
1
Contents
Overview ............................................................ 2
Appropriations Overview ................................... 3
General and Miscellaneous Appropriations
Measures ........................................................... 3
Medical Marijuana, Hemp, and Associated
Products ............................................................. 5
Agriculture & Rural Measures ............................ 8
Agriculture Funding ........................................... 9
Business & Labor ................................................ 9
Corrections Funding ......................................... 13
Office of Juvenile Affairs Funding .................... 13
Economic Development & Commerce Measures
......................................................................... 14
Commerce Funding .......................................... 16
Historical Society Funding ................................ 17
Common Education ......................................... 17
Career & Technology Education Funding ......... 24
Common Education (K-12) Funding ................. 25
Higher Education ............................................. 27
Higher Education Funding ................................ 29
Hospital Authority Funding .............................. 29
Energy, Environment, & Utilities ...................... 30
Conservation Commission Funding ................. 34
Corporation Commission Funding ................... 34
Election Measures ........................................... 34
County and Municipal Government ................. 37
Public Finance .................................................. 40
State Government ........................................... 42
OMES Funding ................................................. 47
Health Measures ............................................. 47
Health Funding ................................................ 57
Health Care Authority Funding ....................... 60
Mental Health & Substance Abuse Funding .... 60
Human Services ............................................... 60
Human Services Funding ................................. 65
Insurance Measures ........................................ 66
Liquor, Smoking, & Tobacco ............................ 71
Judiciary/Court Measures ............................... 73
Judiciary Funding ............................................ 77
Professions & Occupations ............................. 78
Public Safety .................................................... 82
Public Safety and Law Enforcement Funding .. 91
Public Employees-
Retirement/Insurance/Pay/Benefits ............... 92
Taxation and Tax Exemptions ......................... 94
Tax Commission Funding ................................ 99
Transportation, Vehicle, and License Measures
........................................................................ 99
Transportation Funding ................................ 105
Veteran Measures ......................................... 107
Veterans Funding .......................................... 110
Senate & House Joint Resolutions ................ 110
Vetoed Measures .......................................... 110
Oklahoma State Senate: Session Overview
Oklahoma State Senate
Committee Staff
August 2021
2
Overview
The Oklahoma State Senate convened the 1
st
Session of the 58
th
Legislature on February
1, 2020, to tackle a host of issues ranging
from extending regulatory oversight related
to marijuana, encouraging economic growth
in the aftermath of COVID-19, adjusting
Senate and House Districts to match the
state’s population, and to continue reforming
the criminal justice system. The 58
th
Legislature also tackled the issue of rising
utility bills following the prolonged North
American winter storms of 2021.
The Oklahoma State Senate welcomed 7
new members to the body following the
2020 election, including Senators George
Burns, Jo Ana Dossett, Jessica Garvin,
Warren Hamilton, Jake Merrick, Cody
Rogers, and Blake Stephens.
At the beginning of the 1
st
Session of the
58
th
Legislature, the Senate remained
cautious as COVID-19 continued to infect
Oklahomans. Retaining the option for its
members to vote and appear for Senate
business remotely, the Senate cautiously
returned to normal business to maintain the
safety of the public, its members, and its
staff. Following the release of the vaccine in
March to members of the public, the Senate
began to phase out many of the COVID era
restrictions it imposed in the 2020 Session.
With the successful expansion of medical
marijuana growers and retailers throughout
the state, the Legislature grew concerned
with the emerging black market. To combat
these issues, the Senate voted to tighten
financial and license regulations.
The Senate also addressed matters relating
to criminal justice reform and public safety.
The passage of the Sarah Stitt Act and
various measures relating to “restorative
justice” as well as bail reform for medically
frail patients helps to alleviate crowded
prisons and provides prisoners with a viable
path to reintegration. The newly created
Unified State Law Enforcement
Commission will examine the question of
unifying state law enforcement entities to
both reduce the administrative costs of
public safety as well as increase
coordination.
Mask mandates and the specter of “vaccine
passports” also drove the Senate to action
with the passage of SB 658. The measure
prohibits any school district from
implementing a mask mandate without
consulting the county or state health
department as well as prohibits the use of
documents relating to proof of vaccination
for entry.
3
Appropriations Overview
HB 2900 (Wallace/Thompson) became law
on May 24, 2021, with the approval of the
Governor. The measure provided $9.1
billion in total appropriations, which
included a $212 million increase for
common education. Additionally, the Health
Care Authority a $28 million budget
increase to incorporate newly eligible
Oklahomans that qualify for Medicaid
services.
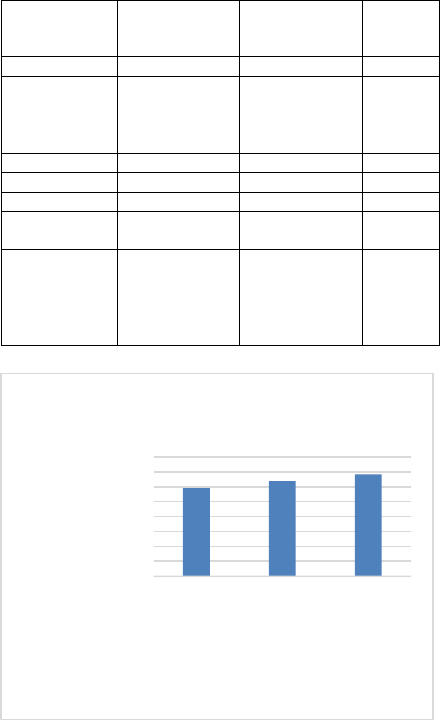
Subcommittee
Budget
FY21 Total
FY22 GA Bill
Changes
from
Original
Education
$3,953,211,053
$4,165,614,219
5.37%
General
Government
and
Transportation
$1,019,645,842
$1,005,808,701
-1.36%
Health
$1,543,540,021
$1,761,300,769
14.11%
HHS
$844,317,829
$849,821,728
0.65%
NRR
$172,828,417
$157,248,036
-9.01%
Public Safety
and Justice
$859,247,741
$891,232,291
3.72%
Total FY'21
Appropriation
vs. Total
FY'22
Appropriation
$3,953,211,053
$4,165,614,219
5.37%
Additionally, the Legislature needed to
encourage economic recovery in the
pandemic’s aftermath. The Senate chose to
lower individual and corporate income taxes
in HB’s 2962 and 2960 respectively to
encourage investment and job growth.
General and Miscellaneous
Appropriations Measures
SB 1076 (Thompson/Wallace) directs the
Oklahoma Tourism and Recreation
Department to make available matching
funds to multicounty organizations using
funds appropriated to it in HB 2900.
SB 1077 (Thompson/Wallace) extends the
maximum 7% workers’ compensation
premium assessment for the Multiple Injury
Trust Fund for a five-year period until fiscal
year 2027.
SB 1083 (Thompson/Wallace) sunsets
provisions of law relating to the Oklahoma
Capitol Improvement Authority issuing
notes, bonds, or other evidences of
obligation for the construction of the State
Health Laboratory on July 1, 2025, if the
Authority has failed to issue such evidences
of obligation by the sunset date.
HB 2780 (Pfeiffer/Rader) adds unpaid
mixed beverage gross receipts tax to taxes
for which corporations, limited liability
corporations and other legal entities are
personally liable. The measure provides that
a claim for refund of erroneously paid sales
taxes may only be made if a vendor refuses
to honor proof of eligibility for sales tax
exemptions. Additionally, the measure
authorizes the Oklahoma Tax Commission
(OTC) to enter into a contract with a state
agency to assist in the collection of any state
tax, penalty, or interest in which that agency
has authority to collect and control. The
Commission must charge a collection
assistance fee to the agency equal to 10% of
the total amount collected. OTC may also
enter into the same type of contract with the
Oklahoma Employment Security
Commission and have the authority to
collect and enforce unemployment tax,
penalties, and interest. The OTC may
$2,000,000,000
$3,000,000,000
$4,000,000,000
$5,000,000,000
$6,000,000,000
$7,000,000,000
$8,000,000,000
$9,000,000,000
$10,000,000,000
FY20 Appropriation
FY21 Appropriation
FY 22 Appropriation
Total Appropriations
4
garnish the accrued earnings of a delinquent
taxpayer by sending notice and specific
procedures to the taxpayer’s employer and
places liability on the employer for the total
amount of delinquent taxes if they willfully
disregard or refuse a notice from OTC
regarding the delinquency of an employee.
The measure also increases the time period
from 5 days to 15 days, in which delinquent
taxes must be remitted when OTC contracts
with a debt collections agency. Additionally,
the measure removes the name of the
County Government Education Technical
Revolving Fund and alters it to an agency
special account to be used for the collection
and distribution of documentary stamp
revenues, the apportionment of which shall
start in the fiscal year ending June 30, 2022.
Any funds remaining in the revolving fund’s
reserve account on November 1, 2021, shall
be transferred to the special agency account.
The measure also allows OTC to distribute
funds from the agency special account to the
Oklahoma State University Center for Local
Government Technology or the Oklahoma
Cooperative Extension Service County
Training Program. The measure also limits
the liability of incentive payments made for
film production rebates to the balance of the
Oklahoma Film Enhancement Rebate
Program Revolving Fund.
HB 2870 (Wallace/Thompson) authorizes
the Commissioners of the Land Office to
pay fees to multiple custodial banks as well
as investment consultants from certain
funds. The measure also directs the CLO to
require written competitive bids for
custodial banks every 10 years rather than
every 5 years.
HB 2893 (Wallace/Thompson) modifies the
apportionment of taxes and fees collected
from the insurance premium tax to the
Oklahoma Firefighters Pension and
Retirement Fund, the Oklahoma Police
Pension and Retirement System, the Law
Enforcement Retirement Fund, and the
Education Reform Revolving Fund.
HB 2894 (Wallace/Thompson) eliminates
the second year of an insurance premium tax
apportionment change provided in HB 2741
(2020).
HB 2897 (Wallace/Thompson) creates a
revolving fund in the state treasury for the
Ethics Commission to be known as the
“Ethics Commission Online Filing
Revolving Fund.” The fund shall be a
continuing fund and the deposits to the fund
shall consist of the first $200,000.00
designated for deposit to the fund. Monies in
the fund may be used by the Commission to
develop, maintain, and administer the
Commission’s online filing system and for
payment of fees and charges to other state
agencies for information technology
services.
HB 2898 (Wallace/Thompson) provides that
all monies submitted by sheriffs to the
Oklahoma State Bureau of Investigation as
processing fees for applications for a
handgun license are to be deposited in the
General Revenue Fund beginning July 1,
2022.
HB 2907 (Wallace/Thompson) directs the
Oklahoma Conservation Commission’s
Master Irrigator Program to utilize
appropriated dollars as follows:
1) $90,000.00 for training and
2) $50,000.00 for research on the Ogallala
Aquifer
HB 2910 (Wallace/Thompson) authorizes
certain state agencies to establish a Capital
Account Fund consisting of funds from the
agencies’ standard appropriations for the
5
purpose of maintaining, repairing and
improving agency property.
HB 2911 (Wallace/Thompson) exempts the
Department of Tourism and Recreation from
the requirement that state agencies allocate
1.5% of expenditures for capital projects to
the Oklahoma Arts Council to fund the Art
in Public Places Act.
HB 2951 (Wallace/Thompson) creates the
State-Tribal Litigation Revolving Fund for
the purpose of hiring legal counsel and
paying expenses related to legal
controversies between the State and tribal
governments. The measure provides that if
these provisions are found unconstitutional,
the balance of the Fund shall be reverted to
the General Revenue Fund.
Medical Marijuana, Hemp, and
Associated Products
SB 460 (Paxton/Fetgatter) authorizes
industrial hemp growers to remediate any
industrial hemp so long as all THC is
removed and it is processed as Cannabidiol.
SB 862 (Paxton/Bush) provides that
buildings owned by a county or municipal
government as well as trusts or authorities
with a county or municipal government as
the beneficiary to be designated as smoke
free locations. Such locations prohibit the
use of tobacco, nicotine, marijuana, or other
lawful products consumed in a smoked or
vaporized manner.
SB 1033 (Leewright/Fetgatter) caps the
number of patients a caregiver may cultivate
medical marijuana plants for at no more than
5 licensed patients. The measure provides
for medical marijuana establishments to
maintain a building within 1000 feet of a
new school building provided the license for
such an establishment was granted prior to
the establishment of the building or there
was an error of measurement as it relates to
the distance of the dispensary from the
school. The measurement shall be based on
the distance in a straight line from the school
door nearest the front door of the retail
marijuana establishment to the front door of
the retail marijuana establishment. The
measure also clarifies that any original
medical marijuana business license issued
on or after June 26, 2018, by the Authority,
for a medical marijuana commercial grower,
a medical marijuana processor, or a medical
marijuana dispensary shall be deemed to
have been grandfathered into the location on
the date the original license was first issued
and provides for the grandfathered status to
be transferred is a change in ownership
occurs. The Medical Marijuana Authority
shall not deny any issuance or renewal of
licensure, deny any transfer of licensure due
to a change in ownership, or revoke any
license due to mistake in measurement by
the Authority. The measure authorizes
municipalities to object to the continued
licensure of the grandfathered medical
marijuana dispensary when it is operating
contrary to the required setback distance
from a public or private school. Upon the
municipal government providing the
required documentation outlined in the
measure, the Authority shall not renew or
transfer the medical marijuana dispensary
license and shall cause the license to be
revoked. The measure also clarifies that
“marijuana” shall not include any plant or
material containing delta-8 or delta-10
tetrahydrocannabinol which is grown,
processed or sold pursuant to the provisions
of the Oklahoma Industrial Hemp Program.
