, which contains a copy of OpenSSL. If you cannot use Powershell for any
reason, then you need to use the manual setup instructions provided above.
To use the RabbitMQCertificate utility:
1. Download the RabbitMQCertifcateUtility from the Community.
2. Unzip the RabbitMQCertificateUtility.zip file and open the RabbitMQCertificateUtility folder.
3. Navigate to the File tab in your file explorer.
4. Select Open Windows PowerShell and then select Open Windows PowerShell as
administrator.
5. Run the script by typing .\RabbitMQCertificateTool.ps1 and clicking Enter.
6. Select one of the following options:
n
Option 1 to set up RabbitMQ with a self-signed certificate.
o
Provide a password, which will be used when creating the private key.
o
The password must not contain ! or &.
o
Restart the service when prompted.
o
Export the newly created certificate and install it on all web, agent, and Invariant servers.

Pre-Installation Guide 15
n
Option 2 to use a PFX.
o
The PFX must be in the C:\Users\{RSA}\AppData\Roaming\RabbitMQ folder.
o
The PFX must be called RabbitMQ.pfx.
o
You must know the password for this PFX file, as you will be prompted for it when run-
ning this option.

Pre-Installation Guide 16
4 User and group accounts
Configure the following user and group accounts in your environment.
4.1 Relativity service account
Make sure that the Relativity services account has local administrator privileges on each of the servers
where you want to install Relativity. You must log in under this account when installing this software. You
can find additional requirements for this account under the sections describing how to configure specific
servers. For additional information about this account, see Relativity service account information on
page83.
The Windows Service Component and the Relativity COM Plus Component run under the Relativity Service
Account. Verify that this account is configured as follows:
n
Create account in Active Directory.
n
Add account to the Administrators group on all machines running Relativity components.
n
If using a workgroup, verify that the account has identical credentials on all Relativity servers.

Pre-Installation Guide 17
5 Database server setup
Set up the database server by completing the steps in this section.
Note: The SQL sa account must exist with the name sa, and be enabled during installs.
5.1 Required software
The following software must be installed on the database server:
n
Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, or Windows Server 2012 R2
n
SQL Server 2017 or SQL Server 2019
o
SQL Server 2019 requires Windows Server 2016 or 2019.
n
Relativity supports in-place upgrades from SQL Server 2016 to any higher supported version. For
details on SQL Server upgrade, follow the EDDS migration Guide. To determine if you should
upgrade your current SQL Server version to SQL Server 2019, note the following considerations.
Contact Relativity Support if you have further questions.
o
The base operating system of your SQL Server must be at a minimum Windows Server 2016.
Any Windows Server version below 2016 will require an EDDS migration to be performed to a
server with a proper operating system version and SQL version. Relativity does not support in-
place operating system upgrades. .
o
SQL Server version lower than SQL 2016 will require an EDDS migration since upgrading to
SQL Server 2019 from versions lower than SQL Server 2016 has not been tested by Relativity.
n
.NET 4.7.2 or 4.8
n
.NET 3.5
Additional considerations:
n
Each environment is different, research settings that your specific environment may utilize before
performing any upgrades.
n
Ensure that you have tested backups before performing any upgrades.
n
Although an in-place SQL upgrade is supported by Relativity. Performing an EDDS migration is the
cleanest way to perform a SQL upgrade.
Notes:
n
Relativity requires Full Text Search from the Database Engine Services feature as part of the SQL
Server installation.
n
For information about the service bus and server software versions, see Compatibility considerations
for the Service Bus for Windows Server in the System Requirements guide.
5.2 Enable Microsoft DTC
Microsoft DTC must be enabled on the SQL Server along with the following configuration changes:

Pre-Installation Guide 18
1. Add the Application Server role and select Distributed Transactions. Select Incoming Remote
Transactions and Outgoing Remote Transactions.
Note: As of Windows Server 2016 the Application Server role has been deprecated. Use the
Distributed Transaction Coordinator, if it is not present on your machine download the Microsoft
Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC) 2016 Management Pack for Microsoft System
Center located here, download.
2. Type dcomcnfg on your Start menu and press Enter to open Component Services.
3. Expand Component Services > Computers > My Computer > Distributed Transaction Coordin-
ator.
4. Right-click Local DTC and click Properties.
5. Click the Security tab.
6. Select the following check boxes. For additional details on DTC enablement, see the Deployment
workbook on the Relativity Community.
n
Allow Remote Clients
n
Allow Inbound

Pre-Installation Guide 19
n
Allow Outbound
7. Click Apply.
8. Click Yes to restart the MSDTCservice.
9. Click OK.
5.3 Assign admin permissions to the Relativity service account
You must configure permissions for the Relativity service account on the SQL Server as part of the
database setup process. Make sure that the Relativity service account has local administrator and system
admin permissions on the SQL Server.
5.4 Create SQL Server login
The following login must be added to the SQL Server environment. Set this account to Never Expire and
Not Enforce Password policy.
Note: The Relativity installer creates this SQL Server account if it does not already exist.
The EDDSDBO account is the login used by the owner of all objects in the EDDS system databases. Follow
these guidelines for configuring this account:
n
Authenticate this user with SQL Server Authentication.
n
Give this account only the following server roles:
o
bulkadmin
o
dbcreator
o
public
n
If you have multiple SQL Servers, create this account on each server with the same name, per-
missions, and credentials.
n
Make sure that password for EDDSDBO account doesn't contain an equals sign (=), carats (< or >),
double quotes ("), parenthesis, curly braces ({or } ), or semicolons (;).
5.5 Set authentication mode
After creating a SQL Server login, you must set the Windows authentication mode property on the server.
Complete the following steps to set the authentication mode:
1. Log in to Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio.
2. Right-click on your server in the Object Explorer, and then click Properties in the menu.

Pre-Installation Guide 20
3. On the Server Properties dialog box, click the Security page.
4. Under Server authentication, click SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode.
5. Click OK.
5.6 Create BCP share
Create a directory on the SQL Server in a location where the Relativity Service Account can read and write.
In addition, give SQL services permissions to read from this directory. For more information about
transferring data with BCPPath, see RDC transfer modes in the Desktop Client Guide or the Data Transfer
Guide. Follow these guidelines for setting up this directory:
n
Make sure that this directory is an actual folder, not merely a drive letter.
n
Confirm that the account running SQL has access to this directory. If it does not have access to this
folder, it cannot create new cases. This directory is used for temporary files during imports, exports,
case creations, and dtSearch queries.

Pre-Installation Guide 21
n
Place this share on the drive housing the backup files for optimal performance. This share should be
named BCPPath in every instance.
n
If you have multiple SQL Servers, create this share on each server and use the BCPPath as the
share name on all servers.
n
Make sure the account running the SQL services has rights to the BCPPath. Bulk import fails when
this account does not have these rights.
Note: Consider setting up an SQL Service Account that is a domain account with local admin rights. You
should review the security requirements of your organization before setting up this account. To create a
SQL Server Service account available from Microsoft, see Configure Windows Service Accounts and
Permissions, http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143504.aspx.
Complete the following steps to share the folder:
1. Right-click the folder and go to Properties.
2. Open the Sharing tab and click Share.
3. Enter the Relativity Service Account name, domain\account, and click Add.
4. Select the service account on the share list and set the Permission Level to a minimum of
Read/Write.
5. Click Share.
6. When the share completes, click Done.
7. On the Document Properties dialog box, select the Security tab.
8. Verify that the Relativity Service Account has Full Control security permissions to the folder itself.
5.6.1 Update the permissions on the BCPPath file share
In the Failover Cluster Manager, you must update the permission settings for the BCPPath file share to
ensure the case creation occurs properly on the failover cluster. When you create the BCPPath on a
clustered disk, verify that Enable continuous availability option is not selected under Settings on the
BCPPath Properties page. See the sample settings on the following screen shot:

Pre-Installation Guide 22
Note: You must configure this setting only for SQL Server 2012, 2014, and 2016.
5.7 Optionally configure an authentication token-signing cer-
tificate
When you run the Relativity installer, it automatically adds an authentication token-signing certificate,
named RelativityIdentityCertificate, to the certificate store on your primary database server. However, you
also have the option to use your own certificate rather than the one created by the Relativity installer.
Note: You only need to install an authentication token-signing certificate if you do not want to use the
default certificate called provided by the Relativity installer.
Before you begin installing Relativity, you may want to configure the token-signing certificate in the store on
your primary database server. The other servers in your Relativity installation automatically retrieve this

Pre-Installation Guide 23
certificate information from the EDDS database server, so you do not need to configure their certificates
individually.
Note: For a clustered environment, you need to export a copy of your RelativityIdentityCertificate from the
primary database server, and install the certificate to each database server hosting the EDDS.
5.7.1 Pre-installation steps for a token-signing certificate
You may want to install your custom token-signing certificate on the database server before you install
Relativity in your environment. However, you can also complete these steps after installation.
Use this procedure to configure your certificate:
1. Obtain a signed certificate and install it on the certificate store on your primary database server.
2. Copy the thumbprint of the certificate for later use. You need this value to update the instance setting
after you install Relativity. See Post-installation steps for a token-signing certificate on page83.
3. Install Relativity on the database and other servers. For more information, see Relativity installation
or Upgrading your primary SQL Server on the Relativity Server 2022 Documentation site.
After you install Relativity complete the steps in Post-installation steps for a token-signing certificate on
page83.
5.8 Optionally restrict account permissions for third party applic-
ations
This section describes how to allow a user to execute worker operations in a user account that is
independent of the default account used in Processing. This user account can be configured without admin
level permissions in order to make the file conversions execute un-managed code in a highly secure
fashion.
To restrict account permissions:
1. Create the desired user account on the worker machines that will be doing work for Processing.
n
The user account is not required to have permissions to access a file share or network.
n
The user account does need to be able to read and write local temporary files.
n
A single account name and password will be used for all workers in use by Invariant. This can
be a local user account created on each worker.
2. Store the user account name and password in Secret Store so that Processing can access them. This
information can be configured in Secret Store either through the InvariantResponse.txt file used dur-
ing installation or using the Secret Store client utility.
Note: The date format settings for this user account should be set up the same way as the
Relativity service account. For example, if a service account is set up with the date format of
DD/MM/YYYY, then the restricted user account must follow this format. Otherwise, applications
executed under the restricted user account can be affected by mismatched date formatting. To
verify your date format settings, see the regional format date and time configuration under the

Pre-Installation Guide 24
workers Windows settings.

Pre-Installation Guide 25
6 Web server setup
This section describes how to prepare your web server for installing Relativity. Install the following software
on the web server:
n
Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, or Windows Server 2012 R2
n
.NET 4.7.2 or 4.8
n
.NET 3.5
6.1 Setting IIS options
Make these updates on all web servers in your Relativity installation:
1. Install the required versions of the .NET Framework Full Profile on all web servers.
2. Configure the Legacy Unhandled Exception Policy on all web servers:
a. Browse to the following directory on your web server: C:\Win-
dows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\v4.0.30319\
b. Open the Aspnet.config file in a text editor.
c. Locate the tag <legacyUnhandledExceptionPolicy>.
d. Set the enabled attribute to true. This sample code illustrates the attribute that you need to
update:
<legacyUnhandledExceptionPolicy enabled="true" />
e. Save the changes to the file.
6.1.1 HTTP Strict Transport Security
IIS 10.0 provides native support for HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS). If you enable this and check
Redirect HTTP to HTTPS you must also configure Service Host Manager for HTTPS connections across
the entire environment.

Pre-Installation Guide 26
6.2 IIS role service configuration
Relativity requires that you configure several role services in the IIS. You also have the option of using a full
installation of the Web Server (IIS) role.
6.2.1 IIS roles on Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows Server 2016
For the IIS on Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2016, use this procedure to view the minimum
role service requirements for Relativity:
1. Open the Server Manager on Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2016.
2. Click Manage to display a drop-down menu.
3. Click Add Roles and Features. The Add Roles and Features wizard appears.
4. Click Next on the Before you begin dialog box.
5. Click Next on the Select installation type dialog box.
6. On the Select destination server dialog box, select Server Roles.
7. Select Web Server (IIS), and then click Install.
8. On the pop-up window, ensure that Include management tools (if applicable) is checked, and then
click Add Features.
9. Click Next to go to the Features page.
10.
Review the following illustration for Features configuration settings:

Pre-Installation Guide 27
11. Click Next to confirm the applicable Features.
12. Click Next on the Web Server Role (IIS) page.
13. On the Role Service page, review the following illustration for minimum role service requirements for
Relativity:

Pre-Installation Guide 28

Pre-Installation Guide 29
14. Click Next to confirm the Role Services.
15. Click Install.
6.3 Enabling the WebSocket protocol
If you are using Windows Server 2012 R2, Relativity requires that you have the WebSocket protocol
enabled on the IIS to support documentation conversion and imaging. Confirm that you have this protocol
enabled on your web server. If you do not currently have it enabled on the IIS, see the WebSocket
<webSocket> page on the Microsoft web site for instructions about setting it up. It is available at this URL:
https://www.iis.net/configreference/system.webserver/websocket.
6.4 Configuring log file options
If you enabled logging on the IIS, you can avoid performance and other issues by limiting the size of log
files, as well as the number of trace files stored on the IIS. This section describes how to configure these
features in your environment for optimum performance.
6.4.1 Log file options for Windows Server 2012 R2
Use the instructions in this section to configure logging settings for Windows Server 2012 R2.
6.4.1.1 Setting file size for IIS requests log
Logging is a default role installed on the IIS and enabled in most environments. Use the following
instructions to set the maximum size for the log files:
1. Open the Server Manager.
2. On the Tools menu, select Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
3. Expand the server node to display the Features View.
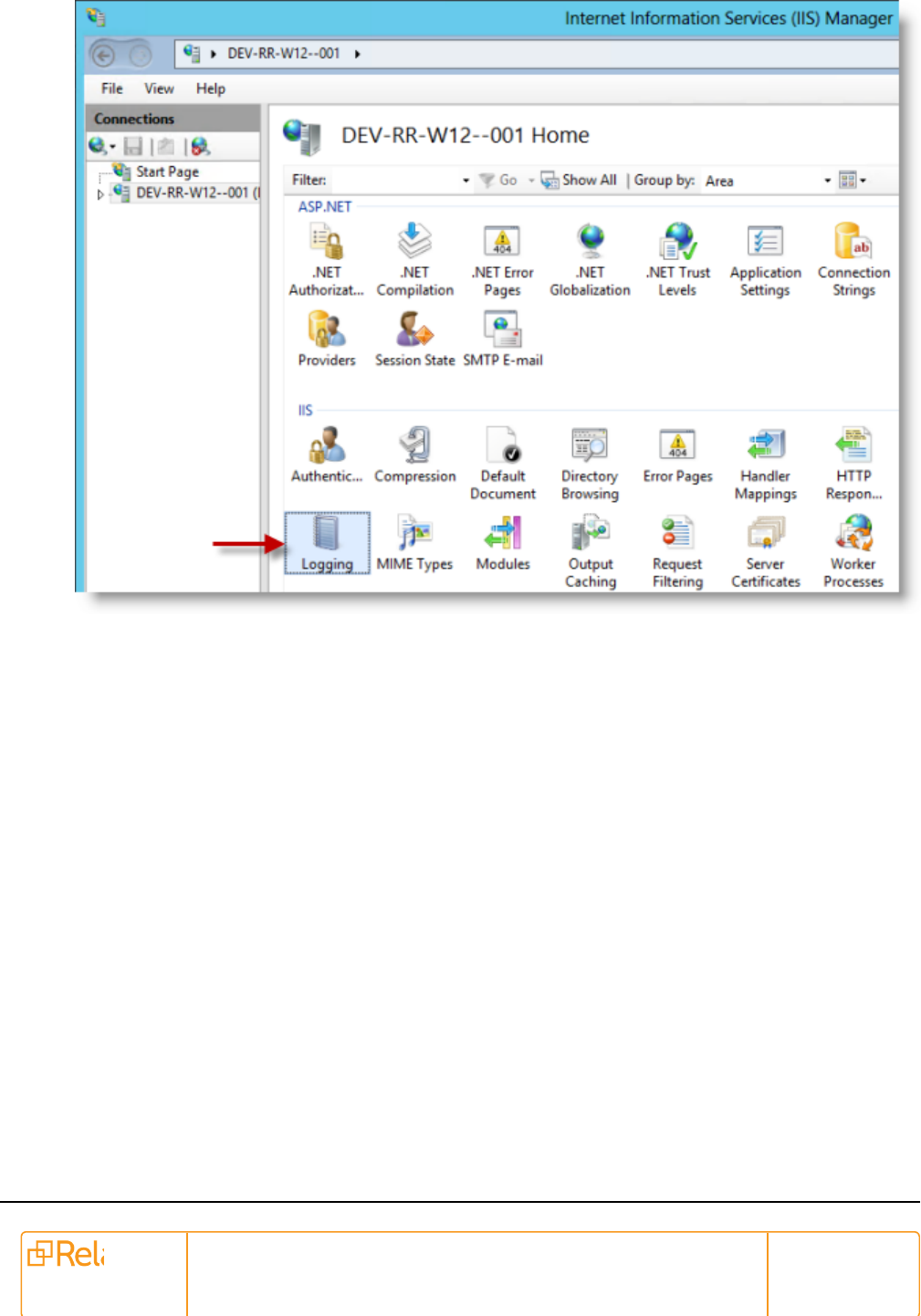
Pre-Installation Guide 30
4. Double-click the Logging icon to display the Logging page.
5. Update the maximum file size for your environment if necessary. The following illustration shows the
maximum file size used to restrict the log files from growing larger than 3 MB.

Pre-Installation Guide 31
6.4.1.2 Setting the file size for failed trace logging
If you manually installed the failed trace logging through the Role Services on your IIS, complete the
following steps to set the maximum number trace files stored.
1. Open the Server Manager.
2. On the Tools menu, select Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
3. Expand the server node to display the Features View.
4. Highlight the Default Web Site.

Pre-Installation Guide 32
5. Double-click the Failed Request Tracing icon to display the Failed Request Tracing Rules page.
6. Right-click on the rules to display a pop-up menu, and then click Edit Site Tracing.
7. Update the value in the Maximum number of trace files box. This value should be set no higher
than 500.

Pre-Installation Guide 33
6.5 Configuring SSL on a web server
Before installing Relativity, we recommend that you set up SSL on the IIS for your Relativity instance. This
configuration provides added security for the communication between the web server and the browser on a
client computer. Your browser uses this secure connection to verify that it is communicating with the
Relativity server. It also provides additional protection against the theft of cookies used to maintain a
session between the browser and the server.
Note: You are not required to configure SSL on the web server hosting Relativity. If you decided not to
use HTTPS in your environment, you must set the CookieSecure instance setting to False before logging
in to Relativity, or you receive an error message. You can also complete this setup after installation but
before logging in to Relativity. For more information, see Instance setting table on the Relativity Server
2022 Documentation site.
The process for configuring SSL on your web server includes these steps:
n
Obtaining a certificate for your web server below
n
Installing a certificate on your web server below
n
Configuring HTTPS site bindings below
n
Updating the SSL setting on the IIS on the next page
n
Setting up HTTPS for Service Host Manager on page35
6.5.1 Obtaining a certificate for your web server
To set up SSL on your web server, you must obtain a certificate, which is digital identification document
used by the browser to authenticate the server. A server certificate contains detailed identification
information, such as the name of the organization affiliated with the server content, the name of the
organization that issued the certificate, and a public key used to establish an encrypted connection. It
provides a way for the browser to confirm the authenticity of web server content and the integrity of the SSL-
secured connection before transmitting information.
You can obtain a certificate from Microsoft Certificate Services or from a mutually trusted CA. A CA confirms
your identity to ensure the validity of the information contained in your certificate. In general, you must
provide your name, address, organization, and other information.
Note: If you do not issue your server certificate through Microsoft Certificate Services, a third-party
certification authority must approve your request and issue your server certificate.
6.5.2 Installing a certificate on your web server
After obtaining an SSL certificate, install it in the certificate store on your web server. For more information,
see Import or export certificates and private keys on the Microsoft Windows website.
6.5.3 Configuring HTTPS site bindings
The IIS resets after you configure the HTTPS site bindings and update the SSL setting as described in the
following section.
Use these steps to configure HTTPSsite bindings:

Pre-Installation Guide 34
1. Open the IIS Manager.
2. In the IIS Manager Connections pane, expand Sites.
3. Right -click on the Default Web Site, and then click Edit Bindings on the menu.
4. Click Add to display the Add Site Binding dialog box.
5. In the Type drop-down menu, select https.
6. In the SSL certificate drop-down menu, select your certificate.
7. Click OK. You now see https listed in the Type column.
8. Click Close.
6.5.4 Updating the SSL setting on the IIS
Use the following steps to configure SSL settings on the IIS:
1. Open IIS Manager.
2. Navigate to the Relativity virtual directory, and then select Relativity.
3. Double-click SSL Settings.

Pre-Installation Guide 35
4. Select Require SSL.
5. Click Apply in the Actions pane.
6.5.5 Setting up HTTPS for Service Host Manager
You also need to enable HTTPS for the Service Host Manager service, which must run on all web and agent
machines that use Relativity. For a detailed overview of this service and configuration steps, see Service
Host Manager on the Documentation Server 2022 site.

Pre-Installation Guide 36
7 Agent server setup
An agent server performs background processing. It requires the following software:
n
Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, or Windows Server 2012 R2
n
.NET 4.7.2 or 4.8
n
.NET 3.5
In most environments, the Relativity installer automatically enables Microsoft DTC and HTTP activation.
You may require the following instructions if you need to troubleshoot your installation or if its configuration
requires you manually complete these steps.
7.1 Enabling Microsoft DTC
You must enable Microsoft DTC on the Agent server along with the following configuration changes:
1. Add the Application Server role and select Distributed Transactions. Select Incoming Remote
Transactions and Outgoing Remote Transactions.
Note: As of Windows Server 2016 the Application Server role has been deprecated. Use the
Distributed Transaction Coordinator, if it is not present on your machine download the Microsoft
Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MSDTC) 2016 Management Pack for Microsoft System
Center located here, download.
2. Type dcomcnfg on your Start menu , and then press Enter to open Component Services.
3. Expand Component Services > Computers > My Computer > Distributed Transaction Coordin-
ator.
4. Right-click Local DTC, and then click Properties.
5. Click the Security tab.
6. Select the following check boxes:
n
Allow Remote Clients
n
Allow Inbound
n
Allow Outbound
7. Click Apply.
8. Click Yes to restart the MSDTCservice.
9. Click OK.
7.2 Enabling HTTP activation
You must enable HTTP activation on your agent server as follows for Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R:
1. Click Start > Administrative Tools > Server Manager.
2. In the Server Manager Dashboard, click Manage > Add Roles and Features.