The State Department of Health is
authorized by the measure to enter into and
negotiate the terms of a Memorandum of
Understanding between the Department and
other state agencies concerning the
enforcement of laws regulating medical
marijuana by the measure. Additionally, the
6
measure requires each medical marijuana
research facility, medical marijuana
education facility, and medical marijuana
waste disposal facility develop written
standard operating procedures outlining the
way it operates its seed-to-sale tracking
system. Additionally, the measure authorizes
a publicly traded company as defined in the
measure may purchase up to 40% of the
equity in an existing Oklahoma business that
holds a valid Oklahoma medical marijuana
grower, processor or transporter license.
Such a business must hold a valid medical
marijuana grower, processor or transporter
license for at least 18 months prior to the
investment. A licensed medical marijuana
dispensary shall not be qualified for
investment or equity purchase. The measure
also expands medical marijuana waste to
include any products deemed to have failed
laboratory testing and cannot be remediated
or decontaminated. Medical marijuana waste
shall also include products from a medical
marijuana business facility deemed to have
gone out of business or products that are
unable to be lawfully transferred or sold the
to another commercial licensee. After
November 1, 2021, the measure eliminates
the cap on medical marijuana waste licenses
that may be issued. The State Department of
Health is authorized by the measure to enter
into a contract with the Oklahoma Tax
Commission to collect and enforce the 7%
tax on retail medical marijuana sales. The
assessment, collection, and enforcement
authority shall apply to any tax and any
penalty or interest liability on retail medical
marijuana sales existing at the time of
contracting. The Commission may charge
the Department a 1.5% fee on the gross
collection proceeds.
HB 2272 (Josh West/Murdock) requires
current medical marijuana business licensees
and applicants seeking licensure as a
medical marijuana business to respectively
submit an attestation confirming or denying
the existence of any foreign financial
interests in the medical marijuana business
operation and to disclose such ownership
within 60 days to the Oklahoma State
Bureau of Narcotics and Dangerous Drugs
Control or the Medical Marijuana Authority.
Failure to submit the attestation or
accompanying information to the Bureau
within the specified 60-day period shall
result in the immediate revocation of the
medical marijuana business license.
HB 2279 (Josh West/Kidd) creates the
Oklahoma Industrial Hemp Remediation
Program and provides definitions for terms
used in the act, including Hemp Program,
which is defined as the Oklahoma Hemp
Industrial Reform Program and any final
ruling from the USDA. The measure allows
a person licensed by the Oklahoma
Department of Agriculture, Food, and
Forestry whose hemp is deemed
noncompliant with the Hemp Program to
request approval from the Department to
remediate the hemp. The licensee must
promptly have the hemp extracted by a
licensed processor into concentrated form
and sampled by a certified laboratory for
THC levels if approved. If the samples are
below USDA levels for THC, the hemp is
compliant and can be sold commercially. If
the samples are noncompliant, the
Department must be notified and the
samples must be destroyed.
HB 2646 (Echols/Taylor) changes several
provisions of law relating to medical
marijuana usage, production, and disposal.
The measure provides that patient licenses
must be signed by an Oklahoma physician
licensed by and in good standing with the
State Board of Medical Licensure and
Supervision or the State Board of
Osteopathic Examiners. Patients are
authorized by the measure to request the
7
withdrawal of their caregiver’s license at
any time. The measure extends the time for
the Department of Health to review
dispensary licenses from 2 weeks to 90 days.
Additionally, the measure authorizes
dispensaries to package and sell prerolled
marijuana to licensed medical marijuana
patients and licensed caregivers. Such
products shall contain only the ground parts
of the marijuana plant and shall not include
marijuana concentrates or derivatives and
may not exceed 1 gram. Dispensaries are
also prohibited from displaying or offering
for sale products not contained in a sealed or
separate package. Commercial growers are
authorized by the measure to sell pre-rolled
marijuana to dispensaries. Such products
shall be subject to the same limitations
placed on dispensaries as it relates to
prerolled marijuana. Additionally, the
measure provides that the State Department
of Health may issue 2 types of processor
licenses for hazardous and non-hazardous
materials. Licensed commercial growers
may transfer medical marijuana that has
failed testing to a licensed processor only for
the purposes of decontamination or
remediation. The measure clarifies that the
Department may also inspect a processing
facility up to 2 times a year. The Department
is also directed to establish regulations
which require a medical marijuana business
to submit information to the Oklahoma
Medical Marijuana Authority deemed
reasonably necessary to assist the Authority
in the prevention of diversion of medical
marijuana by a licensed medical marijuana
business. Business licensees are required to
submit a sample or unit of medical
marijuana or medical marijuana product to
the quality assurance laboratory when the
Department has reason to believe the
medical marijuana or medical marijuana
product may be unsafe for patient
consumption. The measure establishes fines
for fraudulently reporting within a 2-year
period information as well. The fine is set at
$5,000.00 for the first violation and
$10,000.00 for second and subsequent
violations. Licensees whose license was
suspended or revoked during the 5 years
preceding an application shall be denied a
license. The Department is authorized by the
measure to issue a written order to any
licensee the Department has reason to
believe has committed a violation. The
written order shall state with specificity the
nature of the violation and shall become a
final order not more than 30 days after the
order is served to the licensee. The licensee
may request an administrative hearing. The
Department is authorized by the measure to
issue an emergency order in certain
circumstances. Entities failing to comply
with the emergency order shall be subject to
a $10,000.00 fine per day of noncompliance.
Additionally, unless the Department
determines otherwise, an application that has
been resubmitted but is still incomplete or
contains errors that are not clerical or
typographical in nature shall be denied. The
measure directs the Department to issue
medical marijuana transporter licenses to
licensed medical marijuana research
facilities, medical marijuana education
facilities and medical marijuana testing
laboratories upon issuance of such license
and upon renewal. Laboratories may not be
owned by any person with a business
interest in a licensed medical marijuana
business or any person who is related to a
person with an interest in the commercial
aspects of the industry. The measure
specifies that distance from schools is to be
measured from the nearest property line of
the school to the nearest perimeter wall of
the dispensary. Properties that are not used
for classroom instruction on core curriculum
and are not on the same campus as a
building used for such do not constitute a
school. The establishment of a school within
1,000 feet of an already existing dispensary
8
shall not be cause for revocation or
nonrenewal of the license. The measure also
authorizes the Department to appoint 8
additional members to the Medical
Marijuana Advisory Council. The measure
requires the makeup of the council to
include members of the medical marijuana
industry. Any person who manufactures,
distributes, dispenses, prescribes,
administers or uses for scientific purposes
any controlled dangerous substances within
or into this state without first obtaining a
registration issued by the Director of the
Oklahoma State Bureau of Narcotics and
Dangerous Drugs Control shall be subject to
the same statutory and administrative
jurisdiction of the Director as if that person
were an applicant or registrant.
Agriculture & Rural Measures
SB 775 (Murdock/Dempsey) authorizes the
Oklahoma Department of Agriculture, Food,
and Forestry to create a Livestock Offender
Registry and to provide access to this
registry to the public on the Department’s
website. Counties in which the offender is
convicted shall submit a certified copy of
the judgment and sentence confirming the
conviction for entry in the Livestock
Offender Registry to the Oklahoma
Department of Agriculture, Food, and
Forestry or to a statewide livestock
organization designated by the Department.
SB 812 (Murdock/Fetgatter) provides for the
court to order a person to surrender his or
her hunting or fishing license to an officer
from the Department of Wildlife
Conservation present at the hearing upon
conviction of a violation relating to certain
violations. The measure also authorizes the
court clerk to transmit the conviction
information by using an electronic method
authorized by the Department of Wildlife
Conservation.
SB 839 (Dahm/Sean Roberts) specifies that
a game warden shall not have the authority
to use or place a game or wildlife camera on
private property without the permission of
the owner or controller of the property.
SB 844 (Dahm/Gann) repeals the provision
of law entering Oklahoma into the Southern
Dairy Compact.
HB 1001 (Bush/Hall) clarifies the data
required to be maintained by a scrap metal
dealer. The measure provides that any
federally recognized identification card can
be used and requires a vehicle identification
number to be recorded if no license plate is
affixed. Items purchased by a buyer or sold
by a dealer must be captured digitally and
records of the transaction must be
maintained for at least 2 years after the date
of sale. The measure removes separate
requirements for recording data about
purchases of scrap metal under 35 pounds
and of purchases 35 pounds and over. The
person selling the scrap must provide either
a certificate of title, a notarized power of
attorney from the individual on the title
authorizing the seller to dispose of the
vehicle on their behalf, or a statement of
ownership from the seller accompanied by a
bill of sale from the lawful owner. The
measure places any copper wire that is 4
gauge or larger and any copper wire from
which the insulation or coating has been
burned or melted, as well as remote storage
batteries, under the provisions of the Scrap
Metal Dealers Act.
HB 1032 (Mize/Pugh) changes the name of
the Home Bakery Act of 2013 to the
Homemade Food Freedom Act. The
measure provides that the production and
sale of homemade food products that meet
the certain conditions outlined in the
measure shall be exempt from licensing
requirements. Such conditions shall regulate

9
the sale and delivery of non-time- or -
temperature-controlled-for-safety
homemade food products and requires such
products to be sold directly to the consumer
from the producer. Producers are also
required to complete at least 8 hours of
training approved by the Oklahoma
Department of Agriculture, Food, and
Forestry. Homemade food products must
also have a label affixed to its packaging.
HB 1620 (Mize/Montgomery) prevents any
political subdivision or the state government
from prohibiting agritourism activities,
which is defined as using livestock or other
animals for entertainment or educational
purposes.
HB 1631 (David Hardin/Murdock) requires
nutrient management plans for new or
expanding poultry feeding operations to be
prepared by the operator or designee of the
operator. The plan must be submitted to the
Oklahoma Department of Agriculture, Food
and Forestry for review and approval. Every
nutrient plan must be updated and submitted
to the Department every 6 years. The
measure also allows a current operator to
submit a 1-page amendment to the most
recently submitted plan in lieu of a renewal
plan.
HB 2214 (McDugle/Murdock) provides that
every annual license issued by the
Oklahoma Wildlife Conservation
Commission shall be valid for a full 365
days after issuance notwithstanding any
provision of law or rule to the contrary.
HB 2325 (Frix/Bergstrom) provides that
escort vehicle requirements shall not apply
to retail implement dealers transporting farm
implements from a retail distribution point
to a farm or other location within a 150 air-
mile radius from the distribution point.
HB 2364 (Burns/Murdock) prohibits anyone
from labelling a bovine product as
“Oklahoma Certified Beef” unless the
product was bred, born, raised, and
slaughtered in the state.
HB 2467 (Kerbs/Murdock) repeals the Fuel
Alcohol Act.
HB 2471 (Dick Lowe/Kidd) allows the
Department of Agriculture to establish
expiration dates and renewal due dates for
pesticide applicator licenses.
Agriculture Funding
HB 2906 (Wallace/Thompson) directs the
Department of Agriculture to utilize
appropriated dollars as follows:
1) $3 million for the Oklahoma State
University College of Veterinary Medicine;
2) $2 million for the Oklahoma State
University Agriculture Extension Service;
3) $1 million for the Oklahoma State
University Agriculture Experiment Stations;
4) $150,000.00 for facility improvements for
cattle stock shows; and
5) $300,000.00 to hire additional meat
inspectors.
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
From
Original
Department
of
Agriculture
$26,989,607
$31,527,896
16.81%
Business & Labor
$0
$10,000,000
$20,000,000
$30,000,000
$40,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Department of Agriculture
10
SB 200 (Montgomery/Pae) authorizes a
victim of domestic violence, sexual
violence, or stalking to terminate a lease
without penalty by providing written notice
and a protective order within 30 days of the
incident to his or her landlord. The landlord
may waive the 30-day deadline.
Additionally, the measure prohibits any
landlord from denying renewal of or
terminating a lease because the applicant or
tenant is a victim or alleged victim of
domestic violence, sexual violence, or
stalking regardless of whether there exists a
current protective order. The measure also
prohibits any landlord from denying an
applicant tenancy or retaliate against a
tenant because the applicant or tenant has
previously terminated a rental agreement
using the provisions outlined in this
measure.
SB 228 (Montgomery/O’Donnell) modifies
certain provisions of the Oklahoma General
Corporation Act. The measure authorizes
written notice to be provided in an electronic
format as it applies to organization meetings
of a corporate board and notification
applying to the transfer of stock. The
measure additionally authorizes members of
a board to consent to an action that will be
effective at a future time, provided the
action occurs within 60 days. The measure
also creates a new section of law governing
the document form, signature requirements,
and delivery requirements of electronic
documents. The measure provides for the
issuance of capitol stock to be issued in one
or more transactions in a manner outlined in
a resolution passed by the board. The
resolution must fix a maximum number of
shares that may be issued and a schedule of
issuance. Stock may be issued in a manner
dependent upon facts ascertainable outside
the formula adopted by the board, provided
the manner in which such facts shall operate
upon the formula is clearly and expressly set
forth in the formula or in the resolution
approving the formula. The measure states
that a corporation may not send defective
corporate act to its shareholders for
ratification provided there are no shares of
valid stock outstanding and entitled to vote.