Pre-Installation Guide 37
3. In the Add Roles and Features, choose Server Selection.
4. Select the server running the agents is selected in the Server Pool box, and then click Next.
5. Click Features in the sidebar of the wizard.
6. Select the following check boxes in the Feature box:
n
.NET Framework 3.5 Features
Note: Ensure all check boxes below .NET Framework 3.5 Features are checked.
n
.NET Framework 4.5 Features
Note: Ensure all check boxes below .NET Framework 4.5 Features are checked.
Make sure that HTTP Activation is installed and selected when you expand each of these sections.
7. Install any missing features are necessary.
8. When the installation is complete, expand .NET Framework 3.5 Features and .NET Framework 4.5
Features to verify that HTTPActivation is installed. See the following screen shot:
7.3 Message broker options
Relativity requires that you install and configure a message broker before you install or upgrade Relativity.
While Relativity supports both Service Bus for Windows Server and RabbitMQ, we strongly recommend that
Pre-Installation Guide 38
you use RabbitMQ for Relativity Server 2022. Depending on the message broker you decide to use,
complete the following steps:
n
RabbitMQ
n
Service Bus for Windows Server
7.3.1 RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is the most widely deployed open source message broker with more than 35,000 production
deployments. Additionally, RabbitMQ is fully supported on the latest Windows operating systems, features
full support for TLS 1.2, and includes superior monitoring, administration, and performance capabilities. For
more information, see the RabbitMQ website. The process for installing and configuring RabbitMQ includes
these steps:
Use the following guidelines to optimize the RabbitMQ installation:
n
RabbitMQ installation—for a typical installation, install RabbitMQ on a server or VM that is access-
ible throughout your Relativity instance. Must be accessible by all Web and Agent servers. Minimum
of 2 GB of RAM, 2 CPU cores, and 10 GB of free disk space. Recommend 4-8 GB of RAM, 4 CPU
cores, 40 GB of free disk space. Additionally, in environments where large batch jobs may be sent to
RabbitMQ, such as mass conversions with greater than 25,000 documents, disk IO may become a
factor in performance. Relativity recommends RabbitMQ’s mnesia database be located on a drive
with less than 15ms latency and at least 30 mb/sec read/write speeds. For information about con-
figuring RabbtitMQ’s directories, see the RabbitMQ website.
n
Clustering and High Availability—a typical Relativity installation requires only a single RabbitMQ
server. However, high availability can be achieved by deploying multiple RabbitMQ servers in a
cluster. For more information, see Setting up RabbitMQ for high availability.
Before installing RabbitMQ, complete the following prerequisites:
n
If you wish to have RabbitMQ and Relativity communicate over TLS, see Certificate requirements for
RabbitMQ.
n
Ensure that you have the prerequisites for RabbitMQ. You need to meet these requirements to set up
your cluster correctly.
n
For a typical installation, identify the server or VM where you want to install RabbitMQ. To install Rab-
bitMQ on multiple hosts, identify the servers or VMs for this purpose. The cluster can have any num-
ber of servers, but three servers is recommended. For more information, see Best practices for
RabbitMQ.
n
Relativity agent and web servers must be able to communicate with the cluster over the following
ports:
o
TCP: 5672 (non TLS configurations) and/or 5671 (TLS configurations)
o
HTTP(S): 15672 (non TLS configurations) and / or 15671 (TLS configurations)
n
Install Erlang and RabbitMQ
n
Configure RabbitMQ
Installing Erlang and RabbitMQ

Pre-Installation Guide 39
Note: The RabbitMQ 3.10 series became unsupported by the vendor on 12/31/2023. We cannot
guarantee compatibility of RabbitMQ 3.10.x with Server 2022 or Server 2023 after 12/31/2023 and
recommend upgrading to a supported version of RabbitMQ. For details on RabbitMQ's version policies,
see RabbitMQ versions. If you are upgrading to 3.12.x, review the RabbitMQ upgrade overview
beforehand to avoid issues during the upgrade process.
Note: You must use RabbitMQ version 3.11.x or 3.12.x and a compatible version of Erlang; however, you
cannot currently run version 3.12.x with any supported version of Erlang above v25.x. If you intend to use
RabbitMQ 3.10.x, or Erlang version 25.0 or higher, you must have (released on January 5, 2023)
installed, and you must have valid Community credentials to access and download it. Ensure that you're
using the 64-bit version of Erlang, or else the system will be constrained to 2GB of memory.
Complete the following steps to install Erlang and RabbitMQ:
1.
Download and install the latest version of Erlang that is compatible with RabbitMQ 3.11.x, or 3.12.x.
Note that you cannot currently run version 3.12.x with any supported version of Erlang above v25.x.
With how frequently both RabbitMQ and Erlang upgrade their products, we recommend you review
the RabbitMQ-Erlang version requirements here. Make sure to run the installer in Administrator
mode.
2. Complete the steps in the Installation Configuration Wizard.
3. When the installation process completes, click Close. You have now installed Erlang.
4.
Download and install RabbitMQ 3.11.x or 3.12.x here. Be sure to run the installer in Administrator
mode.
5. Complete the steps in the Installation Configuration Wizard.
6. When the installation process completes, click Finish. You have now installed RabbitMQ.
7. Search "RabbitMQ Command Prompt (sbin dir)" on your machine. Open the RabbitMQ command
prompt.
8. In the RabbitMQ command prompt, run the following command:
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
This command enables the management plugin, management UI, and management API. Relativity's
RabbitMQ provider requires the management API to perform certain operations.
9. Restart the RabbitMQ Windows Service.
10. Open a browser and navigate to http://localhost:15672/
11. Log in with the following credentials:
n
Username: guest
n
Password: guest .
Note: The default user guest can only log in from local host.
You should see an overview and your server displaying various green statistics.

Pre-Installation Guide 40
Configuring RabbitMQ
Note: RabbitMQ requires .NET 3.5
After installing Erlang and RabbitMQ, you need to complete the following steps to configure RabbitMQ:
n
Create a new virtual host to be used by Relativity
n
Create a new user to be used by Relativity
Create a new virtual host to be used by Relativity
Complete the following steps to create a new virtual host to be used by Relativity:
Note: Virtual hosts in RabbitMQ are analogous to Namespaces in Azure Service Bus and Service Bus for
Windows Server.
1. Open a browser and navigate to http://localhost:15672/
2. Log in using the following credentials:
n
username: guest
n
password: guest
Note: The default user guest can only log in from local host.
3. Click Admin > Virtual Hosts.
4. Expand Add a new virtual host.
5. Enter a name for a virtual host to be used in the Name field, ex: Relativity.
6. Click Add virtual host.
Create a new user to be used by Relativity
Complete the following steps to create a new user to be used by Relativity:

Pre-Installation Guide 41
1. Open a browser and navigate to http://localhost:15672/
2. Log in using the following credentials:
n
username: guest
n
password: guest
Note: The default user guest can only log in from local host.
3. Click Admin > Users.
4. Expand Add users.
5. Enter a user name and password in the Username and Password fields.
6. Select Admin, under the Tags field.
7. Click Add user.
8. Expand All users.
9. Click on the user you just created.
10. Expand Permissions.
11. Select the virtual host you created in the previous steps in the Virtual Host drop-down menu.
12. In the Configure regexp, Write regexp, and Read regexp fields ensure the value is set to .* .
13. Click Set permission, the permissions now display under current permissions.
Note: For advanced deployment and configuration options, see the RabbitMQwebsite.
Adding a new RabbitMQ policy for SignalR
A SignalR policy ensures all SignalR queues are deleted after five minutes without a consumer, rather than
the default setting of one hour. In addition, high availability policies are not applied to SignalR queues,
limiting the performance impact of many queues.
To add a SignalR policy:
1. Open your browser and navigate to http://localhost:15672/.
2. Log in using the following credentials. The default user guest can only log in from local host.
n
username: guest
n
password: guest
3. Click Admin > Policies.
4. Expand the Add / update a policy section.
5. Select a virtual host to be used, specifically Relativity.
n
Name - SignalR
n
Pattern - SIGNALR
n
Priority - 10
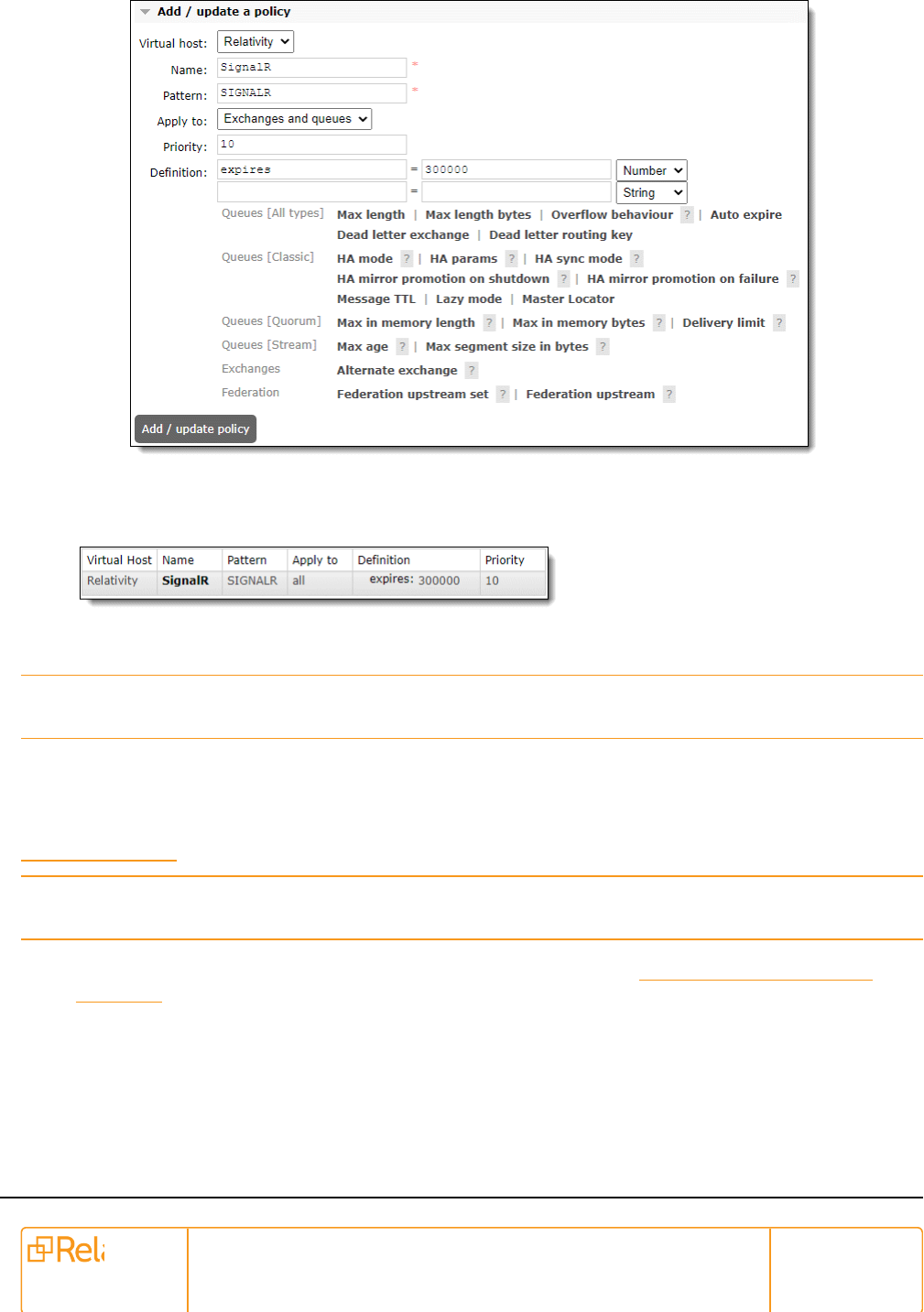
Pre-Installation Guide 42
n
Definition - expires = 300000 | Number
6. Click Add / update policy to save the policy. Confirm the policy has been saved in the following
format:
Configure RabbitMQ For TLS
Note: TLS is optional and controlled by the TLSENABLED response file input and
EnableTLSForServiceBus instance setting.
In order to setup RabbitMQ to use TLS for secure communication you must update the server side
configuration of RabbitMQ. To enable SSL communication with the RabbitMQ server in Relativity, you must
also update the instance setting. The following section documents the minimum requirements for using
RabbitMQ over TLS with Relativity. For complete documentation of RabbitMQ with TLS, see the
RabbitMQwebsite.
Note: Relativity only supports TLS 1.0, 1.1, and 1.2. SSL3 is NOT supported. When TLS is enabled for
Relativity the ports 5671 and 15671 must be open and available for use by RabbitMQ.
1. Before you begin, you need a certificate. For more information, see Certificate requirements for
RabbitMQ.
2. Navigate to your RabbitMQ directory. On Windows, this defaults to
C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Roaming\RabbitMQ, <user> is the user account used to install the
service.

Pre-Installation Guide 43
3. Depending on the version of RabbitMQ, download the advanced.config file. The slashes in the
advanced.config file must be forward slashes (/); entering backward slashes will result in an error.
Below RabbitMQ 3.8.15+ RabbitMQ 3.8.15+ or above
advanced.config advanced.config
[
{ssl, [
{versions, ['tlsv1.2', 'tlsv1.1']}
]},
{rabbit, [
{consumer_timeout, 5400000},
{ssl_listeners, [5671]},
{ssl_options,
[{cacertfile, "C:/Path/To/Your/CACert/caCert.pem"},
{certfile, "C:/Path/To/Your/Cert/cert.pem"},
{keyfile, "C:/Path/To/Your/Key/key.pem"},
{verify, verify_none},
{fail_if_no_peer_cert, false},
{versions, ['tlsv1.2', 'tlsv1.1']}
]}
]},
{rabbitmq_management, [
{listener, [
{port, 15671},
{ssl, true},
{ssl_opts, [
{cacertfile, "C:/Path/To/Your/CACert/caCert.pem"},
{certfile, "C:/Path/To/Your/Cert/cert.pem"},
{keyfile, "C:/Path/To/Your/Key/key.pem"}
]}
]}
]}
].
Note: Before editing the advanced.config file, ensure the certificate files are converted into the
.PEM format. For more information, see Convert certificates to PEM Format.
The below image is an example of the advanced.confg file setup for TLS utilizing a self-signed

Pre-Installation Guide 44
certificate:
Notes:
n
In the advanced.confg file, ports 5671 and 15671 are specified in the file and are required for Relativ-
ity.
n
The settings verify and fail_if_no_peer_cert are used for Client Certificates. Relativity does not sup-
port Client Certificates with RabbitMQ at this time, and requires username password authentication.
As a result, verify must be set to verify_none, and fail_if_no_peer_cert must be set to false.
n
For more information on how to configure RabbitMQ for TLS, see TLS Support and Configuring
Cipher Suites.
Setting up RabbitMQ for high availability.
In order to deploy RabbitMQ in a high availability configuration, create a cluster of servers, nodes, hosting
RabbitMQ. Once configured, Relativity can continue to function in the event that any individual RabbitMQ
node goes down. While this section provides the basic steps necessary set up a RabbitMQ cluster,
clustering in RabbitMQ supports many different configurations and network topologies. For more
information, see clustering on the RabbitMQ website.
Optional configuration topics not included in this section include:
n
Alternative Cluster Formation Techniques
n
TLS for Inter-node (Clustering) Traffic
Planning the cluster
To achieve high availability, your cluster must include at least two nodes, servers, hosting RabbitMQ, and it
is generally recommended to have at least three nodes. It is highly recommended that all nodes
communicate over a reliable LAN. A reliable network connection between nodes is important for avoiding
partitions. For more information, see partitions on the RabbitMQwebsite.
n
Review the port requirements, see ports on the RabbitMQwebsite.
n
Relativity agent and web servers must be able to communicate with the cluster over the following
ports:

Pre-Installation Guide 45
o
TCP: 5672 (non TLS configurations) and / or 5671 (TLS configurations)
o
HTTP(S): 15672 (non TLS configurations) and / or 15671 (TLS configurations)
n
Options for handling node failures:
o
Manual Fail Over
l
No special network configuration required.
l
Manual updates to relativity configuration and service restarts needed in the event of
node failure.
o
Load Balancer/Proxy
l
Configure Relativity’s service bus instance settings to connect to a load balancer for the
cluster.
l
HTTP and TCP traffic should be load balanced across at least two nodes in the cluster.
l
The load balancer must allow for long lived TCP connections to avoid a degradation in
performance.
l
In the event of a node failure, Relativity processes connected to the node will attempt to
reconnect until successful allowing the load balancer to the direct the connection to a
healthy node.
l
Round Robin or other more advanced routing techniques can be used.
o
Dynamic DNS
l
Configure Relativity to connect to a domain name which is dynamically routed to the
RabbitMQ nodes with a very short time to live.
l
Effectively a Round Robin Load Balancer.

Pre-Installation Guide 46
Creating the Cluster
Note: The following steps assume a windows server based RabbitMQ deployment.
1.
Before forming a cluster, install Erlang and RabbitMQ on each server you which to include in the
cluster. For more information, see Installing Erlang and RabbitMQ.
2. Obtain an Erlang cookie to be used by the cluster. This cookie is used for inter-node authentication
and is randomly generated on start-up if not present. For a cluster, the values much match on every
host. For more information, see the RabbitMQwebsite.

Pre-Installation Guide 47
1. Log into the host server.
2. Navigate to C:\WINDOWS\system32\config\systemprofile.
3. Copy the .erlang.cookie file to a central location. This will serve as the shared cookie for the
cluster.
3. For each host server:
1. Run rabbitmqctl stop_app in the RabbitMQ command prompt.
Note: If you run into issues while running RabbitMQ commands, trying restarting the
RabbitMQ windows service. If you still see issues, try rebooting the server.
2. Run rabbitmqctl reset.
3. Replace the .erlang.cookie file at C:\WINDOWS\system32\config\systemprofile with the
one you copied to a central location.
4.
Run rabbitmqctl join_cluster
rabbit@%ComputerNameOfHostThatCookieWasCopiedFrom%.
Note: Do not use the FQDN of the server or the command will error without the RABBITMQ_
USE_LONGNAME setting in RabbitMQ set. Also, the host name is case sensitive.
5. Replace the .erlang.cookie file at C:\Users\%USERNAME_THAT_INSTALLED_
RABBITMQ%\.erlang.cookie with the one you copied to a central location.
6.
Open RabbitMQ command prompt.
4. Run rabbitmqctl cluster_status on any host in the RabbitMQ command prompt and confirm the out-
put for nodes and running nodes contains all hosts.
Note: Ensure the management plugin is enabled on each node. For more information, see
Installing Erlang and RabbitMQ.
5. Verify the status of the cluster on the RabbitMQ management page.

Pre-Installation Guide 48
Notes:
n
If any of the nodes are missing, log into that node and complete the steps found under
Creating a cluster.
n
If any of the nodes are yellow, this likely means the management plugin has not been enabled.
Log in to that host and run rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management in the
RabbitMQ command prompt. For more information, see Installing Erlang and RabbitMQ.
Configuring the Cluster
By default, each queue and exchange only exists on a single node in the cluster. This means that those
queues and exchanges are no longer be available if those nodes go down. For high availability, it is also
necessary to ensure the individual queues and exchanges on the cluster are mirrored across multiple
nodes. For more information, see the RabbitMQwebsite.
Notes:
n
If your cluster has more than three nodes, it may be beneficial to configure your queues and
exchanges to be mirrored across an exact number of nodes in order to limit internode com-
munication.
n
The following steps can be used to configure all queue and exchanges to be mirrored across all
nodes.
1. Open a browser and navigate to http://localhost:15672/
2. Log in using the following credentials:
n
username: guest
n
password: guest
Note: The default user guest can only log in from local host.
3. Click Admin > Policies.
4. Expand Add / update a policy.
5. Select a virtual host to be used, ex: Relativity.

Pre-Installation Guide 49
6. Enter the following information:
n
Name—Ha-all
o
This will apply to all queues that are not SignalR or Conversion. In addition to the normal
HA values, it also places a default expiration on all queues of 24 hours. The addition of
the expiration value should help to clean up miscellaneous orphaned queues, such as
ResourcePoolStatus queues for agents that no longer exist.
o
The 24-hour expiration only starts after the policy has been applied. This means the
orphaned queues will not be cleaned up immediately, but will be cleaned up 24 hours
after creating the policy.
n
Pattern—leave blank, means the policy will apply to everything.
n
Priority— -10
n
Definition
o
expires = 86400000 | Number
o
ha-mode = all | String
o
ha-sync-mode = automatic | String
7. Click Add policy. The policy now appears under User policies.
8. Add another policy for Relativity Document Conversions by first selecting Relativity again as the vir-
tual host to be used.
9. Enter the following information:
n
Name—Conversion
o
This policy applies to all conversion queues. This includes all values from the new HA-
All policy as well as lowering the message time to live to 1 hour, down from 24 hours.
The reduced message time to live will help discard conversion requests for especially
large documents that are taking a very long time to convert.

Pre-Installation Guide 50
o
The messages will not be discarded if they are currently in an unacked/in progress state,
and restarting or deleting and recreating conversion agents may still be required.
n
Pattern—Conversion
n
Priority— 0
n
Definition
o
expires = 86400000 | Number
o
ha-mode = all
o
ha-sync-mode = automatic
o
message-ttl = 3600000 | Number
10. Confirm that all policies are properly logged. From the queues page, all SignalR queues should dis-
play SignalR under features. All conversion queues should display Conversion under features. All
other queues should display HA-All under features.