The measure also defines a stock ledger to
mean records administered by or on behalf
of the corporation in which the names of all
the corporation’s shareholders of record, the
address and number of shares registered in
the name of each such shareholder, and all
issuances and transfers of stock of the
corporation are recorded. The measure
removes outdated language relating to
telegrams and replaces it with electronic
transmissions as it relates to granting
consent for certain actions. The measure
requires corporation merger agreements to
clearly show any changes made to the
certificate of incorporation of the surviving
corporation or a statement showing that the
merger shall not amend the certificate if the
merger includes a domestic corporation. In
cases of consolidation, the certificate must
be as set forth in the consolidation
agreement.
SB 273 (Quinn/Miller) requires any person
preparing or persons charging a fee for the
preparation or assistance in preparation of
lien notices on personal property to register
with the Oklahoma Tax Commission and
submit a $50.00 annual registration fee. Any
person found to prepare or assist in the
preparation of a lien notice without
registration shall be assessed a $100.00
penalty. The provisions of this measure do
not apply to a lawful possessor or employee
of a lawful possessor of the property for
which such notices are issued.
SB 335 (Pederson/Newton) provides a
mechanism to revert burial sites to public or
private cemeteries. The measure requires the
site to be unused for 75 years and a
11
reasonable search to find the owner is to be
conducted by the entity responsible for the
site. A reasonable search, as defined by the
measure, includes sending a certified letter
to the last known address associated with the
site on record and publishing a description
of the site in a newspaper qualified to
publish public notices. If no address is on
file, no letter will be required. If no person
proves their claim on the site within one
year of publication in the paper, the site will
be deemed abandoned. Any person with a
legitimate claim on a site deemed abandoned
shall be compensated with a plot equal in
value to the site deemed abandoned.
SB 549 (Standridge/Frix) provides that
neither a relocation permit nor any outdoor
advertising sign permit shall be issued in
those areas in which a municipality or
county has lawfully enacted a prohibition on
the erection of an outdoor advertising sign.
SB 552 (Murdock/Martinez) increases the
maximum bracket amounts a pawn shop
may levy on finance charges by the
following amounts:
1) $250.00 from $100.00 for 20%,
2) $500.00 from $250.00 for 15%,
3) $1,000.00 from $500.00 for 10% and,
4) $5,000.00 from $1,000.00 for 5%
SB 568 (Montgomery/Hilbert) exempts sales
of securities offered by corporations that
meet the requirements of the federal
exemption for intrastate offerings sold to
persons residing in the state from the
provisions of the Oklahoma Uniform
Securities Act of 2004. Such sales shall be
limited to $5 million transactions and shall
not exceed $5,000.00 per individual. The
issuer shall be required to hold the funds in
an escrow account and shall be required to
make certain notifications. Certain entities
are prohibited from offering securities using
the provisions of the measure.
SB 792 (Leewright/Manger) provides for the
Insurance Commissioner to authorize a
bondsman exceeding the maximum amount
of Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
basic deposit coverage when a state of
emergency or disaster is declared. The
measure also requires bondsmen to deposit
cash or other forms of compensation within
2 business days after receiving such
compensation in an established, separate
non-interest-bearing trust account.
Additionally, the measure provides for
bonds posted for a petition for revocation of
a suspended sentence, a petition for
acceleration of a deferred sentence or any
violation of a probationary term to be
exonerated by operation of law in certain
circumstances. Premiums for a bail bond
shall be considered earned when the
defendant on the bond is released from
custody and is not incarcerated in any
capacity or if the bondsman and the payor of
the bond premium have agreed in writing
that the purpose of the bond is to secure the
transfer of the defendant to another
jurisdiction. The payor of the premium or
the depositor of any collateral may request
the return of any unearned bond premiums.
SB 794 (Leewright/Wallace) requires the
Oklahoma Employment Security
Commission (OESC) to shift its filing
methods to prefer electronic e-filing and
provides for the Commission to complete
the process during its OESC 2020-21
business process transformation. All
claimants and employers tendering
documents to the Commission will be
expected to tender the documents
electronically. The measure also exempts
employees of private for-profit entities that
provide to or on behalf of an educational
institution from the requirement to pay
unemployment benefits in on the same terms
and subject to the same conditions as
12
benefits payable on the basis of other service
subject to the Employment Security Act of
1980. Additionally, the measure specifies
that an individual, seasonal employee shall
only be eligible for payments based on the
wages of the nonseasonal employment. The
OESC is required by the measure to send
notice of overpayment to any individual
receiving more compensation than he or she
is entitled to. If the individual disagrees with
this determination, the individual may file
an appeal of the determination with the
Appeal Tribunal within 10 days of receipt.
The OESC is also authorized to enter into an
agreement with the Department of Human
Services for information required to identify
persons that owe child support obligations.
The measure also requires the OESC to
return overpayments received in the
Employer's Unemployment Tax Account.
The measure directs the OESC to return the
remaining balance of the employer’s
unemployment tax account to the employer
upon terminating the employer’s account,
unless the balance has remained the same
for over 180 days and the employer has not
requested a refund.
SB 796 (Leewright/McEntire) increases the
cap on loan finance charges for supervised
lenders from 27% to 32% per year on that
part of the unpaid balances of the principal
which is $7,000.00 or less and adjusts the
other tiers accordingly. The measure also
provides for lenders to assess a up to a
$28.85 closing fee.
SB 1013 (Daniels/Kannady) provides for
litigation files and investigatory reports of
the Workers’ Compensation Commission to
be considered confidential. The measure
also allows an attorney of the Compliance
Division of the Commission or an
investigator of the Division to provide
testimony on matters the employee has
received through the performance of the
employee’s duties.
HB 1034 (Mize/Pugh) requires banks and
credit unions to transfer the money to the
known heirs of the deceased without
requiring the heirs to open an additional
account if the owner of a bank or credit
union account with $50,000.00 or less dies
and has no payable-on-death beneficiary if
no probate proceedings are pending. The
affidavit sworn to and signed by the known
heirs establishing jurisdiction, heirship and
intestacy may contain a clause indemnifying
the bank from any damages relating to the
release of the funds. The measure provides
that in the event of pending probate
proceedings, the release of the deposits in
the account shall be determined by the court.
HB 1112 (Talley/Allen) eliminates statutory
hunting seasons and authorizes the Wildlife
Conservation Commission to establish
hunting season timeframes.
HB 1772 (Sims/Pugh) requires the State
Board of Health to provide a multi-seasonal
license for snow cone stands that sell hot
beverages in addition to snow cones. Snow
cone stands that do not sell hot beverages
will be classified as a seasonal food
establishment.
HB 2026 (O’Donnell/Daniels) amends the
definition of employee as it relates to the
Administrative Workers’ Compensation Act
to no longer exclude persons who provide
services in a medical care or social services
program or participants in a work or training
program administered by the Department of
Human Services.
HB 2238 (May/Rader) provides that persons
are not prohibited from soliciting rides,
donations, employment, or business from
occupants of vehicles on roadways

13
maintained by a city or town if they are in
compliance with a permit and regulations
adopted by ordinance.
HB 2397 (Russ/Howard) includes
judgement liens and their holders as it
relates to current law regulating title
insurers.
HB 2398 (Russ/Howard) includes
judgement liens in certain requirements
regarding debt payments on real estate. The
measure also allows an agent representing a
mortgagor or debtor to request the release of
a mortgage or lien if the holder has failed to
do so within 30 days after payment of the
debt.
HB 2501 (Culver/Bullard) defines
“authorized agent or representative” within
the Oklahoma Abstractors Act. The measure
authorizes the release of an abstract to an
authorized agent or representative of the
owner.
HB 2568 (Chad Caldwell/Murdock)
authorizes Oklahoma banks and credit
unions to offer savings promotion raffles as
defined in the measure and provides that
such raffles shall not constitute a violation
of the provisions of Oklahoma lottery and
gambling laws.
HB 2677 (Marti/McCortney) modifies
several provisions of the Pharmacy Audit
Integrity Act. The measure strikes language
relating to appeal procedures to be
specifically described in a contract between
a pharmacy and the entity conducting the
audit and requires the auditing entity to give
the required written notice by certified letter.
A 30-day notice is required to be given prior
to a wholesale purchase audit as well. Audits
are reduced from 75 prescriptions per year
per pharmacist to 50 per year per pharmacist
and must be delivered within 10 days.
Pharmacists may reverse and resubmit
claims within 30 days of receipt of the final
audit report. Auditors are required to
conduct each pharmacy audit under identical
standards, regularity, and parameters as
similarly situated pharmacies. Additionally,
pharmacists are not required to open for
single-patient-use only packaging nor are
they required to submit a full dispensing
report in a wholesale purchase review.
Corrections Funding
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
From
Original
Department of
Corrections
$531,112,247
$544,278,904
2.48%
Pardon and
Parole
$2,273,400
$2,273,400
0.00%
Office of Juvenile Affairs Funding
Law Enforcement Funding
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
From
Original
Office of
Juvenile
Affairs
$96,795,111
$93,033,434
-3.89%
$480,000,000
$500,000,000
$520,000,000
$540,000,000
$560,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Department of Corrections
$2,200,000
$2,250,000
$2,300,000
$2,350,000
$2,400,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Pardon and Parole Board

14
Economic Development & Commerce
Measures
SB 71 (Bergstrom/McDugle) requires the
Oklahoma Department of Commerce to, in
addition to the other rulemaking
requirements relating to the Oklahoma Local
Development and Enterprise Zone Incentive
Leverage Act, establish reporting
requirements for the purpose of collecting
data.
SB 587 (Howard/Boles) adds entities subject
to the jurisdiction of the State Board of
Career and Technology Education or the
Oklahoma State Regents for Higher
Education to the list of eligible local
government entities as it relates to the
Oklahoma Community Economic
Development Pooled Finance Act.
SB 608 (Hall/Fetgatter) creates the Filmed
in Oklahoma Act of 2021. The measure
provides for the establishment of an
incentive rebate program for certain film
projects and eligible television series
projects filmed or produced in Oklahoma
that meet the requirements outlined in the
measure. Such projects must provide
evidence that all Oklahoma crew and local
vendors have been paid and that there are no
pending liens against the production
company, file appropriate tax returns,
provide evidence of financing for production
prior to the commencement of principal
photography, provide evidence of a
certificate of general liability insurance with
a minimum coverage of $1 million and a
workers’ compensation policy, and provide
evidence that the projects are completed.
Companies cannot simultaneously claim the
rebate and the sales tax exemption provided
for in current law or the rebate provided in
the Compete with Canada Film Act. If a
production company has received the
exemption from sales taxes and submits a
claim for rebate pursuant to the provisions
of this act, the company shall be required to
fully repay the amount of the exemption to
the Tax Commission. The program shall be
administered by the Oklahoma Department
of Commerce and the Oklahoma Tax
Commission. The Department shall be
required to submit an annual report to the
President Pro Tempore of the Seante,
Speaker of the House, the Chair of the
Appropriations and Budget Committee of
the House of Representatives, the Chair of
the Appropriations Committee of the Senate,
and the Director of the Legislative Office of
Fiscal Transparency detailing the program
and incentive rebate payments on October 1
of each year. The total amount of rebate
payments conditionally pre-qualified by the
Department of Commerce each fiscal year
shall not exceed $30 million. The measure
also caps the amount of rebates awarded to
projects based on the expenditure of the
individual project. The base incentive
amount for a project filmed in this state shall
be a maximum of 20% of the qualified
production expenditure amount. An
incentive for a project filmed in this state for
wages paid to nonresident crew, not
including above-the-line personnel, before
July 1, 2023, shall be provided in the
amount of 7.5%. The measure provides
additional incentives to projects that film or
locate in certain areas outlined in the
measure. The measure also requires projects
to utilize apprentices and display a
Department-approved logo in the end credits
to qualify for the rebate. Additionally, the
$90,000,000
$92,000,000
$94,000,000
$96,000,000
$98,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Office of Juvenile Affairs
15
measure creates the Filmed in Oklahoma
Program Revolving Fund and provides for
$30 million to be transferred to the Fund
using monies derived from the income tax.
SB 609 (Coleman/Hilbert) provides that the
minimum investment into real property must
be valued at a minimum of $500,000.00 to
qualify for the investment income tax
exemption during calendar year 2022. The
amount shall increase annually based on the
previous year’s increase in the Consumer
Price Index-All Urban Consumers. To
qualify for the exemption using newly
created jobs, the measure requires
corporations to maintain an average
annualized wage which equals or exceeds
the average wage requirement in the
Oklahoma Quality Jobs Program Act for the
year in which the real or personal property
was placed into service, depending on
location. Additionally, the measure expands
eligibility for the program to include
facilities engaged in the manufacturing,
compounding, processing or fabrication of
materials into articles of tangible personal
property. The measure also modifies the
definition of facility and facilities to specify
that the land, buildings, structures, and
improvements must be used directly and
exclusively in the manufacturing process.
Effective January 1, 2022, and for each
calendar year thereafter, for establishments
with a manufacturer exemption permit and
facilities engaged in manufacturing activities
classified in the NAICS Manual under
Industry numbers 311111 through 339999,
facility and facilities also includes
machinery, fixtures, equipment, and other
personal property used directly and
exclusively in the manufacturing process.