Pre-Installation Guide 51
7.3.2 Service Bus for Windows Server
Note: Microsoft has announced that it will not be making any future updates to Service Bus for Windows
Server. Microsoft support for Service Bus for Windows Server ended in January 2023 and the product is
no longer receiving security updates. Additionally, Microsoft only officially supports Service Bus for
Windows Server for Windows Server 2012 and SQL Server 2012. While Service Bus for Windows Server
is still supported for Relativity Server 2021, we plan to remove support in subsequent Relativity Server
releases. RabbitMQ is the recommended message broker for Relativity Server 2021.
You can perform an online installation for Service Bus for Windows Server that requires an internet
connection, or an offline installation that requires the internet only to download the installer. For additional
information, see the Relativity Service Bus guide.
Note: You can optionally install the Service Bus for Windows Server on multiple hosts.
The process for installing and configuring Service Bus for Windows Server includes these steps:
n
Best practices for Service Bus for Windows Server below
n
Pre-installation steps for Service Bus for Windows Server on the next page
n
Online installation for Service Bus for Windows Server on page53
n
Offline installation for Service Bus for Windows Server on page54
n
Configuring Service Bus for Windows Server on page57
7.3.2.1 Best practices for Service Bus for Windows Server
Use the following guidelines to optimize the Service Bus for Windows Server installation and farm setup:
n
Service bus installation—For a typical installation, install Service Bus for Windows Server on a
server or VM that is accessible throughout your Relativity instance. Install the service bus on a
machine that meets these minimum requirements: CPU clock speed of 1.6GHz, a CPU core count of
2 or more, and physical memory of 3.5 GB, although 6 GB is recommended. These same guidelines
also apply when installing the service bus on multiple hosts. See Best Practices Analyzer
(https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn441402.aspx).
n
Node—a typical Relativity installation requires only a single node in a farm. For a multiple host install-
ation, ensure that you have an odd number of nodes, but do not exceed the maximum of five nodes.
Three nodes is a common configuration for most environments configured with multiple hosts. While
you can install the service bus on five nodes, determine if your Relativity installation requires these
additional nodes. They may result in unnecessary overhead for your environment.
Note: During installation or upgrade, the machine for the Relativity service bus must be a node in
the farm.
n
SQL Server instance location—any machine in the farm can host the service bus databases. We
recommend hosting the SQL instance on the Invariant database server. However, you can host it on
a SQL instance on a separate machine. The SQL Server instance used for the Service Bus for Win-

Pre-Installation Guide 52
dows Server must meet the minimum requirements that Microsoft specifies in Prerequisites on
MSDN (https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn441411.aspx).in Prerequisites on MSDN.
n
Message containers—For a typical Relativity installation with a single node, we recommend using
the default value of three message containers in the farm.For a multiple host environment, Microsoft
recommends using 2n message containers, where n is the number of nodes. For example, if you
install the service bus on three hosts, then you need six message containers.See step 11 in Setting
up a new farm on page57.
To review the Microsoft recommendations for message containers, see Scaling on MSDN
(https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn441424.aspx).
n
Message backing (SQL) high availability—review the Microsoft recommendations for message
backing with high availability, which suggest using SQL mirroring or SQL AlwaysOn availability
groups. For more information, see Architecture overview on MSDN (https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-
us/library/dn441428.aspx).
n
Server roles—install the Relativity service bus on a single machine that is a node in the Service Bus
for Windows Server farm. In a multiple host environment, install the Service Bus for Windows Server
on multiple machines that you want added to your farm. However, you only need to install the Relativ-
ity service bus on single machine as in a typical installation. For more information, see Relativity
Installation.
Note: Make sure that you set up a farm and configure it before you run the Relativity installer. The
Relativity installer validates that your environment meets this requirement. See Configuring
Service Bus for Windows Server on page57.
7.3.2.2 Pre-installation steps for Service Bus for Windows Server
Before installing Service Bus for Windows Server, complete the following prerequisites:
n
Complete the pre-installation steps for Relativity, such as setting up user accounts and certificates.
For more information, see Certificate requirements for Service Bus for Windows Server on page9.
n
Ensure that you have the prerequisites for Service Bus for Windows Server. You need to meet these
requirements to set up your farm correctly. See Planning Your Deployment (https://msdn.-
microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn441415.aspx).
n
For a typical installation, identify the server or VM where you want to install Service Bus for Windows
Server. To install the service bus on multiple hosts, identify the servers or VMs for this purpose. The
farm requires that you add an odd number of nodes, but you should not exceed a maximum of five
nodes. For more information, see Best practices for Service Bus for Windows Server on the previous
page.
Note: For a typical installation, install Service Bus for Windows Server on a server or VM that is
accessible throughout your Relativity instance. Install the service bus on a machine that meets
these minimum requirements: CPU clock speed of 1.6GHz, a CPU core count of 2 or more, and
physical memory of 3.5 GB, although 6 GB is recommended. These same guidelines also apply
when installing the service bus on multiple hosts. See Best Practices Analyzer
(https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn441402.aspx).
n
Ensure that you install .NET Version 4.7.2 or 4.8 in your environment. You must install.NET Version
4.7.2 or 4.8 before you install Service Bus 1.1 with TLS 1.2. It requires .NET Version 4.7.2 or 4.8.

Pre-Installation Guide 53
7.3.2.3 Online installation for Service Bus for Windows Server
To perform an online installation, you must have an internet connection. This process includes downloading
the Microsoft Web Platform Installer (Web PI) and then installing the service bus on server or VM in your
Relativity environment. See Best practices for Service Bus for Windows Server on page51.
Review the following installation considerations:
n
For a typical installation, install Service Bus for Windows Server on a server or VM that is accessible
throughout your Relativity instance. Consider installing the service bus on the agent server where you
intend to run conversion agents. Follow these same guidelines when installing the service bus on mul-
tiple hosts.
n
In a multiple host environment, install the Service Bus for Windows Server on each machine that you
want added as a node in the farm. However, you only need to install the Relativity service bus on
single machine that is a node in the farm. For more information, see Relativity Installation.
n
Notice that the installer for the Service Bus for Windows Server adds the database files for the service
bus to the default locations used by your SQL Server. These database locations differ from those
used for the Relativity databases specified in the RelativityResponse.txt file installation input file.
You can use the default locations for the Service Bus for Windows Server databases. However, if you
want to change these locations, see View or Change the Default Locations for Data and Log Files
(SQL Server Management Studio) on the Microsoft website, https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-
us/library/dd206993.aspx.
If you do not have an internet connection, you can perform an offline installation. For more information, see
Offline installation for Service Bus for Windows Server on the next page.
Use the following steps to install Service Bus for Windows Server:
1. Download the Web PI from the Web Platform Installer Direct Downloads page, https://-
docs.microsoft.com/en-us/iis/install/web-platform-installer/web-platform-installer-direct-downloads.
2. In the WebPI 5.0 section, click the appropriate link for your machine.
3. Locate the WebPlatformInstaller_amd64_en-US.msi that was downloaded by the installer. It
appears in the lower left corner of the browser, or in your download folder.
4. Double-click the file to launch the Web PI. When the Security Warning dialog box appears, click Run.

Pre-Installation Guide 54
5. On the Spotlight tab, search for Service Bus 1.1 with TLS 1.2 Support.
6. Select Windows Azure Pack: Service Bus 1.1 with TLS 1.2 Support in the search results.
7. Click Add > Install.
8. Click I Accept to accept the license terms and start the installation.
9. When the installation process completes, click Finish. You have now installed Service Bus for Win-
dows Server.
10. Complete the steps for configuring the service bus. For more information, see Configuring Service
Bus for Windows Server on page57.
7.3.2.4 Offline installation for Service Bus for Windows Server
To perform an offline installation, you only need an internet connection to download the installer. You can
then complete the offline installation process on server or VM in your Relativity environment. See Best
practices for Service Bus for Windows Server on page51.
Review the following installation considerations:
n
For a typical installation, install Service Bus for Windows Server on a server or VM that is accessible
throughout your Relativity instance. Consider installing the service bus on the agent server where you
intend to run conversion agents. Follow these same guidelines when installing the service bus on mul-
tiple hosts.
n
In a multiple host environment, install the Service Bus for Windows Server on each machine that you
want added as a node in the farm. However, you only need to install the Relativity service bus on
single machine that is a node in the farm. For more information, see Relativity Installation.
n
Notice that the installer for the Service Bus for Windows Server adds the database files for the service
bus to the default locations used by your SQL Server. These database locations differ from those
used for the Relativity databases specified in the RelativityResponse.txt file installation input file.
You can use the default locations for the Service Bus for Windows Server databases. However, if you
want to change these locations, see View or Change the Default Locations for Data and Log Files
(SQL Server Management Studio) on the Microsoft website, https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-
us/library/dd206993.aspx.
Pre-Installation Guide 55
After you complete the installation, call the WebPICmd executable using the following command line
switches in a command prompt window:
n
/list—displays a list of available products.
n
/listoption:—acts as a sub-command used for filtering on a list.
n
/install—installs products available through the Web PI.
n
/offline—downloads the products for use offline. This command downloads products so you can be
installed later by running the /install command.
n
/Products:—acts as a sub-command of both the /offline and /install commands. You can use it to
indicate which of the available products you want to download and install, respectively.
Downloading the Web Platform Installer
You need an internet connection to download the Web Platform Installer (Web PI) used to install the Service
Bus for Windows Server.
Use the following steps to download the installer:
1. On a machine with an internet connection, complete steps 1-4 listed in Online installation for Service
Bus for Windows Server on page53. You should now have installed the Web PI on your machine.
2. Verify that the WebPICmd.exe file was installed on your machine by locating it in the following folder:
%ProgramFiles%\Microsoft\Web Platform Installer
3. Open a Windows PowerShell command prompt. Select Run as Administrator.
4. Run the following /list command to display ServiceBus_1_1 in a list of service bus products:
webpicmd /list /listoption:Available|?{$_.Contains(“ServiceBus”) }
5. Use the following command to download the files for installing Service Bus 1.1 with TLS 1.2 Support:
webpicmd /offline /Products:"ServiceBus_1_1_TLS_1_2" /Path:C:\ServiceBusOfflineFiles

Pre-Installation Guide 56
6. Verify that PowerShell displays information about the products that are cached and processed, and
the feeds being built.
These processes succeeded if you see the message listed in the following screen shot. The path
command indicates where the files are downloaded. You can modify this path as necessary.
7. After the download completes, copy the entire /Path directory to the machines in your offline envir-
onment where you want to install Service Bus for Windows Server.
Installing Service Bus for Windows Server
For a typical Relativity installation, install the Service Bus for Windows Server on the machine that you want
added as a node in the farm. For a multiple host environment, repeat this installation process on all the
machines that you want added as nodes in the farm.
Use the following steps to install the service bus:

Pre-Installation Guide 57
1. Open a Windows PowerShell command prompt. Select Run as Administrator.
2. Change to the directory containing the installation files that you downloaded using the /offline com-
mand and copied to this machine. See step 7 in Downloading the Web Platform Installer on page55.
For example, if you download the files to a directory on your hard drive called ServiceBusOfflineFiles,
you would execute this command:
cd C:\ServiceBusOfflineFiles\
3. Run the following command to install Service Bus 1.1 with TLS 1.2 Support. Update the initial part of
the path displayed after the /xml command with the directory where your files are located. For
example, you would replace C:\ServiceBusOfflineFiles with your file path:
.\bin\WebpiCmd.exe /install /Products:"ServiceBus_1_1_TLS_1_2" /xm-
l:C:\ServiceBusOfflineFiles\feeds\latest\webproductlist.xml
4. Accept the licensing agreement to install the service bus.
5. After the installation completes, verify that you see a message like the one in the screen shot:
6. Complete the steps for configuring the service bus. For more information, see Configuring Service
Bus for Windows Server below.
7.3.2.5 Configuring Service Bus for Windows Server
After installing Service Bus for Windows Server, you need to complete several configuration steps, which
include setting up a new service bus farm. A farm consists of one or more servers, or nodes that use the
service bus. For troubleshooting information, see the Relativity Service Bus guide.
Setting up a new farm
You set up a new farm by adding a single server to it. After completing this process, you can optionally add
multiple hosts to the farm. For more information, see Optionally adding multiple servers to an existing farm
on page62.
Note: Before you can add a server to a farm, you must install the Service Bus for Windows Server on it.
Use the following steps to set up a new farm:

Pre-Installation Guide 58
1. Locate the Service Bus Configuration tool on your desktop. The service bus installer automatically
installs this tool for you.
2. Launch the Service Bus Configuration tool, and then click With Custom Settings.
3. Complete the fields in the Service Bus Configuration wizard. See Fields in Service Bus Configuration
wizard below.
4.
After you set the fields in the wizard, click the to display a summary of the information used to con-
figure the service bus.
5.
Click the to start the configuration process.
6. Set the DNS for the service bus farm. Execute the following commands with the Service Bus Power-
Shell tool. This DNS must match the name in the Issued to field on the certificate used for the service
bus.
Stop-SBFarm
Set-SBFarm -FarmDns 'YOUR_DNS'
Update-SBHost
Start-SBFarm
7. Verify that the service bus is configured properly by entering your URL into a web browser, and con-
firming that the following page is displayed. Use this format for the URL: https://<Your_
DNS>:<Your_HTTPS_Port>/<Your_Namespace>.
Fields in Service Bus Configuration wizard
In the Service Bus Configuration wizard, you need to set the following fields, including the suggested or
required values for them.
Configure Farm Management Database
In this section, click the Advanced Options drop-down to display additional fields.
n
SQL Server Instance—enter the name or address of the SQL Server where you want to host the
SbManagementDB. This SQL instance hosts the databases for your farm.
n
Enable SSL connection with the SQL Server instance—optionally, click this checkbox to use
SSL.
n
Authentication—complete one of the following tasks to set up authentication for the SQL instance:
o
Windows Authentication—select this option if your instance supports Windows authen-
tication.

Pre-Installation Guide 59
o
SQL Server Authentication—select this option to use SQL server authentication. Enter cre-
dentials in the User Name and Password fields for a sysadmin account or the EDDSDBO
account.
n
Use the above SQL Server instance and settings for all databases—click this checkbox.
n
Database Name—optionally, update the name for your database. You can also just use the default
name, which is SbManagementDB.
n
Test Connection—click this button to ensure that you have enter the correct settings for your SQL
Server.
Configure Gateway Database
n
SQL Server Instance—do not modify the default setting for the Gateway database.
n
Database Name—do not modify the default name for the Gateway database.
n
Test Connection—click the button for the database instance. appears next to the server instance
when the installer verifies a connection.
Configure Message Container Database
n
SQL Server Instance—do not modify the default setting for the Message Container database.
n
Database Name Prefix—do not modify the default name for the Message Container database.
n
Number of Containers—enter a value for the number of containers. For a typical Relativity install-
ation with a single node, we recommend using the default value of three message containers in the
farm. For a multiple host environment, Microsoft recommends using 2n message containers, where n
is the number of nodes. For example, if you install the service bus on three hosts, then you need six
message containers. For more information, see Best practices for Service Bus for Windows Server
on page51.
Note: If you previously configured the number of containers and need to update this value, see
Adding a new message container on page64.
n
Test Connection—click this button for the database instance. appears next to the server instance
when the installer verifies a connection.
Configure Service Account
n
User ID—enter the user ID for the Relativity service account.
n
Password—enter the password for the Relativity service account.
Note: You must use the Relativity service account credentials for the service account on the
Service Bus for Windows Server. For more information, see User and group accounts on page16.
Configure Certificate
Use one of the following methods to configure a certificate. You can auto-generate a certificate.
Alternatively, you can use an existing certificate with the same domain as the FQDN of the service bus
server, or you can issue a certificate through an CA. For more information, see Certificate requirements for
Service Bus for Windows Server on page9.

Pre-Installation Guide 60
n
Auto-generate—select this checkbox to automatically create a certificate. If you select this option ,
you must enter a value in the following fields:
o
Certificate Generation Key—enter a certificate generation key of your choice, any com-
bination of characters, if you are auto-generating a certificate. This key is required if you want
to add more hosts to the farm in the future. Complete the steps required to distribute the gen-
erated certificate to all agent, web, queue manager, and worker servers agent and web serv-
ers. See Configuring an auto-generated SSL certificate on the next page.
Note: A certificate is required on the queue manager and worker servers as part of the
connection between Invariant and Service Bus.
o
Confirm Certificate Generation Key—re-enter the key from the previous field.
n
Farm Certificate—if you did not auto-generate a certificate, click Browse to select the certificate that
you want to use for HTTPS communication between the service bus and the clients. For more inform-
ation, see Certificate requirements for Service Bus for Windows Server on page9.
n
Encryption Certificate—if you did not auto-generate a certificate, click Browse to select the cer-
tificate used to encrypt all the connection strings in the SbManagementDB database and registry.
You configured the SbManagementDB database in Configuring HTTPS site bindings on page33. For
more information, see Certificate requirements for Service Bus for Windows Server on page9.
Configure Ports
n
Consider using the port numbers in the following table. These port numbers are suggested con-
figuration values.
Port name
Port
number
Description
HTTPS Port 9455
Specifies the HTTPS port used for communication with Service Bus for
Windows Server. To avoid port conflicts with Data Grid, this value differs
from Microsoft's default value.
TCP Port 9454
Specifies the TCP port used for communication with Service Bus for Win-
dows Server. To avoid port conflicts with Data Grid, this value differs from
Microsoft's default value.
Message
Broker Port
9456
Specifies the port used for message broker communication by Service
Bus for Windows Server. To avoid port conflicts with Data Grid, this value
differs from Microsoft's default value.
Resource Pro-
vider HTTPS
Port
9459
Specifies the port used for communication with the Service Bus Man-
agement Portal. To avoid port conflicts with Data Grid, this value differs
from Microsoft's default value.
AMQP Port 5682
Specifies the AMQP port used for communication with the Service Bus
via the AMQP protocol. The default value of 5672 is the industry default
for AMQP communication. We recommend changing this value to 5682 to
avoid potential port conflicts.
AMQPS Port 5681
Specifies the AMQPS port used for communication with the Service Bus
via the AMQP protocol over SSL. The default value of 5671 is the industry
default for AMQPS communication. We recommend changing this value
to 5681 to avoid potential port conflicts.

Pre-Installation Guide 61
Port name
Port
number
Description
Internal Com-
munication Port
Range
9000
Specifies the ports used for communication between hosts in the Service
Bus farm. Use the default recommended by Microsoft default. It does not
have any port conflicts with Relativity components.
n
Enable firewall rules on this computer—select this checkbox. When you select this option, the ser-
vice bus automatically sets up the necessary rules to communicate over the firewall. If you do not
select this option, then the client must configure the necessary rules or the service bus will not func-
tion properly.
Configure Admin Group
n
Configure Admin Group—enter the name of an admin user group. This group has access to the ser-
vice bus databases and admin access to the farm, including full admin rights on the Service Bus for
Windows Server. By default, the Admin Group box is set to BUILTIN\Administrators group, but you
can modify the users in this group as necessary.
Note: If the admin group is a local group, make sure that it exists on all servers in the farm and the
SQL instance specified in Configuring HTTPS site bindings on page33.
Configure Service Bus Namespace
n
Create a default namespace—select this check box. Optionally, enter a name for the namespace in
the text box. You can use the default value, since Relativity creates an new namespace during install-
ation.
Note: After you complete these fields, you must return to step 4 in Setting up a new farm on page57 to
complete the installation process. Additional steps include setting up the DNS for the service bus farm,
and verifying that the service bus is working properly.
Configuring an auto-generated SSL certificate
You can auto-generate SSL certificates for remote clients and then export the CA and Certificate revocation
list (CRL) to them.
Use the following steps to configure a certificate on a remote client:
1. Log in to the machine where you installed Service Bus for Windows Server.
2. Open the Service Bus PowerShell tool.
3. To export the CA and CRL from a farm node, execute the following cmdlet:
Get-SBAutoGeneratedCA
If you do not provide file names, the cmdlet exports the CA and CRL to the service bus root folder with
the name AutoGeneratedCA.cer and AutoGeneratedCA.crl respectively. The following example
illustrates how to run this cmdlet with file names:
Get-SBAutoGeneratedCA -CACertificateFileName "C:\CACert.cer" -Revoc-
ationListFileName "C:\RevocationList.crl"

Pre-Installation Guide 62
4. Import the CA and CRL files to your Relativity servers that need access to the service bus. For
example, you need to import the auto-generated service bus certificates to the web, agent, worker,
and worker manager servers.
5. On the client machine, open a Microsoft Management Console (MMC) window. On the Start menu,
click Run, enter MMC, and then click OK.
6. In the MMC window, click File > Add/Remove Snap-in. The Add/Remove Snap-in dialog box
appears.
7. Add the Certificates snap-in by selecting the Computer Account and Local Computer options.
Click OK.
8. In the MMC window, right-click the Certificates\Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
9. Open All Tasks, and select Import.
10. Select the AutoGeneratedCA.cer file and import it.
11. In the MMC window, right-click on the Intermediate Certification Authorities.
12. Open All Tasks, and select Import.
13. Select the AutoGeneratedCA.crl file and import it.
Optionally adding multiple servers to an existing farm
You can optionally add more servers or nodes to increase the computing power of the service bus. A typical
Relativity installation requires only a single node in the farm. For a multiple host installation, you can
optionally add three or five nodes to the farm. Three nodes is a common configuration for most
environments using multiple hosts.
Before adding more nodes to your farm, review these guidelines:
n
Add nodes that reside in the same domain.
n
Use the fully qualified domain name as the instance address for each machine that you add.
n
Ensure that you have an odd number of nodes. A service bus farm must have an odd number of
nodes. For example, it can include one, three, or five nodes. See Best practices for Service Bus for
Windows Server on page51.
n
Do not exceed the maximum of five nodes in the farm. To avoid extra overhead, determine whether
your environment needs the additional nodes.
Use the following steps to add another server:

Pre-Installation Guide 63
1. Open the Service Bus Configuration tool.
2. Click Join an Existing Farm.
3. In SQL Server Instance box, enter the name or address of the SQL Server where the SbMan-
agementDB is hosted.
4. Enter the SQL Server instance address. Use the fully qualified domain name for the machine as the
instance address.
5. In the Database Name box, enter the name of the database if you modified the default name.
6. Under Advanced Options, click one of these options to set up authentication for the SQL instance:
n
Enable SSL connection with the SQL Server instance—select this option for SSL.
n
Windows Authentication—select this option if your instance supports this authentication
type.
Pre-Installation Guide 64
n
SQL Server Authentication—if you select this option, enter credentials in the User Name
and Password fields.
7. On the Join Service Bus Farm page, enter the User ID and Password for the Relativity service
8. Select Enable firewall rules on this computer. If you auto-generated the certificate, you must enter
the certificate generation key in the Provide Certificate Generation Key box. You must enter the
same farm key you used to auto-generate the certificate for the service bus farm.
9.
Click the , and then to start the configuration process.
Adding a new message container
After you configure your service bus farm, you can continue to add new message containers to your
environment. Adding containers scales the data tier of the service bus. The larger data tier increases the
availability of the SQL layer to store messages, queues, topics, and other entities. Review following
guidelines to determine the number of message containers required for your service bus:

Pre-Installation Guide 65
n
Single node installation—For a typical Relativity installation with a single node, we recommend
using the default value of three message containers in the farm. See step 11 in Setting up a new farm
on page57.
n
Multiple node installation—For a multiple host environment, Microsoft recommends using 2n mes-
sage containers, where n is the number of nodes. For example, if you install the service bus on three
hosts, then you need six message containers. To review the Microsoft recommendations for mes-
sage containers, see Scaling on MSDN (https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn441424.aspx).
Use the following PowerShell cmdlets to add a new message container. For more information, see Service
bus PowerShell cmdlets in the Relativity service bus guide.
n
Execute a cmdlet from outside the farm—when you execute a cmdlet from outside the farm, the
SBFarmConnectionString points to the management databases of the service bus farm.
New-SBMessageContainer –ContainerDBConnectionString <Connection string
for the database with message containers> -SBFarmConnectionString <Con-
nection string for the SbManagementDb>
n
Execute a cmdlet from inside the farm—when you execute a cmdlet inside the farm, you call the
cmdlet without the SBFarmConnectionString. In this example, the database is called container2. You
must specify a unique database name for use in your environment when you run the New-SBMes-
sageContainer command.
New-SBMessageContainer -ContainerDBConnectionString "data source-
e=localhost\sqlexpress;database=container2;integrated security=true"
Troubleshooting the service bus farm
Review the following list of errors and resolutions to troubleshoot your service bus configuration. For
additional troubleshooting information, see Service bus PowerShell cmdlets in the Relativity Service Bus
guide.
Service Bus Gateway service will not start
If you cannot start the Service Bus Gateway service, then you may need to install a Windows update. To
install this update, see https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/3086798.
Timeout error occurs when creating or joining service bus farm
If you receive a timeout error when attempting to create or join a service bus farm, you may have a port
conflict in your environment. You can check the availability of a port in your environment by running the
following netstat command:
netstat -na | find "<Your Port>"
See the following sample command:
netstat -na | find "9455"
If the command doesn’t return a value, then the port is free. For a list of recommended ports, see Configure
Ports on page60.
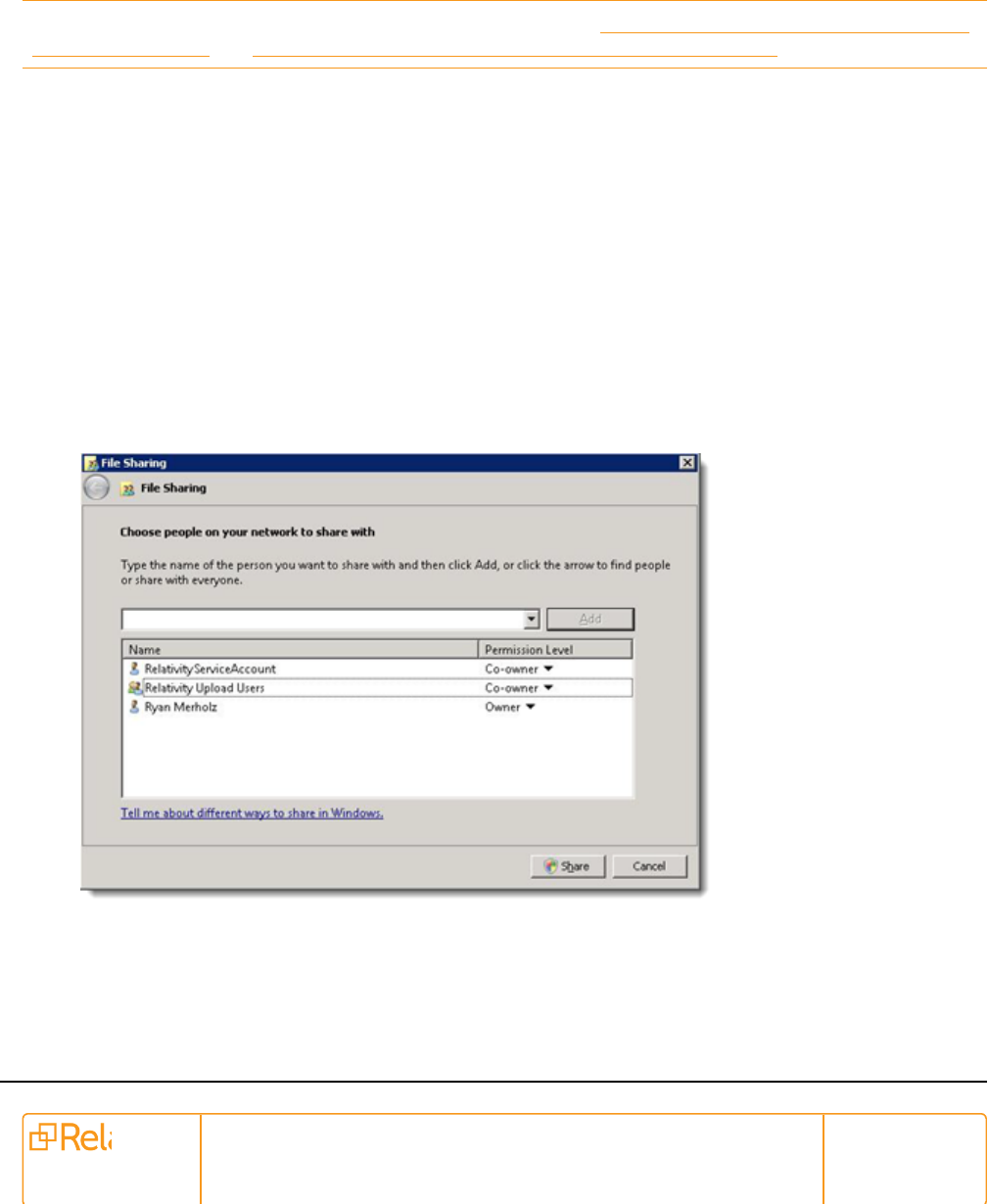
Pre-Installation Guide 66
8 File (document) share or server
You can use a file share or server as a repository for documents stored in Relativity. You must create a
directory that is used as the root of the directories and documents created through the Relativity system.
This file share must be a folder rather than a drive letter. For example, C:\Fileshare instead of just the C
drive.
In addition, confirm that the Full Text, .ldf files, .mdf files, and Backups are all specified to the folder level. Do
not specify them to only a drive.
Note: For information about setting up processing servers, see Database server for processing or native
imaging on page77 and Worker server for processing or native imaging on page79.
8.1 Create share
The document root directory is exposed to the Relativity application through a shared drive. Use these steps
to share the folder:
1. Right-click the folder, and go to Properties.
2. Open the Sharing tab, and click Share.
3. Enter the Relativity Service Account name, domain\account, and then click Add.
4. Select the service account on the share list, and then change Permission Level to Co-owner.
5. Enter the Relativity Upload Users group, and then click Add.
6. Select the group on the share list, and then set the Permission Level to Co-owner.
7. Click Share.
8. When the share completes, click Done.
9. On the Document Properties dialog box, select the Security tab.

Pre-Installation Guide 67
10. Verify that the users and groups you added to the share also have Full Control security permissions
to the folder itself.

Pre-Installation Guide 68
9 Cache location server
The cache location server requires the same permissions as the file share. For more information, see Pre-
installation on page5.
Note: During installation or upgrade, Relativity automatically creates a cache location server based on
the location of your file repository. You can also manually add cache location servers. For more
information, see Cache location servers on the Relativity Server 2022 Documentation site.

Pre-Installation Guide 69
10 Analytics server setup
Before completing the steps for upgrading to Analytics Server 2022, make sure you have completed the
steps contained in this section.
10.0.1 Required software
The following software must be installed on the analytics server:
n
Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, or Windows Server 2012 R2
n
.NET Version 4.7.2 or 4.8
10.1 CAAT 4.5.0 and above
The following table breaks down which versions of Microsoft Visual C++ are required for which versions of
CAAT.
Required Microsoft Visual C++ version (Redistributable x86 and x64)
CAAT version 2010 2012 2013 2015
CAAT 4.2.5 and above
√ √ √ √
10.1.1 Create installation index directory
1. Create a folder called CAAT on the root of the C: drive.
2. The Analytics index directory must also be created before installing Analytics. We recommend that
you not keep the index directory on the C: drive due to the size requirements. We recommend you
use locally-attached storage referenced by a drive letter, such as E:\AnalyticsData, rather than a
UNC path. For more information, see Index directory requirements in the Analytics Guide. Do not cre-
ate a local drive map to a UNC. For example, do not open \\servername\CAAT1 and map it to drive Z:.
This is because drive mappings are specific to each Windows user and may not be available to the
Relativity Service Account.
10.1.2 Assign permissions to the analytics directories
You must configure permissions for the necessary directories on the analytics server. Follow these steps to
assign the proper permissions:
1. Add the Relativity Service Account user to both the Administrators and the Users group.
2. Navigate to C:\CAAT\ and add Full Control permissions to both the Administrators and the Users
group.
n
Right-click on C:\CAAT.
n
Navigate to the Security tab.
n
Edit the Users group permissions and add Full Control.

Pre-Installation Guide 70
n
Edit the Administrators group permissions and add Full Control.
n
Click Apply.
3. Navigate to the index directory and add Full Control permissions to both the Administrators and the
Users group.
n
Right-click on the index directory folder.
n
Navigate to the Security tab.
n
Edit the Users group permissions and add Full Control.
n
Edit the Administrators group permissions and add Full Control.
n
Click Apply.
4. Reboot the server after all user and/or permission changes.
10.1.3 Required setup
1. The web server needs to be able to communicate with the analytics server via TCP ports 445, 8080,
and 8443. .
2. Disable anti-virus programs. At minimum it needs to be set to ignore the C:\CAAT installation folder
as well as the index directory.
3. Ensure that proxy settings are disabled on the analytics server by performing the following steps:
n
Go to Internet Options via the Control Panel.
n
Select the Connections tab.

Pre-Installation Guide 71
Select LAN Settings and ensure the Proxy server section is cleared:

Pre-Installation Guide 72
4. Click OK to save your changes.
5. Ensure that the required display language is set on the analytics server by performing the following
steps:
n
On the Analytics server, click the Start button.
n
Click Control Panel.
n
Click Change date, time, or number formats.
n
Click the Administrate tab.
n
Select Copy settings and ensure the correct language is set:

Pre-Installation Guide 73
n
Click OK to save your changes.
10.2 Elasticsearch server setup
10.2.1 Required software
The following software must be installed on the Elasticsearch server:
n
Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server 2019

Pre-Installation Guide 74
11 Index share - dtSearch repository
Create a root directory for the directories created by dtSearch index builds within the system.
11.1 Create share
The dtSearch index directory is exposed to the Relativity application through a shared drive. Use these
steps to share the folder:
1. Right-click on the folder, and then go to Properties.
2. Open the Sharing tab, and then click Share.
3. Enter the Relativity Service Account name, domain/account, and then click Add.
4. Select the service account on the share list, and then set the Permission Level to Co-owner.
5. Click Share.
6. When the share completes, click Done.
7. On the Document Properties dialog box, select the Security tab.
8. Verify that the Relativity Service Account also has Full Control security permissions to the folder
itself.

Pre-Installation Guide 75
12 SMTP server setup
Relativity requires access to an SMTP server to handle the delivery of error messages, job notifications, and
billing statistics to both internal contacts and to us at Relativity. We provide an easy to use SMTP
connectivity tool, which Customer Support runs against your system to verify the servers can properly
communicate with your specified SMTP server.
Note: Make sure that the newly created agent and web servers used in your Relativity environment are
configured to permit the relay of messages to external recipients. If you do not provide this permission, job
notifications and other messages are blocked.

Pre-Installation Guide 76
13 Environment modification for processing or native
imaging
Before running the Invariant, worker manager server, installer, you must perform the following steps to
modify your environment.
Component
Environment Configuration Settings
Database
n
Disable User Access Control (UAC).
n
Enable your firewall according to the Ports Diagram and Relativity Server Security doc-
ument on the Relativity Community portal under the Security Resources folder.
Queue Man-
ager
None
Workers
n
Enable the Desktop Experience Windows Feature.
n
Disable User Access Control (UAC). Disabling UAC on the worker server suppress
pop-ups from the application in which the processing engine opens files.
n
Enable your firewall according to the Ports Diagram and Relativity Server Security doc-
ument on the Relativity Community portal under the Security Resources folder.
n
Set Windows Updates to download, but allow you to choose whether to install. You
can set this option through the Control Panel under System and Security.
For more information, see the Worker manager server Installation guide.