The measure specifies that districts that are
wholly or partially comprised or become
comprised of industries operating under
NAICS code 518210 shall not be subject to
certain findings requirements.
SB 659 (Rosino/Hilbert) creates the
Unmanned Aircraft Systems Development
Act of 2021. The measure establishes the
Oklahoma Aeronautics Commission as the
Clearinghouse for Unmanned Aircraft
Systems (UAS). The Clearinghouse shall
create a partnership between those persons
and entities that currently operate UAS,
those that desire to use this technology in the
future, and any other entity that supports the
research and development of UAS. The
measure also directs the Clearinghouse to
coordinate with other government entities to
develop UAS in the state. Additionally, the
measure updates several terms within the
Oklahoma Aeronautics Commission Act.
SB 739 (Leewright/Bashore) transfers the
regulatory authority relating to the
Oklahoma Tourism Development Act from
the Tourism and Recreation Department to
the Oklahoma Department of Commerce.
The measure also provides for the
Department of Commerce to prepare the
report required to determine the company’s
qualifications. The fee for utilizing the
Department in this manner is set at no less
than $5,000.00.
SB 893 (Pugh/Fetgatter) clarifies that
“qualified program” as it relates to the
income tax credit for aerospace employees
shall include graduate and undergraduate
programs. The undergraduate and graduate
programs of the same discipline of
engineering at an institution shall be part of
the qualified program if either program is
ABET accredited. The measure modifies
“qualified employee” to require such
persons to possess either an undergraduate
or graduate degree from a qualified program
by an institution or be a licensed
Professional Engineer.
16
SB 922 (Howard/Kendrix) creates the Invest
In Oklahoma Act. The measure directs the
Oklahoma Department of Commerce to
create the Invest In Oklahoma Fund to
provide entities funds with opportunities to
invest in Oklahoma-based private equity
funds, venture capital funds, and growth
funds. The Department is directed to select
venture capital funds to qualify for
investments within the Invest In Oklahoma
Fund based on factors outlined in the
measure. Qualified public entities may
invest up to 5% of their principal into the
Fund. The Department is directed to
maintain a list of entities participating in the
program.
SB 949 (Hall/Hill) transfers all
administrative rules and responsibilities
relating to the Oklahoma Film and Music
Office to be transferred from the Oklahoma
Tourism and Recreation Department to the
Oklahoma Department of Commerce.
HB 1124 (Phillips/Leewright) directs the
Department of Commerce to promulgate
rules and procedures for the establishment of
the State Broadband Deployment Grant
Program with the participation and advice of
the Rural Broadband Expansion Council.
The State Broadband Deployment Grant
Program shall include development of a
competitive grant program to award funding
to applicants seeking to expand access to
broadband Internet service. The measure
also creates the State Broadband
Deployment Grant Program Fund.
HB 2040 (McCall/Leewright) provides
definitions for certain telecommunications
and broadband related terms, including
“Broadband”, “Eligible entity”, “Served
area”, “Underserved area”, “Unserved area”,
and “Wireless Internet service provider”.
The measure also directs the Rural
Broadband Expansion Council to develop a
set of broadband incentive award guidelines
to recommend to the Legislature.
HB 2860 (Wallace/Thompson) creates the
Oklahoma Remote Quality Jobs Incentive
Act. The measure provides for quarterly
incentive payments for a 10-quarter period
for qualifying proxy establishments as
defined in the measure. Proxy
establishments must meet certain
qualifications to receive payments. Such
qualifications shall include roof of basic
health benefits plans for its remote workers
and meeting a certain threshold of
employees and wages. Establishments that
receive these incentive payments are not
eligible to receive credits or exemptions
provided by the Oklahoma Quality Jobs
Program Act, the Small Employer Quality
Jobs Incentive Act or the 21st Century
Quality Jobs Incentive Act. The measure
also directs the Department of Commerce
and the Tax Commission to prepare a
triennial report and to submit the report to
the President Pro Tempore of the Senate,
Speaker of the House, and Governor no later
than March 1, 2023 and every 3 years
thereafter.
HB 2928 (McCall/Leewright) directs
broadband service providers in the state to
submit a report containing their network
area coverage map to the Department of
Commerce and the Rural Broadband
Expansion Council by October 31, 2021.
The providers would be required to update
this map and report annually. OneNet must
provide mapping of all assets and network
coverage. Internet service providers are also
directed by the measure to disclose the
properties they serve, and average minimum
upload and download speeds at which they
provide services to those properties.
Commerce Funding

17
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Department of
Commerce
$52,739,680
$22,077,680
-58.14%
Historical Society Funding
SB 1081 (Thompson/Wallace) apportions
the appropriations made to the Oklahoma
Historical Society in HB 2900 in the
following manner:
1) $150,000.00 shall be used to hire a grant
writer for Black Towns in Oklahoma
2) Not less than $150,000.00 shall be used to
provide grants for schools to provide
transportation to The Freedom Center &
Clara Luper Civil Rights Center, The
Greenwood Historic District, and The
Oklahoma City National Memorial &
Museum
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Historical
Society
$21,524,457
$23,461,601
9.00%
Common Education
SB 13 (Stanley/Baker) requires a teacher
whose certificate was suspended by the State
Board of Education to be placed on
suspension while proceedings for revocation
or other action are pending before the Board.
These actions do not preclude the initiation
of due process procedures under the Teacher
Due Process Act.
SB 21 (Floyd/McEntire) requires rather than
allows each school district to adopt a policy
related to suicide awareness and training.
The measure requires a board of education
to provide districtwide training to all staff on
a biennial basis addressing suicide
awareness and prevention. It requires rather
than allows school districts beginning in the
2021-22 school year to provide a suicide
prevention training program, provide
curriculum made available by the
Department of Mental Health and Substance
Abuse Services or provide a suicide
prevention training program selected from a
list maintained by the Department of Mental
Health and Substance Abuse Services.
Additionally, the measure provides for
suicide awareness and prevention training
for students in grades 7-12 beginning in the
2022-23 school year.
SB 22 (Floyd/Tammy West) modifies the
powers and duties of school district boards
of education. The measure gives a right of
first refusal to purchase real or personal
property to a nonprofit organization that is
leasing the real or personal property from a
board of education when the decision is
made to dispose of the property, whether
such disposal is by public sale, public bid or
private sale. The measure states that if a
board of education receives a bid or offer for
the real or personal property, the board is to
provide notice to the nonprofit organization
leasing the property. The measure gives the
$0
$10,000,000
$20,000,000
$30,000,000
$40,000,000
$50,000,000
$60,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Department of Commerce
$0
$5,000,000
$10,000,000
$15,000,000
$20,000,000
$25,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Historical Society
18
nonprofit organization 30 days after receipt
of such notice to inform the board whether it
elects to purchase the property on the same
terms and conditions provided in the notice.
The measure states that if any portion of the
consideration in the purchase price is not in
cash, the nonprofit organization can pay fair
market value in cash of such non-cash
consideration.
SB 54 (Montgomery/Pae) directs the State
Department of Education beginning in the
2022-23 school year to designate a school
campus as a Purple Star School campus if
the school meets certain qualifications
related to availability of services for
military-connected students.
SB 68 (Simpson/Wolfley) directs a student
to be considered in compliance with the
residency requirements for school
attendance if the parent or legal guardian of
the student is transferred or is pending
transfer to a military installation within the
state while on active military duty. It directs
school districts to accept enrollment
applications for such students by electronic
means and directs the parent or legal
guardian of such a student to provide proof
of residence to the school district within 10
days after the published date of arrival. It
defines what shall constitute proof of
residence.
SB 69 (Simpson/Wolfley) allows a student
to enroll in a statewide virtual charter school
if the parent or legal guardian of the student
is transferred or is pending transfer to a
military installation within the state while on
active military duty. It directs statewide
virtual charter schools to accept enrollment
applications for such students by electronic
means and directs the parent or legal
guardian of such a student to provide proof
of residence to the statewide virtual charter
school within 10 days after the published
date of arrival. It defines what shall
constitute proof of residence.
SB 89 (Haste/Baker) creates the Health
Education Act. The measure directs the
State Department of Education to develop a
micro-credential for teachers teaching health
education and professional development
programs no later than the 2022-2023 school
year. It directs school districts by the 2023-
2024 school year to provide instruction
addressing all health education subject
matter standards adopted by the State Board
of Education. It allows health education to
be integrated into one or more existing
subjects. The measure requires teachers
assigned to teach health education as a
stand-alone course to be certified in physical
and health education. The measure also
directs the State Textbook Committee to
include a review of health and physical
education instructional materials as part of
its textbook review and adoption cycle. The
bill creates the Health Education Revolving
Fund to carry out the act and directs the
Healthy and Fit School Advisory Committee
within schools to study and make
recommendations regarding implementation
of the Health Education Act.
SB 121 (Hicks/Hasenbeck) requires each
school district board of education to adopt a
policy allowing school employees who are
lactating to take paid break time to maintain
their milk supply. The measure allows the
break time to run concurrently with any
break time and requires school district
boards of education to make reasonable
effort to provide a private, sanitary room for
employees to express milk or breastfeed a
child.
SB 128 (Rader/Dick Lowe) creates the
Seizure-Safe Schools Act. The Act requires
each school district with a student who has a
seizure disorder beginning Jan. 1, 2022, to
19
have at least 1 employee who has training to
administer or assist with self-administration
of seizure medication and recognize
symptoms of seizures and take steps to
respond. The measure states that before
seizure medication can be administered, the
parent or legal guardian of the student is to
provide written authorization to the school,
provide a statement from the student’s
health care provider, provide medication to
the school and collaborate on a seizure
action plan. It requires such authorization to
be renewed annually. The measure exempts
from disciplinary proceedings school
employees who take action in compliance
with the act. It provides immunity from civil
liability to a school employee who takes
action in compliance with the act, unless the
actions rise to the level of reckless or
intentional misconduct. It states that a
school nurse shall not be responsible for and
shall not be subject to disciplinary actions
for actions taken by a volunteer.
SB 211 (Dugger/Luttrell) modifies the
powers and duties of the Oklahoma Board of
Private Vocational Schools. The measure
authorizes the Board to develop applications
for sustained licenses, develop and present
optional training, conduct announced and
unannounced site visits, invoice a travel fee
for site visits, and collect data required to be
reported to the U.S. Department of
Education or any state or federal agency.
The measure allows for schools accredited
by a U.S. Department of Education-
approved accrediting organization for
multiple years to obtain a sustained license.
Additionally, the measure modifies fees for
reviewing a revised or replacement catalog
and provides fees for review of
documentation to be forwarded to the U.S.
Department of Education or another state or
federal agency, for optional training, for
review of enrollment agreements and for in-
state site visits. The measure also directs that
the Board’s base fees will increase by 7% in
fiscal year 2022.
SB 252 (Stanley/Baker) requires all public
and charter high schools to offer a minimum
of one computer science course beginning in
the 2024-25 school year. It also requires all
public and charter elementary and middle
schools to offer instruction in computer
science beginning in the 2024-25 school
year. It allows the courses to be offered in an
in-person setting or as a virtual or distance
course when a traditional classroom setting
is not feasible.
SB 302 (Coleman/Kannady) grants visiting
teams in all regular high school athletic
competitions the same rights to radio
broadcast, video stream and provide
telegraphic play-by-play accounts as the
home team in all seasonal high school
athletic competitions beginning in the 2021-
22 school year. To utilize these rights, the
visiting team must have either a valid
agreement between a media organization
and the school’s board of education or a
curricular program for students that provides
streaming for home games. The bill applies
to contracts for rights to radio broadcast,
video stream and provide telegraphic play-
by-play accounts entered into or renewed on
or after July 1, 2021.
SB 619 (Bullard/Kevin West) requires the
Oklahoma Tax Commission to pay interest
on tax refunds not paid within 45 days for
returns filed electronically and 90 days for
all other returns after the return is filed or
due, whichever is later. The measure also
allows the Commission to provide a later
due date for the returns of individuals and
certain entities if a state of emergency is
declared by the Governor or upon
declaration by the Internal Revenue Service
to postpone deadlines in disaster areas.
Lastly, the measure modifies the period of
20
underpayment for corporations to be 30 days
after the due date for returns established
under the Internal Revenue Code. The
measure authorizes the State Board of
Education to determine if apprenticeships,
internships, and mentorships are eligible for
academic credit toward meeting the
graduation requirements.
SB 642 (Pugh/Dustin Roberts) requires each
public school district and public charter
school in the state to offer students in grades
10 through 12 the opportunity to take the
Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery
(ASVAB) test and consult with a military
recruiter beginning in the 2021-22 school
year. It directs the ASVAB test to be
administered during normal school day
hours at a time that doesn’t conflict with
extracurricular activities. It requires the
district or charter school to provide notice of
the date, time and location of the test to
students in grades 10 through 12 and their
parents or legal guardians. The bill allows a
district or charter school to provide an
alternative test that is free and assesses a
student’s aptitude for success in a career
field that does not require postsecondary
education.
SB 658 (Standridge/Kevin West) requires
the State Department of Education and
school districts to provide in any notice or
publication provided to parents regarding
immunization requests the immunization
requirements of the school, including the
requirement to either provide current, up-to-
date immunization records or a signed and
completed exemption form. The measure
also prohibits any school district, institution
of Higher Education, the State Board of
Education, or the State Board of Career and
Technology Education from requiring a
vaccination against COVID-19 as a
condition of admittance to or attendance of
the school or institution. Such entities are
also prohibited from requiring a vaccine
passport as a condition of admittance or
implementing a mask mandate for students
that are not vaccinated against COVID-19.
Additionally, the measure also provides that
a board of education for a school district or
technology school district may only
implement a mandate to wear mask or any
other medical device after consultation with
the local county health department or city-
county health department. Such a mandate
must explicitly list the reasons for the
mandate and shall reference the specific
masks or medical devices that would meet
the requirements of the mandate. Any
mandate to implement wearing a mask or
any other medical device shall be
reconsidered at each regularly scheduled
board meeting.
SB 705 (Dahm/Gann) repeals sections of
law creating the Oklahoma Center for Rural
Development Act, which was established to
improve the effectiveness of citizens,
enterprises, and communities in rural
Oklahoma to better meet the quality of life
challenges in the new century.
SB 783 (Pugh/Boles) modifies the
Education Open Transfer Act. It states that
beginning Jan. 1, 2022, the transfer of any
student from one district to another shall be
approved at any time during the year unless
the number of transfers exceeds the capacity
of a grade level for a school site within a
district. If the number of transfer
applications exceeds the capacity of a school
site, the school district is to select transfer
students in the order in which they were
received. It allows a student to be granted a
one-year transfer, with the school district
retaining the ability to deny the continued
transfer if the student has a history of
absences or has committed certain acts that
are subject to out-of-school suspension. The
bill prohibits a student from transferring
21
more than twice per school year to one or
more districts. The measure directs each
school district board of education by Jan. 1,
2022, to adopt a policy to determine the
number of students a district has the
capacity to accept in each grade level for
each school site. It directs such capacity to
be established by the first day of January,
April, July and October, and it directs school
districts to post the capacity information on
their websites and report it to the State
Department of Education. It allows a denied
transfer request to be appealed within 10
days to the receiving school district board of
education. If the receiving school district
board of education denies the appeal, the bill
allows an appeal to be filed within 10 days
to the State Board of Education. It directs
each school district board of education to
submit to the State Department of Education
the number of student transfers approved
and denied and the reason for denial, and it
requires the Department to publish the data
on its website and share it with the Office of
Educational Quality and Accountability. The
measure directs the Office of Educational
Quality and Accountability to randomly
select 10% of the districts in the state to
conduct an audit of approved and denied
transfers. If the Office finds inaccurate
reporting of capacity levels, the bill directs
the Office to set the capacity levels. The bill
removes language regarding the transfer
application timeline. It clarifies that students
who are the dependent children of a member
of the active uniformed military services of
the United States on full-time active duty
status and students who are the dependent
children of a member of the military reserve
on active duty orders are to be eligible to
enroll in any school district regardless of the
district’s capacity. It removes language
allowing a receiving school district to
approve the transfer of a student whose
parent or legal guardian is employed as a
teacher. It also repeals statutory language
regarding emergency transfers.
SB 807 (Kidd/Baker) directs that school
support employees be entitled to pay for any
time lost when a school district is closed
because of an epidemic or when a closing
order is issued by an authorized health
officer.
HB 1018 (Sterling/Quinn) removes
language requiring the State Superintendent
of Public Instruction to compile and publish
the school law book.
HB 1046 (Kerbs/Montgomery) requires
school districts to provide a copy or a
hyperlink to a copy of the school district’s
most recent audit on the school district’s
website.
HB 1103 (Vancuren/Haste) requires schools
beginning in the 2022-23 school year to
administer biennially the Oklahoma
Prevention Needs Assessment Survey, a
mental health prevention survey, for 6th, 8th
, 10th and 12th grade students, or an
alternative survey. It directs the Department
of Mental Health to maintain the survey and
provide technical assistance. If a school
chooses to administer an alternative survey,
it must apply for a waiver from the
Department of Mental Health. The bill states
that the requirement for the survey is subject
to availability of federal funding, and if
funding is insufficient, administration of the
survey is not required.
HB 1104 (Vancuren/Montgomery) amends
the Student Data Accessibility,
Transparency and Accountability Act of
2013. It modifies the definition of “student
data” to include tribal affiliation and other
data associated with students who have been
identified with American Indian heritage.
22
HB 1568 (Boatman/Haste) creates Maria’s
Law. The measure directs the State Board of
Education beginning with the 2022-23
school year to require that all schools
include instruction in mental health as part
of any health education curriculum with an
emphasis on the interrelation of physical and
mental well being. It directs the Board, in
consultation with the Department of Mental
Health and Substance Abuse Services, to
revise the Oklahoma Academic Standards
for Health and Physical Education to include
a focus on mental health and develop a list
of age-appropriate resources for students in
grades K-12. It also allows school districts
to enter into agreements with nonprofit
entities or other community partners to assist
in providing mental health education if such
entities or partners are approved by the
Department of Education and the
Department of Mental Health.
HB 1569 (Rosecrants/Pugh) creates the
Oklahoma Play to Learn Act. It allows
educators to create a learning environment
that facilitates child-directed experiences. It
allows school districts to provide ongoing
early childhood professional development
for early childhood educators and
administrators. It also states that a school
district shall not prohibit a teacher from
using play-based learning in early childhood
education.
HB 1593 (Provenzano/Stanley) directs
school district boards of education to require
a professional development program for
teachers that emphasizes the importance of
digital teaching and learning standards. It
requires the program to be completed the
first year a certified teacher is employed by
a school district and then at a frequency
determined by the board. The bill also
directs boards of education to require a
training program for teachers that
emphasizes the importance of recognizing
and addressing the mental health needs for
students. It requires the program to be
completed the first year a certified teacher is
employed by a district and once every third
academic year. It directs boards of education
to require a program for 7th through 12th
grade teachers that emphasizes the
importance of incorporating workplace
safety training into curriculum. It requires
the program be completed the first year a
certified teacher is employed by a district
and then at a frequency determined by the
board. The measure also requires training or
a workshop on alcohol and drug abuse to be
completed the first year a certified teacher is
employed by a district and then once every
third academic year.
HB 1773 (Conley/Garvin) requires the State
Board of Health to provide a multi-seasonal
license for snow cone stands that sell hot
beverages in addition to snow cones. Snow
cone stands that do not sell hot beverages
will be classified as a seasonal food
establishment.
HB 1796 (Miller/Pugh) allows the State
Board of Education, in consultation with the
Commission for Educational Quality and
Accountability, to grant an exception to the
subject-area examination for initial
certification in a field that does not require
an advanced degree if the candidate has an
advanced degree in a subject that is
substantially comparable to the content
assessed on the subject-area exam. It
requires the degree to be from an institution
accredited by a national or regional
accrediting agency recognized by the
Secretary of the U.S. Department of
Education.
HB 1801 (Conley/Stanley) requires school
boards, beginning 2021-2022, to coordinate
with local emergency medical service
(EMS) providers to develop an Emergency
23
Action Plan for each school facility. The
Emergency Action Plan must be rehearsed
annually with school officials and local
EMS providers. Prior to any athletic event
with visiting teams, the Plan shall be
digitally transmitted to the school’s
administrator or coach.
HB 1875 (Tammy West/Stanley) prohibits
an educational agency or institution, if it is
not the primary custodian of student
directory information of students attending
the institution, from releasing or selling any
or all student directory information unless
such disclosure is authorized by federal law.
If this prohibition does not apply, the
educational institution is authorized to
designate specific information to be
classified as directory information for
students attending the institution.
HB 1882 (Stark/Rader) creates the Out-of-
Schooltime Task Force. The Task Force is
directed to identify, evaluate and
recommend a set of best practices for
children, youth and families which will
improve and increase the number of quality,
affordable out-of-school programs in the
state. The Task Force shall be comprised of
19 members. The measure requires
appointments to the Task Force be made no
later than December 1, 2021. Members of
the Task Force shall not receive
compensation or travel reimbursements. The
State Superintendent shall call the first
meeting no later than February 1, 2022, and
must meet at least 6 times prior to the sunset
date of December 31, 2022. Administrative
support for the task force shall be provided
by the House of Representatives. The task
force shall issue a report of its findings to
the President Pro Tempore of the Senate,
Speaker of the House, and Governor no later
than December 1, 2022.
HB 1968 (Nollan/Stanley) modifies
language regarding specific information to
be included in a school district’s report on
gifted child educational program
expenditures. It requires all districts to
report expenditures in the Oklahoma Cost
Accounting System. It removes language
that required districts receiving above $1
million or 6% or more of their total State
Aid for gifted and talented programs to
report such expenditures by major object
codes and program classifications and other
districts to report by major object codes.
HB 2030 (O’Donnell/Pugh) directs the
subject matter standards for history, social
studies and U.S. government include the
study of historical documents including the
Declaration of Independence, the U.S.
Constitution, the Federalist Papers and the
Emancipation Proclamation. The bill also
requires rather than allows that the U.S.
naturalization test be administered to
students beginning in the 2022-23 school
year. It requires the subject matter standards
for U.S. government to include the structure
and relationship between national, state,
county and local governments and
simulations of the democratic process. The
bill requires students to pass the U.S.
naturalization test in order to graduate from
a public high school beginning with 9th
graders in the 2021-22 school year. It
requires districts to offer the naturalization
test to students at least once per school year
beginning as early as eighth grade, and it
allows a student to retake the exam as often
as desired until earning a passing score of 60
out of 100. It provides an exemption for
students whose individualized education
program indicates alternative achievement
standards.
HB 2223 (Randleman/Pemberton) directs
the State Department of Education to
maintain the dyslexia handbook created by

24
the Dyslexia and Education Task Force and
review and make revisions to it a minimum
of every three years. It requires revisions to
the handbook to include information
regarding screening students in kindergarten
through third grades.
HB 2329 (Lawson/Simpson) allows the
State Board of Education to grant an
exception to the requirements for
certification examinations for teacher
candidates who are deaf. It allows the Board
to grant such an exception upon certain
criteria being met. It allows those granted
such exceptions to teach in American Sign
Language immersion programs, the
Oklahoma School for the Deaf, programs for
the deaf or other classroom settings where
American Sign Language is used as the
language of instruction.
HB 2691 (Hasenbeck/Bergstrom) directs the
Commission for Educational Quality and
Accountability to issue a report by Oct. 31,
2021, to the President Pro Tempore of the
Senate, Speaker of the House, and Governor
detailing factors in the education system that
contribute to improvements, including
improvements in graduation rates,
assessment scores, timely postsecondary
graduation and career readiness. It allows
the Commission to contract with a private
consultant to assist with the report and to use
state, federal, private funds or grants.
HB 2748 (Baker/Stanley) directs the State
Board of Education to issue a 1-year
alternative teacher certificate renewable for
up to 3 years to teach early childhood
education or elementary education. It
establishes qualifications, including a
declaration of intent to earn standard
certification within 3 years and completing
certain credit hours in classroom
management, reading instruction child
development and math instruction.
HB 2749 (Baker/Pugh) amends the Reading
Sufficiency Act to require districts that
receive more than $2,500 in RSA funding to
spend no less than 10% on professional
development for pre-K through 5th grade
teachers beginning in the 2022-23 school
year. It directs the professional development
to include training in the science of how
students learn to read. The bill directs the
State Department of Education to approve
and publish a list by June 30, 2022, of
professional development programs that can
be used.
HB 2750 (Baker/Pugh) states legislative
intent that institutions of higher education
not require an Advanced Placement exam
score of more than 3 for course credit. It
allows a score of 3 or more to be required
for granting additional course credit. The
bill directs all AP exam credit policies be
posted on campus websites for the 2021-22
fall term and each academic term thereafter.
It directs institutions to conduct biennial
reviews of their AP credit policies. It directs
noncompliance to be reported to the chairs
of the House and Senate education
committees by Dec. 1 each year.
HB 2752 (Baker/Stanley) directs the State
Department of Education to establish a
micro-credential program within 120 days of
the effective date of the act to allow a
teacher candidate or teacher to earn micro-
credentials in science, technology,
engineering and mathematics (STEM)
endorsement areas, including computer
science. It directs SDE and the Commission
for Educational Quality and Accountability
to convene a working group to determine
how a micro-credential will be used.
Career & Technology Education Funding
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original

25
Department
of Career &
Technology
Education
$137,471,871
$138,852,412
1.00%
Common Education (K-12) Funding
SB 229 (Montgomery/Hilbert) creates the
Redbud School Funding Act. The measure
provides that, in fiscal year 2022, the first
$65 million raised from the 7% gross tax on
medical marijuana sales shall be apportioned
to the State Public Common School
Building Equalization Fund (59.23%), the
Oklahoma Medical Marijuana Authority
(34.62%), and the Oklahoma State
Department of Health for drug and alcohol
rehabilitation programs (6.15%). Surplus
collections raised from the tax shall be
apportioned to the General Revenue Fund of
the State Treasury. Additionally, the
measure provides that sales taxes
apportioned to the State Public Common
School Building Equalization Fund shall not
exceed the state sales tax generated by
medical marijuana sales in the preceding
fiscal year beginning in fiscal year 2023 and
each year thereafter. Additionally, the
measure clarifies that except as explicitly
authorized by state law, a charter school
shall not be eligible to receive state-
dedicated, local, or county revenue. The
measure directs the State Board of
Education to disburse redbud school grants
annually from the State Public Common
School Building Equalization Fund to public
schools and eligible charter schools in a
manner outlined in the measure. The State
Department of Education shall consider each
eligible charter school as separate from the
school district that sponsors it when making
these calculations. Eligible charter schools
shall not include a charter school sponsored
by the Statewide Virtual Charter School
Board. The SDE is authorized to reserve not
more than 0.5% of the funds for the purpose
of administrating the fund. The Department
is directed to create a dedicated page on its
website listing annual redbud school grant
recipients and to provide the Chair of the
House Appropriations and Budget
Committee and the Chair of the Senate
Appropriations Committee an estimate of
the upcoming year’s redbud school grant
allocation.