Pre-Installation Guide 77
14 Database server for processing or native imaging
The following sections provide basic information about setting up the database server for processing or
native imaging. For more information, see the Worker manager server Installation guide.
Note: If you are only installing Collect or Legal Hold, you do not need this pre-requisite.
14.1 Required software
Install the following software on the database server:
n
Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, or Windows Server 2012 R2
n
SQL Server 2017 or SQL Server 2019
o
SQL Server 2019 requires Windows Server 2016 or 2019.
n
Relativity supports in-place upgrades from SQL Server 2016 to any higher supported version. For
details on SQL Server upgrade, follow the EDDS migration Guide. To determine if you should
upgrade your current SQL Server version to SQL Server 2019, note the following considerations.
Contact Relativity Support if you have further questions.
o
The base operating system of your SQL Server must be at a minimum Windows Server 2016.
Any Windows Server version below 2016 will require an EDDS migration to be performed to a
server with a proper operating system version and SQL version. Relativity does not support in-
place operating system upgrades. .
o
SQL Server version lower than SQL 2016 will require an EDDS migration since upgrading to
SQL Server 2019 from versions lower than SQL Server 2016 has not been tested by Relativity.
n
.NET 4.7.2 or 4.8
n
.NET 3.5
Additional considerations:
n
Each environment is different, research settings that your specific environment may utilize before
performing any upgrades.
n
Ensure that you have tested backups before performing any upgrades.
n
Although an in-place SQL upgrade is supported by Relativity. Performing an EDDS migration is the
cleanest way to perform a SQL upgrade.
14.2 Relativity Service Account
The Relativity Service Account must be the owner of all objects in the processing databases and have
permissions for logging in to the SQL Server environment. It must be set up as follows:
n
Configure the account with Windows Authentication.
n
Ensure that the account has local administrator rights to perform the installation of the native imaging
database and queue manager.

Pre-Installation Guide 78
n
Ensure that this account has SQL administrator rights.
n
Do not include special characters in the Relativity service account active directory account name.
14.3 Create Invariant worker network file path share
Create a directory on the SQL Server in a location where the Relativity Service Account can read and write.
Make sure that SQL services can also read from this directory. This directory must be an actual folder, not a
drive letter. It stores the installation files for worker servers.

Pre-Installation Guide 79
15 Worker server for processing or native imaging
The following sections provide basic information about setting up the worker server for processing or native
imaging. For more information, see the Worker manager server Installation guide.
Note: If you are only installing Collect or Legal Hold, you do not need this pre-requisite.
15.1 Required software
Install the following software on the worker server:
n
Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server 2012 R2
n
.NET Version 4.7.2 or 4.8
n
Desktop Experience (Windows Server feature)
n
Microsoft Office 2010 Professional SP2 (32-bit) or Microsoft Office 2013 Professional (32-bit)* or
Microsoft Office 2016 Professional (32-bit)**
Note: *Some features found in files created in different versions of Office may not be available or render
correctly when processed or imaged using a different version than the file was originally created in. For
more information about features differences between Office versions, please consult the appropriate
Microsoft documentation.
Note: **Note the following details regarding our support of Office 2016:
n
You must install a version no earlier than 16.0.4783.1000, the December 2018 update for Microsoft
Office.
n
We recommend that you upgrade Invariant prior to upgrading Microsoft Office. If you upgrade
Microsoft Office first, your workers will fail to validate, and Invariant will not run until you upgrade it.
n
We recommend that you uninstall Microsoft Office 2013 before installing Office 2016.
n
OneNote 2016 cannot export files containing more than 300 pages to PDF. Processing extracted
text will fail in this case, as well.
n
With the introduction of Office 2016 support, the font used to image text files is now Google's Noto
Sans; previously, this was Microsoft's Arial Unicode.
n
Microsoft Works 6–9 File Converter
n
Microsoft Visio 2010 Professional or Standard SP2 (32-bit) (recommended) or Microsoft Visio 2013
Professional or Standard SP1 (32-bit)
n
Microsoft Project 2010 Professional or Standard SP2 (32-bit) (recommended) or Microsoft Project
2013 Professional or Standard SP1 (32-bit)
n
(optional) Lotus Notes v8.5 and higher
n
Lotus Notes v8.5.3 with Fix Pack 6
n
Lotus Notes v8.5.2 with Fix Pack 4
n
Lotus Notes v9.0

Pre-Installation Guide 80
n
Lotus Notes v9.0.1
n
Lotus Notes v10.0.1
n
Solidworks eDrawings Viewer 2017 (64-bit) version only with SP5 or above.
n
Solidworks eDrawings Viewer 2018 (64-bit)
n
Solidworks eDrawings Viewer 2019
n
Solidworks eDrawings Viewer 2020
n
JungUm Global Viewer v9.1 or higher
Note: Microsoft Project and Visio are not required to install and use Processing. These components are
only required if you intend to process Project and Visio files, specifically.
15.2 Required Microsoft Visual C++ redistributables
15.3 Relativity Service Account
The following table breaks down which versions of Microsoft Visual C++ are required for which versions of
Relativity/Invariant. Note that you are required to install each version of Microsoft Visual C++ only if you are
upgrading to the Relativity/Invariant version listed and not if you are installing it for the first time.
Required Microsoft Visual C++ version (Redistributable
x86 and x64)
Relativity/Invariant ver-
sion
2010 2012 2013 2015
10.3.287.3/5.3.282.2
√ √ √ √
Server 2021/ 6.1.1798
√ √ √ √
Server 2022/7.1.431.1
√ √ √ √
The Relativity Service Account must be given local administrator rights to each worker server. The
installation process uses this account. It must remain logged in to each server to run local processes during
native imaging.

Pre-Installation Guide 81
16 Obtaining applications for native imaging and
processing
On the Relativity Native Imaging/Processing worker, you must install additional software to support
imaging/processing.
Note: If you are only installing Collect or Legal Hold, you do not need this pre-requisite.
For convenience, this section includes links to download pages for specific software, which may require
licensing or may be downloaded for free:
n
Lotus Notes v8.5.2 with Fix Pack 4 or Lotus Notes v8.5.3 with Fix Pack 6
Note: When you visit the IBM site to download Lotus Notes, you have the option of buying the
software online or downloading a free trial of it. If you select the free trial, you are required to sign in
with an IBM user ID, which you must create if you don't already have one.
n
SolidWorks eDrawings 2015 (64-bit), with the option to view 3D XML and PRO/E files
n
JungUm Global Viewer v9.1 or higher available at https://www.jungum.-
com/ReNew/En/Download/EtcDownload.html

Pre-Installation Guide 82
17 Default log file location
The default file location for Relativity logs is set by the %RELATIVITY_LOGS% environment variable.
Define the variable on all machines in your Relativity environment, web servers, agent servers, except SQL
Servers.

Pre-Installation Guide 83
18 Post-installation considerations
After you install Relativity, review the post-installation considerations listed in this section.
18.1 User group for uploading documents
You can improve performance when documents are uploaded with the Win Relativity component by
creating a group of users with Full Control permissions on the file share used as a document repository. This
group can import and export documents in Direct mode, which is significantly faster than Web mode.
18.2 Relativity service account information
The Relativity installer automatically creates the Relativity service account. It assigns this account an email
address, as the user name, and a default password. We highly recommend that you change the default
Forms password through the Relativity UI after the software is deployed. However, you should not disable
this account or modify any other authentication information assigned to it.
The Active Directory (AD) domain also includes a Relativity services account, which has the same user
name. The Relativity services account on this domain must log in to Relativity to perform various tasks.
Tasks like running agents and authenticating against the Relativity Services API. The audit history for
Relativity often lists the Relativity services account as the user who performed a task. To avoid destabilizing
your environment, we recommend that you do not change the user settings in Relativity for this account or
the AD domain for this account. Since Relativity uses AD authentication for the Relativity services account
only for performing agent tasks, you can change the Forms authentication password through the Relativity
UI without encountering any environment issues.
As previously mentioned, the Relativity service account is sometimes used to identify the user who
performed certain tasks in the software. For example, you might set up a dtSearch index job that includes a
private search created by one of your users. The Relativity service account needs access to this private
search in order to build the index automatically. It is the only account that can provide this functionality within
Relativity.
18.3 Post-installation steps for a token-signing certificate
Note: To minimize any interruption to your Relativity workflows, we recommend that you complete the
following process during off-hours.
After installation, perform the following steps for a token-signing certificate:
1. On the primary SQL server, navigate to the Relativity install directory and then navigate to the
Procuro folder (typically C:\Program Files\kCura Corporation\Relativity\Procuro).
2. Run the kCura.EDDS.Procuro.exe application as an administrator.

Pre-Installation Guide 84
3. On the EDDS Database Upgrade window, click Back.

Pre-Installation Guide 85
4. Select the certificate that you wish to use as the signing certificate. The certificate must already be in
the Personal store on the machine for it to appear in the drop-down.
5. Click Update Certificate.
6. Restart all of the Relativity services in the environment and IIS.
18.4 Logo customization
Customize your Relativity web interface with your company’s logo. To accommodate variable space
requirements, provide two logos with different sizes. The height may be 50 pixels and the width is
discretionary. You can hide the logo using a setting in the Instance setting table. The name of the logo file is
also set in the Instance setting table. Add the logos to the images folder at the root of the EDDS directory.
18.5 Resource groups
A workspace does not contain resource servers after you install Relativity. After the agents start up, the
servers self-register. They are not automatically associated with a resource group. To associate these

Pre-Installation Guide 86
servers to a resource group, you must manually add them through the Resource Group tab available only
from Home. For more information, see Servers in the Admin guide.
18.6 License keys
After you install Relativity, you need to either activate new licenses or renew your current ones by
requesting and applying activation keys for the applications you intend to use in your Relativity instance,
including Processing. Relativity licensing includes flexible options that you can tailor to the size, type, and
other requirements of your organization as part of your contractual agreement with us. For more
information, see the Relativity Licensing Guide.
18.7 Relativity instance name
During a first-time installation, you must provide a name for your Relativity instance. This value is displayed
on License details page available through the License tab. It is stored as the Instance setting in the
Relativity.LicenseManager section of the Instance setting table on the EDDS database.
Note: Modifying the instance name by updating this setting in the Instance setting table immediately
invalidates your Relativity and Processing licenses.
When you request a Relativity license, this instance name is included in the request key. Contact the
Customer Support team on the Community site for additional information.
In the RelativityResponse.txt file, the RELATIVITYINSTANCENAME value records the Relativity Instance
Name option when you perform a first-time installation. For more information see, Relativity installation on
the Relativity Server 2022 Documentation site.

Pre-Installation Guide 87
Proprietary Rights
This documentation (“Documentation”) and the software to which it relates (“Software”) belongs to
Relativity ODA LLC and/or Relativity’s third party software vendors. Relativity grants written license
agreements which contain restrictions. All parties accessing the Documentation or Software must: respect
proprietary rights of Relativity and third parties; comply with your organization’s license agreement,
including but not limited to license restrictions on use, copying, modifications, reverse engineering, and
derivative products; and refrain from any misuse or misappropriation of this Documentation or Software in
whole or in part. The Software and Documentation is protected by the Copyright Act of 1976, as amended,
and the Software code is protected by the Illinois Trade Secrets Act. Violations can involve substantial
civil liabilities, exemplary damages, and criminal penalties, including fines and possible imprisonment.
©2024. Relativity ODALLC. All rights reserved. Relativity® is a registered trademark of Relativity
ODA LLC.