SB 1037 (Thompson/Wallace) allows school
district building funds to consist of federal
monies allocated by the Coronavirus
Response and Relief Supplemental
Appropriation Act of 2021 (CRRSA) and
the federal American Rescue Plan Act of
2021 (ARP).
SB 1038 (Thompson/Wallace) modifies the
definition of “student teacher” to allow such
an individual to receive compensation for up
to 1 full school year as part of an internship.
It clarifies that such compensation is not to
be considered compensation for purposes of
teacher retirement or the minimum salary
schedule. The bill also removes language
allowing only students who have completed
minimum teacher internship requirements to
be eligible to participate in a paid internship
program.
SB 1067 (Thompson/Wallace) apportions
monies appropriated to the State Department
of Education from HB 2900 in the following
manner:
1) $2,437,246,699.00 for Local and State-
supported Financial Support of Public
Schools
$110,000,000
$120,000,000
$130,000,000
$140,000,000
$150,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Department of Career &
Technology Education
26
2) $704,456,047.00 for benefits, training,
textbooks, and childhood initiative programs
3) $15,027,640.00 Administrative and
Support Functions of the State Department
of Education
4) $3,827,899.00 shall be transferred to the
School Consolidation Assistance Fund
5) $3,827,899.00 shall be transferred to the
Teachers’ Retirement System Dedicated
Revenue Revolving Fund
6) $1,500,000.00 shall be transferred to the
Oklahoma National Board Certification
Revolving Fund
7) $3,300,000.00 shall be transferred to the
Oklahoma School Psychologist, Speech-
language Pathologist, and Audiologist
National Certification Revolving Fund
Additionally, the measure directs the
Department to budget all funds in the
following categories and amounts:
1) Payroll, Salaries or Wages Including Tax-
sheltered Deferment Contracts and
Longevity Payments Authorized by State
Statutes- $18,227,387.00
2) Professional and Personal Services-
$28,696,456.00 3) Contracts Other
Operating Funds- $3,126,828,823.00 4)
Expenditure of Federal Funds
$2,644,741,337.00
The measure also provides that if the funds
allocated to the Teachers’ Retirement Credit
are insufficient to fully fund the employee
contribution credits, the Department may
reduce in equal proportions funds allocated
to the Education Leadership Oklahoma,
Advanced Placement Incentives, Reading
Sufficiency, Teacher and Leader
Effectiveness Programs, Alternative and
High Challenge Education, Required
Assessments, Ag in the Classroom and
Imagine Math to fund the program.
SB 1080 (Thompson/McCall) modifies the
total credit allocation cap on the Oklahoma
Equal Opportunity Education Scholarship,
the method for awarding credits, and eligible
entities for the program. The measure
provides that any taxpayer who makes a
contribution to an eligible public school
foundation or public school district shall be
entitle to a credit equal to 50% of the
contribution made and those who make a
written commitment to contribute the same
amount for an additional year shall be
entitled to a credit equal to 75% of the
contribution made. Such taxpayers shall
provide evidence of the written commitment
to the Oklahoma Tax Commission at the
time of filing the refund claim. The measure
also defines “eligible public school
foundations”. The measure caps the total
annual amount of credits awarded at $25
million for contributions to public school
foundations and public school districts for
tax year 2022 and each year thereafter. If the
Tax Commission determines the total
amount to be awarded shall exceed the cap,
the Commission shall reduce the credits
awarded on a proportional basis.
Additionally, the measure limits the amount
awarded to each public school district at
$200,000.00 annually. Each school or
foundation receiving funding from the
program shall be required to annually report
to the Tax Commission by September 1 of
each year the information outlined in the
measure relating to the educational
scholarships funded by the organization in
the previous academic year.
HB 2078 (Hilbert/Taylor) amends the State
Aid Funding Formula beginning with the
2022-23 school year. It removes language
allowing the initial and midyear State Aid
allocation calculations to be based on the
weighted average daily membership
(WADM) of a district’s second preceding
school year. Instead, it requires each district
to use its WADM from the preceding school
year to calculate its initial State Aid

27
allocation instead of the higher WADM of
the preceding 2 school years. And, it directs
the midyear adjustment to be based on the
higher WADM of the preceding school year
or the first nine weeks of the current school
year. It increases the allowed general fund
carryover between 3 and 8 percentage points
depending on the total general fund
collections for each district. It also prohibits
a general fund balance penalty from being
imposed on school districts that exceed
prescribed limits during fiscal years 2022
and 2023.
HB 2871 (Wallace/Thompson) directs the
Commissioners of the Land Office when
calculating the 5% cap on investments in
real property to not include the value of real
property under long-term lease to the state,
agencies of the state, or subdivisions thereof.
HB 2890 (Wallace/Thompson) permits
school district to carryover a general balance
fund in excess of limits previously
established by law without a general fund
penalty being assessed. The measure allows
districts to continue this practice through FY
2023. Additionally, the measure provides
that the July calculation of per pupil revenue
be determined by the district’s second
preceding year’s total average daily
membership (ADM).
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Department
of Education
$2,992,729,814
$3,164,386,184
5.74%
Office of
Educational
Quality
$1,567,209
$1,567,209
0.00%
Higher Education
SB 48 (Daniels/Kannady) creates the
Revised Uniform Athlete Agents Act. The
measure updates the Uniform Athlete Act. It
expands the definition of “athlete agent” and
“student athlete” within the Act as well as
adds new requirements to the signing of an
agency contract. Additionally, the Act
provides greater flexibility to students when
choosing between a professional draft or the
continuation of their college education.
Finally, the measure repeals the current
Uniform Athlete Agents Act. Additionally,
the measure creates the Student Athlete
Name, Image and Likeness Rights Act. The
measure specifies that a student athlete may
earn compensation commensurate with
market value for the use of the name, image
or likeness of the student athlete while
enrolled at a postsecondary institution
without penalty or resulting limitation on
participation. A student athlete shall not earn
compensation in exchange for his or her
athletic performance or participation in
intercollegiate athletics or sports
competition.
$2,700,000,000
$2,800,000,000
$2,900,000,000
$3,000,000,000
$3,100,000,000
$3,200,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Department of Education
$1,500,000
$1,550,000
$1,600,000
$1,650,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Office of Educational Quality
& Accountability
28
SB 132 (Bullard/Baker) amends the
Oklahoma Higher Learning Access Program
to allow juniors in public or private high
schools and 16-year-old students who are
educated by other means to enter into
student agreements for the program.
SB 261 (Montgomery/Provenzano) creates
the Oklahoma Student Borrower’s Bill of
Rights Act. The measure directs the
Attorney General to prepare a written
statement that includes an "Oklahoma
Student Borrower's Bill of Rights" for a
student loan borrower who takes out a
student education loan that is serviced by a
student loan servicer. The statement must
include plain and clear language prohibiting
any student loan servicer from engaging in
any act that misleads, deceives, or defrauds
student borrowers. Loan servicers are also
prohibited from making false statements or
omitting material facts when submitting
reports to a governmental agency.
SB 292 (Haste/Nollan) creates until
November 30, 2022, a 14-member task force
to study and make recommendations
regarding current and future concurrent
enrollment needs of the state and pathways
for awarding degrees and certificates
through concurrent enrollment. It requires
the task force to have an organizational
meeting by September 1, 2021. It prohibits
task force members from receiving
compensation or travel reimbursement. It
subjects the task force to the Oklahoma
Open Meeting Act. The bill also requires the
task force to submit a report of its finding to
the Governor, the President Pro Tempore of
the Senate and the Speaker of the House by
November 30, 2022.
SB 639 (Pugh/Baker) directs the Oklahoma
State Regents for Higher Education to
administer a survey to students who receive
an Oklahoma Higher Learning Access
Program award and who withdraw from an
institution within The Oklahoma State
System of Higher Education, a private
institution of higher learning, or a
technology center school before completing
a degree or certificate program.
Additionally, the measure directs the State
Regents to submit to the President Pro
Tempore of the Senate and the Speaker of
the House of Representatives an annual
report on the impact of the Oklahoma
Higher Learning Access Program beginning
December 31, 2022, and each December 31
thereafter.
HB 1775 (Kevin West/Bullard) prohibits an
enrolled student in an institution within The
Oklahoma State System of Higher
Education from being required to engage in
any form of mandatory gender or sexual
diversity training or counseling, but it allows
voluntary counseling. It also prohibits any
orientation or requirement that presents any
form of race or sex stereotyping or bias on
the basis of race or sex. It directs the
Oklahoma State Regents for Higher
Education to promulgate rules to implement
these provisions, pursuant to the
Administrative Procedures Act and subject
to approval by the Legislature. Additionally,
the bill prohibits a teacher, administrator or
other employee of a school district, charter
school or virtual charter school from
requiring or making part of a course certain
concepts, including one race or sex is
inherently superior to another race or sex. It
clarifies that the language does not prohibit
the teaching of concepts that align to the
Oklahoma Academic Standards. It directs
the State Board of Education to promulgate
rules to implement these provisions,
pursuant to the Administrative Procedures
Act and subject to approval by the
Legislature.

29
HB 1821 (McBride/Pemberton) modifies
language relating to the awarding of tuition
aid grants. It allows rather than requires a
tuition aid grant to be awarded annually to
each qualified student. It removes language
regarding the maximum award amount. The
bill directs the State Regents to determine
award priorities based on enrollment status,
unmet financial need, continuous
enrollment, nearness to completion, state
employment needs, eligibility for other
financial aid and availability of funding.
HB 1962 (Nolian/Quinn) modifies the
definition of “qualified higher education
expense” under the Oklahoma College
Savings Plan Act to remove specific
references to tuition, fees, books, etc. and
leaves in place reference to definition under
IRS code.
HB 2396 (Russ/Stanley) directs the
Oklahoma State Regents for Higher
Education to allow a series of in-depth
prevention and education programs
regarding sex trafficking and exploitation to
all freshman students enrolled in institutions
within The Oklahoma State System of
Higher Education. It directs institutions to
provide all freshmen the opportunity to
attend one of three on-campus, voluntary
sex trafficking and exploitation prevention
and education programs. It directs program
materials relating to the programs to be
provided at no cost, with the program
provider being solely responsible for
incurring all costs associated with
implementing the programs and related
materials.
HB 2943 (McCall/Treat) transfers the
University Center of Southern Oklahoma in
Ardmore, Oklahoma to the Murray State
College and redesignates the Center as the
Murray State College at Ardmore. The
transfer shall include all real property,
buildings, furniture, equipment, supplies,
records, assets, current and future liabilities,
fund balances, encumbrances, obligations,
indebtedness, legal agreements, powers,
duties, and responsibilities associated with
the University Center of Southern
Oklahoma.
Higher Education Funding
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Regents for
Higher
Education
$802,070,058
$770,414,742
-3.95%
Hospital Authority Funding
HB 2874 (Wallace/Thompson) provides a
sales tax exemption for sales of tangible
personal property or services to the
University Hospitals Trust. The measure
also provides an exemption for the transfer
of tangible personal property or services
made by or to the University Hospitals Trust
or nonprofit entities that are exempt from
taxation that have entered into a joint
operating agreement with the University
Hospitals Trust.
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
University
Hospitals
Authority
$66,691,554
$86,591,554
29.84%
$740,000,000
$760,000,000
$780,000,000
$800,000,000
$820,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Regents for Higher Education

30
Energy, Environment, & Utilities
SB 246 (Allen/Sean Roberts) lowers the
population requirement for counties where
people or entities located in certain areas are
required to use air curtain incinerators for
land clearing operations and air curtain
incinerators for the burning of clean wood
waste or yard brush. Additionally, the
counties required to use air curtain
incinerators shall also include areas where
the Department-certified ambient air quality
monitoring data documents a violation of
primary National Ambient Air Quality
Standards.
SB 448 (Taylor/Boles) defines various terms
associated with recycling procedures in the
Oklahoma Solid Waste Management Act.
The measure defines the parameters of what
constitutes an advanced recycling facility
and the various procedures used to
depolymerize, gasify, use, and recover
recycled products.
SB 632 (Taylor/McEntire) adds the proceeds
owed for oil and gas drilling and
development, proceeds from the acquisition
of oil and gas rights, and proceeds from an
unfulfilled contract or agreement for the
purchase of mineral rights to the list of
illustrated rights as it relates to oil and gas.
The FS modifies the Nature, Extent, and
Duration of Oil and Gas Lien to include the
provision to secure the obligation of any
person to pay any proceeds for the
acquisition of oil and gas rights.
SB 1006 (David/Sims) modifies the duties
of the Tri-State Commission by directing the
Commission to coordinate with any relevant
federal or state agency or any other entity to
identify ways to improve the navigability of
the McClellan-Kerr Arkansas River
Navigation System.
SB 1021 (David/McBride) creates the
Hydrogen Production, Transportation and
Infrastructure Task Force. The Task Force
shall be comprised of 10 members and shall
disband on December 31, 2021. The
measure requires the Task Force to meet at
least once per month and to hold at least two
separate meetings focusing on the
distribution and production of hydrogen
respectively. The FS additionally provides a
list of representatives the Task Force shall
consult as it investigates the issue. The Task
Force shall be subject to the provisions of
the Open Records Act and its members shall
receive no compensation or travel
reimbursement. The Task Force shall submit
a report of its findings to the Governor,
President Pro Tempore of the Senate, and
Speaker of the House no later than
December 1, 2021.
SB 1022 (David/Boles) authorizes the
Executive Director of the Oklahoma Water
Resources Board to issue temporary and
regular water permits that have not been
subject to a protest from an interested party.
SB 1049 (Thompson/Wallace) creates the
February 2021 Unregulated Utility
Consumer Protection Act. The measure shall
provide financial assistance in the form of a
pooled loan program provided for
unregulated utility entities for the purpose of
reducing the impact of costs related to the
extreme weather event that occurred
$0
$20,000,000
$40,000,000
$60,000,000
$80,000,000
$100,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
University Hospitals Authority
31
between February 7, 2021, and February 21,
2021. The Oklahoma Development Finance
Authority shall issue and administer the
bonds, notes or other forms of evidence of
indebtedness to fund the loans to
unregulated utility entities under this
program. The Public Utility Division of the
Oklahoma Corporation Commission is
directed by the measure to assist the
Authority in determining the costs an
unregulated utility actually and lawfully
incurred by the weather event through
administrative review before a loan is
approved. Unregulated utilities may apply
for a loan from the Authority through an
application process and must provide the
amount of extreme purchase costs and
extraordinary costs requested for recovery,
whether the unregulated utility is requesting
a loan for all or a portion of the extreme
purchase costs and extraordinary costs,
estimated amount of cost savings from or
demonstration of how utility bill impact to
customers would be mitigated by receiving a
loan for the eligible extreme purchase costs
and extraordinary costs, and any other
information deemed necessary by the
Authority. The Authority shall send the
application to the Corporation Commission
for an audit of the amounts requested for
recovery and then the Commission shall
send the application back to the Authority
for approval or rejection. If the Authority
rejects the application, it must provide the
reasoning for its rejection to the utility and
provide for the utility to resubmit its
amended application. The Authority is
authorized to issue credit with loan terms of
and up to 30 years, which shall be at their
discretion. The measure authorizes the
Authority to take a security interest in any
property or revenues of the unregulated
utility. The loans shall be financed from
revenue by the newly created Unregulated
Utility Consumer Protection Fund. The Fund
shall receive monies derived from the bonds,
notes, or any other form of evidence of
indebtedness issued by the Authority and
any other contributions from unregulated
utilities permitted by law. Upon receiving
the loan provided by the Authority, the
utility must base customer charges mitigated
pursuant to this act on the then-current
monthly billing of the customer and shall
lineitem such charges on the monthly bill of
the unregulated utility customer. The
Authority is also directed by the measure to
notify in writing the Governor, the President
Pro Tempore of the Senate, and the Speaker
of the House of Representatives when an
application for a loan is approved or
disapproved and on the date the loan is
issued and prepare an annual report. The
utility revenue bonds or any other
obligations issued shall not at any time be
deemed to constitute a debt of the state or of
any political subdivision thereof or a pledge
of the full faith and credit of the state or any
political subdivision. The measure provides
that the jurisdiction of the Corporation
Commission shall not extend beyond the
audit required for the application process in
this measure. It also authorizes the Authority
to file an application with the Oklahoma
Supreme Court for the approval of bonds
issued and confreres exclusive jurisdiction
upon the Court to hear and determine each
application. The measure also provides that
any bonds issued under this act shall be
reviewed by the Council of Bond Oversight
and also amends the duties of the Authority
to include actions required by this act.
SB 1050 (Thompson/Wallace) creates the
February 2021 Regulated Utility Consumer
Protection Act. The measure shall provide
financial assistance in the form of
securitization and issuance of rate-payer
backed bonds provided to regulated utility
entities for the purpose of reducing costs to
customers related to the extreme weather
event that occurred in February 2021. The
32
Oklahoma Corporation Commission is
authorized by the measure to mitigate costs
relating to the weather event for customers
by using securitization. The Commission
shall consider revenue requirement savings
that may be incurred to the benefit of
customers by relying on lower carrying
charges, customer utility bill impact that
may be mitigated by mandating a longer
amortization period for recovery, and
whether issuance of ratepayer-backed bonds
that may be completed at a sufficiently low
cost such that customer savings are not
exhausted or offset. The Commission is
authorized to utilize financial advisors to
evaluate applications. Expenses incurred for
those purposes shall be recoverable as
administrative expenses of the Oklahoma
Development Finance Authority through the
issuance of ratepayer-backed bonds. The
Commission shall issue a financing order
that determines the rate of maturity for the
bonds, the quantified amount of extreme
purchase costs and extraordinary costs to be
recovered, the frequency of true-up and
reconciliation of the customer repayment
revenues collected, the method by which the
customer repayment charges will be
allocated among the various customer
classes, and the requirement that all funds
received under the irrevocable and
nonbypassable mechanism be provided
immediately to the holder of securitization
property. The bond’s maturity shall not
exceed 30 years. The Commission shall
issue an order no later than 180 days from
the date the Commission receives all
necessary information and documentation.
On the same date a financing order is issued,
a copy of the order shall be delivered to the
Governor, the President Pro Tempore of the
Senate, the Speaker of the House of
Representatives, and the Oklahoma
Development Finance Authority. Regulated
utilities are prohibited from recovering the
extreme purchase costs and extraordinary
costs identified and quantified in the
financing order from customers except
through the transfer of securitization
property and prohibits such utilities from
removing the periodic determination of
factors for customer collection with true-up
and reconciliation. The rights and interests
to receive revenues collected by a regulated
utility through the irrevocable and
nonbypassable mechanism created pursuant
to a financing order shall become a
securitization property right at the time the
ratepayer-backed bond is issued pursuant to
a financing order. The rights of the
securitization property owner are not subject
to setoff, counterclaim, surcharge or defense
by the regulated utility or any other person,
creditor or otherwise, in any bankruptcy or
debt collection proceeding of the regulated
utility. The measure authorizes the creation
of a valid and enforceable lien and security
interest in securitization property via an
agreement with the Oklahoma Development
Finance Authority. The measure authorizes
the Authority to borrow money on the credit
of the revenues to be derived from
securitization property received. The
measure specifies that such ratepayer-
backed bonds shall not be an indebtedness
of the state or of the Authority. Additionally,
the State Treasurer is authorized by the
measure to purchase from the Authority at
private sale all or any part of the bonds
issued in this manner. The measure provides
that the Commission may require an audit of
all amounts received from customers under
an irrevocable and nonbypassable
mechanism and paid to a utility, the amounts
paid by the utility to the Oklahoma
Development Finance Authority, or other
holder of securitization property. Such
audits shall be provided to the Governor, the
President Pro Tempore of the Senate, the
Speaker of the House of Representatives,
and the Authority. The measure provides
that the Authority shall file an application
33
with the Oklahoma Supreme Court for the
approval of bonds issued and confers
exclusive jurisdiction upon the Court to hear
and determine each application. The Court
shall give such an application precedence
over the other business of the Court and
consider and pass upon the application and
any protests which may be filed against such
application as speedily as possible. Notice of
the hearing must be published in a
newspaper of general circulation in the state
at least 10 days prior to the hearing. The
decision of the Court shall be a judicial
determination of the validity of the bonds,
shall be conclusive as to the Authority, this
state, its officers, agents and
instrumentalities and all other persons, and
thereafter the bonds so approved and the
revenues pledged to their payment shall be
incontestable in any court in this state.
HB 1093 (Kerbs/Murdock) directs the
Oklahoma Water Resources Board to update
its water quality standards to allow for
development of watershed trading programs
by November 1, 2026.
HB 1705 (Newton/Murdock) eliminates the
requirement that persons generating or
shipping hazardous waste must create a
disposal plan and submit it to the
Department of Environmental Quality
(DEQ) for approval. The also measure
eliminates the fee for the generator disposal
plan and modifies the fees for monitoring
and small quantity generators.
HB 1815 (McBride/David) directs the
Oklahoma Corporation Commission to issue
a report and recommendations regarding
availability and appropriateness of natural
gas utilities to procure, transport, and deliver
renewable natural gas to consumers no later
than December 1, 2021. Renewable natural
gas is defined to include biogas-derived
methane gas, hydrogen gas or carbon oxide
from renewable sources, or methane gas
derived from any combination of hydrogen
gas or carbon oxide from renewable sources.
The report shall also address production of
educational materials regarding renewable
natural gas, and discuss future reporting
requirements for producers.
HB 2028 (O’Donnell/Allen) prohibits
excavators from commencing excavation or
demolition if they have knowledge that an
operator has unmarked underground
facilities. Work may begin after notice has
been given and such facilities have been
marked. Excavators are required to maintain
and preserve all marks for the duration of
the excavation or demolition. They are also
required to notify the notification center if
marks are no longer visible or removed and
check for positive response at the
notification center prior to excavation or
demolition. The measure provides time
limits for certain notice and potential
liability for excavators in certain
circumstances. During any state of
emergency, time limitations are
inapplicable. Operators are required to
provide a positive response to the
notification center prior to the expiration of
the required notice period. The measure
provides requirements for the response. The
measure requires all operators to be
members in good standing of the notification
center and requires certain documentation to
be maintained by the notification center.
HB 2029 (O’Donnell/Taylor) clarifies a
requirement that a division order include the
name, address, and tax ID number of each
interest owner.
HB 2049 (McCall/Simpson) modifies the
cost at which a conservancy district contract
requires an advertisement for bids in a
newspaper. The measure requires district

34
contracts valued more than $100,000,00 to
be advertised.
HB 2330 (Steagall/Rosino) allows drilling
of municipal water wells inside and outside
of the municipal limits.
HB 2402 (Russ/Jech) authorizes counties,
public trusts, and other political subdivisions
operating a public water supply system or
wastewater treatment system to utilize
design-build as a project delivery method for
those water systems. The measure requires
the Department of Environmental Quality to
incorporate a flexible permitting process to
allow this design-build authorization into its
rules and to authorize up to 5 pilot projects
in the interim before those rules are adopted.
Conservation Commission Funding
SB 535 (Bergstrom/Lepak) increases the
maximum civil liability for violating
pipeline safety rules promulgated by the
Corporation Commission from $100,000.00
to $200,000.00 and from $1 million to $2
million for any related series of violations.
SB 536 (Bergstrom/Lepak) 6 increases the
maximum civil liability for violating the
Hazardous Liquid Transportation System
Safety Act from $100,000.00 to $200,000.00
and from $1 million to $2 million for any
related series of violations.
SB 1059 (Thompson/Wallace) extends the
sunset date for the Corporation Commission
Plugging Fund and its associated fees from
July 1, 2021, to July 1, 2026.
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Conservation
Commission
$16,865,856
$16,876,719
0.06%
Corporation Commission Funding
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Oklahoma
Corporation
Commission
$11,871,018
$13,192,324
11.13%
Election Measures
SB 347 (Paxton/Martinez) prohibits
municipalities and political subdivisions
from holding an election on the second
Tuesday of December 2021 or the second
Tuesday of January 2022 for the offices of
United States Representative, State Senator,
State Representative and County
Commission districts following the
reapportionment of such districts in order for
the State Election Board to properly
implement new precincts associated with
new district boundaries. Additionally, the
measure adds the second Tuesday of June of
an odd-numbered year for a special election
to fill a vacancy to the list of exceptions to
the rule that no regular or special election to
fill an elective office shall be held by any
$0
$5,000,000
$10,000,000
$15,000,000
$20,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Conservation Commission
$0
$5,000,000
$10,000,000
$15,000,000
$20,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Oklahoma Corporation
Commission
35
county, school district, technology center
school district, municipality, fire protection
district or other political subdivision
authorized to call elections.
SB 710 (Jech/Newton) authorizes the
Secretary of the State Election Board to join
the State of Oklahoma as a member in 1 or
more multistate voter list maintenance
organizations and to provide voter
registration data to such organizations upon
joining. The measure provides for the
Secretary to expend such funds as needed
for membership dues. Additionally, if such
organizations identify eligible, but not
registered, citizens or citizens who changed
their address, the Secretary may notify such
citizens about the procedure for becoming a
registered voter or changing the registered
address.
SB 712 (Jech/Dick Lowe) provides for the
Secretary of the State Election Board to
authorize the use of electronic precinct
registries by county election boards. The
Secretary may also purchase any equipment
and software necessary to implement an
electronic precinct registry system, subject
to available funding.
SB 947 (Rosino/Tammy West) requires the
parties responsible for circulating an
initiative petition to indicate whether the
proposal will have a fiscal impact on the
state and if so, the potential source of
funding.
SB 959 (Paxton/Hilbert) modifies
procedures relating to filling a vacancy or
irrevocable resignation in the United States
Senate. The measure provides that an
irrevocable resignation shall occur when a
member of the United States Senate from
Oklahoma provides a written letter of
resignation to the Secretary of State. The
measure requires a special election to be
held for the seat at the next regularly
scheduled statewide Primary, Runoff
Primary, and General Election. If the
vacancy occurs in an even-numbered year
on or before March 1, the special election, if
necessary, shall be held that same year. If
the vacancy is already scheduled to be filled
for a full term at the next available regularly
scheduled election, then no special election
shall be called. The Governor is directed to
appoint a person eligible to hold such office,
who has been a registered voter of the party
of the predecessor in Oklahoma for at least 5
years within 30 days of the vacancy
occurring. The potential appointee shall
submit an oath to the Secretary of State an
oath affirming that the person will not file as
a candidate for the office when it next
appears on the ballot. The Secretary of State
is directed by the measure to publish that
oath.
SB 1066 (Treat/McCall) creates the State
Senate Redistricting Act of 2021. The
measure states that the legislature
determined the United States Census Bureau
failed to meet the deadline to transmit the
tabulations of population of the state, which
necessitates the use of the best alternative
population data. The measure also finds that
the best available population data is United
States Census Bureau’s American
Community Survey for 2015-2019. The
outlined Senate districts shall become
operative on the 15th day following the
General Election in November 2022. The
State Election Board shall conduct the
elections for the Senate in 2022 in
accordance with the provisions of the State
Senate Redistricting Act of 2021. The
measure repeals the provisions of the State
Senate Redistricting Act of 2011. The
measure provides that Senators elected from
even-numbered districts in 2022 shall hold
office until the 15th day succeeding the
General Election in November 2026.
36
Senators elected from odd-numbered
districts in 2020 shall hold office until the
15th day succeeding the General Election in
November 2024. Each Senate district is
based on the following geography as defined
by the U.S. Census Bureau: counties, tracts,
blockgroups, and blocks. The measure
provides that if the State Senate
Redistricting Act of 2021 and the State
House of Representatives Redistricting Act
of 2021 require any county election board to
create precincts with no residents, the
President Pro Tempore of the Senate and
Speaker of the House shall adjust Senate or
House district lines to prevent the creation
of zero population precincts. In no case shall
such an adjustment affect the total
population of a Senate or House district.
HB 1198 (McCall/Treat) creates the State
House of Representatives Redistricting Act
of 2021. The measure designates the Census
Bureau’s American Community Survey
(ACS) Five-Year Estimates for 2015-2019
as the best alternative population data
available for legislative redistricting and
directs the Legislature to use ACS data to
draft redistricting legislation. The new
district boundaries will take effect on the
15th days following the General Election in
November 2022. The State Election Board
will conduct elections for state House
districts in 2022 in accordance with the act
under the new district lines.
HB 1752 (CrosswhiteHader/Rader) sets a
deadline of 30 days from the date the list is
received for the secretary of a county
election board to remove the names of the
deceased from the voter registration
database. A funeral director will be required
to fill out a form from the Secretary of the
State Election Board to notify the secretary
of the county election board of a county
resident’s death. The measure also provides
that an order appointing a guardian shall set
forth findings of fact as to whether the ward
retains sufficient capacity to vote.
HB 1963 (Nollan/Stanley) provides that the
Governor shall appoint the members of a
school board of education of a school
district or technology center school district
that fails to reach a majority due to
vacancies. The Governor shall only appoint
enough members for the school board to
reach a quorum. The appointment or
appointments will be consistent with
existing requirements and only for the
remainder of the term of office.
HB 2087 (McCall/Rader) provides that
officeholder expenses may be expended for
contributions or dues for a political caucus
fund or the costs associated with signage for
naming highways and bridges.
HB 2193 (Stinson/Bergstrom) clarifies that
municipal office as it relates to the
Municipal Campaign Finance and Financial
Disclosure Act shall mean any elective
office established under state or municipal
law.
HB 2564 (Chad Caldwell/Quinn) provides
that a candidate for political office
petitioning for a recount of the vote may
request the vote be counted manually or
electronically. If the candidate or individual
requests that the ballots be recounted by
electronic device, the petition must be
accompanied by a cashier’s check or
certified check in the amount of $600.00 for
the first 3,000 ballots and $300.00 for each
5,000 ballots thereafter. The measure also
provides that the Governor or Attorney
General may request a recount of any state
question. The request shall be in the form of
a petition prescribed by the Secretary of the
State Election Board. The measure also
directs the Secretary of the State Election
Board to order an automatic recount of the
37
state question’s vote if the margin of votes
required for approval is less than 0.5% or
less of the total number of votes cast for and
against a state question involving a statutory
issue or question. The recount shall also be
order if the margin of votes required for
approval is 1% or less of the total number of
votes cast for and against a state question
involving a constitutional issue or question.
The recount will not occur if there is less
than $250,000.00 in the State Question
Recount Revolving Fund. The Fund shall
never exceed $500,000.00.
HB 2663 (Echols/David) modifies the
deadline for absentee ballot requests. The
measure extends the period from the
Tuesday preceding an election to the third
Monday preceding an election. Such
requests must be submitted to the
appropriate election official. Additionally,
the measure modifies the period a person
may request an in-person absentee ballot for
county elections as well as General,
Primary, Runoff Primary Election, or
Presidential Preferential Primary Elections.
For county elections, the deadline for such
requests remains 8 a.m. to 6 p.m. on the
Thursday and Friday immediately preceding
the county election. For Primary, Runoff
Primary Election, or Presidential
Preferential Primary Elections, the measure
provides that ballot requests may be made
on the Saturday preceding the election from
8 a.m. to 2 p.m. General Election absentee
ballots may be requested starting on the
Wednesday immediately preceding the
election from 8 a.m. To 6 p.m.
HB 2939 (Newton/Murdock) directs the
secretary of the county election board to
record a voter’s method of voting. The
voter’s method shall not be disclosed to the
public except for during a regularly
scheduled federal or state election or a
statewide special election for a state
question.
County and Municipal Government
SB 143 (Rader/Boatman) authorizes county
employee recognition awards to be
presented at a formal or informal ceremony,
banquet, reception, or luncheon. Monies
may be expended from the county
department’s or division’s operating fund to
pay for the ceremony, banquet, reception, or
luncheon.
SB 277 (Montgomery/Pae) authorizes
municipalities to requires the owner of a
dilapidated property to provide his or her
contact information and provides for such
information to be kept confidential.
SB 280 (Quinn/Humphrey) authorizes any
county with an excise board to establish a
rainy-day fund and capital reserve fund.
Deposits may be made into the rainy-day
fund by resolution of the county. The fund
may contain 50% of the previous year’s
approved budget. Once deposited in the
fund, the monies are not transferrable. The
measure provides for half of the fund to be
utilized for naturalized disasters, 1/8 of the
fund to be used for supplementing the
budget, and 1/8 of the fund to be used to
supplement the current year’s revenue when
collections come in shorter than estimated
and a revenue failure is declared by the
board of county commissioners. Deposits
into the capital reserve fund are also
nontransferable but may be expended in a
manner determined by the board of authority
on county facilities.
SB 483 (Hall/Burns) requires members of
the county board of equalization to attend
and complete a course of instruction
consisting of at least 6 hours for purposes of
instructing the members about the duties
imposed on the board by law. Additionally,
38
the measure reduces the time members are
afforded to complete the course from 18
months to 12 months. The measure also
establishes an annual 3 hour continuing
education requirement for members. The
Program Director of the Center for Local
Government Technology at Oklahoma State
University is directed to send written
notification of failure to comply with the
educational requirements to the State
Auditor. The State Auditor shall inform the
noncompliant member of their failure to
comply within 30 days of receiving notice.
Members who do not comply with the
provisions of this measure shall not receive
travel reimbursements. Any member that
misses 3 or more meetings shall forfeit their
office. The measure also increases the
maximum compensation a board member
may receive from $50.00 to $100.00.
SB 728 (Paxton/Martinez) provides that the
counties shall be reapportioned by their
respective county board of commissioners
on or before November 30, 2021, following
the final official publication of the Federal
Decennial Census.
SB 736 (Kidd/McEntire) provides for health
districts to also be comprised of multiple
county health departments operating under
agreement to share resources. The measure
also provides for the county board of
commissioner to be able to contract with a
neighboring board of health or board of
county commissioners of any county to
provide the county any or all public health
services. Counties may combine county
millage and designate 1 county as the
operational hub.
SB 828 (Murdock/Newton) provides that
any employee employed to perform duties
that are not in assistance to a county officer
in the performance of the official duties of
the county officer, including, but not limited
to, specialized or technical duties, may
receive a salary in excess of a county
officer. The measure also authorizes a
county to utilize the appropriate State of
Oklahoma pay structure in lieu of the salary
code specified in statute.
SB 838 (Weaver/Nollan) creates the
Oklahoma Public Safety Protection District
Act. The measure authorizes the governing
body of a municipality to create a public
safety protection district by the adoption of a
resolution and placing the question to voters
of the municipality in the next general
election. If a 60% of voters approve the
creation of the district, the municipality shall
exercise oversight and management of the
district. The district will be considered a
political subdivision of the state and will
encompass the borders of the municipality.
An assessment of up to 5 mills may be
levied by the district for the purposes of
paying for police, fire, and jail operations.
The assessment shall not apply to real
property zoned for agricultural or industrial
land use, implements of husbandry,
livestock employed in support of the family,
and personal property owned by for-profit
business entities.
SB 939 (Taylor/Pfeiffer) provides that any
critical infrastructure company or entity that
acts in compliance with or acts consistently
with government rules, guidelines, or laws
applicable to its sector shall not constitute a
nuisance.
SB 958 (Coleman/Burns) provides the board
of directors for each fire protection district
with the power to acquire a certification to
operate an emergency medical services
agency from the Oklahoma State
Department of Health or contract for
services with a certified or licensed
emergency medical service agency. The
district’s emergency medical service agency
39
may respond outside of the district
boundaries if the political subdivisions
having jurisdiction over the area provided
the Department proper documentation of
their support.
HB 1036 (Strom/Daniels) authorizes the
board of county commissioner to purchase
or sell materials, tools, and equipment with
a political subdivision which is not subject
to the Oklahoma Central Purchasing Act at a
price agreed upon by both governing
bodies.
HB 1063 (Boles/Kidd) 3 authorizes the
board of county commissioners to employ
information technology (IT) staff and strikes
language requiring that the data processing
technician’s term may not extend beyond the
term of office of the board appointing them.
HB 1064 (Boles/Kidd) applies a single
method of calculating base salary for county
officers to all counties, and strikes other
methods. The definition of serviceability is
modified to include gross assessed valuation
of all tangible taxable property, rather than
net valuation. The upper limit of the county
officer base salary is increased from
$44,500.00 to $49,500.00. Calculation of
additions to base salary are modified to be
based upon gross assessed valuation rather
than net valuation.
HB 1749 (CrosswhiteHader/Paxton)
authorizes the county treasurer to not bid off
the property in the name of the county and
instead allow the property to remain under
its current ownership. The treasurer is
directed to consider certain factors outlined
in the measure when determining property to
be nuisance property. Determination of a
property as common area nuisance property
could be made at any time. The measure
also provides that all common area nuisance
property bid off in the name of the city or
town shall be for the amount of any
municipal liens due.
HB 1789 (Pae/Howard) authorizes s local
governmental units to create or contract with
a purchasing cooperative to achieve best
value or best terms in contracts. The
measure allows any purchasing cooperative
or interlocal cooperative to utilize a single
legal newspaper of the state to meet its bid
notice requirements of competitive bidding
or bid solicitation. If the project is exclusive
to a county or group of counties, the bid
notice must be published in a legal
newspaper within that county or those
counties.
HB 2225 (Moore/Weaver) authorizes
designees of the chief of police to dispose of
personal property or money seized by the
chief. In the event the property or money
was seized by the police department in
connection with a criminal investigation or
arrest, this determination shall be made by
the court which has jurisdiction over the
criminal offense. If the property has an
actual or apparent value over $250, written
notice must be given to the person last in
possession of the property 3 days prior to the
hearing. A description of the property shall
be included in the notice. If authorized by
ordinance, the municipality may transfer any
currency received into a depository account
for the benefit of its known or unknown
owners prior to any court order for
disposition of the money or legal tender. No
forfeiture proceeding shall be necessary to
authorize the destruction of property that
cannot be returned lawfully to its owner.
The measure also allows a municipality to
provide written notice at the time of arrest
that certain property would be available for
return within 90 days, if it was not seized as
evidence. If the property is worth less than
$250, no further notice is required prior to
obtaining a court order for disposition of the
40
property. If an affidavit of ownership or
affidavit of right of possession is used to
establish ownership or right of possession,
the claimant may also be required to sign an
agreement to indemnify and defend the
custodians of the property in the event of an
adverse claim to the property.
HB 2506 (Kannady/Allen) modifies the
definition of dilapidated building as it relates
to condemnation procedures. The time a
building must have been boarded and
secured in order to be considered dilapidated
is reduced from 18 months to 6 months.
HB 2747 (Ford/Haste) requires municipal
employers to recognize a bargaining agent
selected by a majority of the firefighters of
the fire department or police officers of the
police department of that municipality as the
exclusive bargaining agent for the
firefighters or police officers of that
municipality until a majority of the
firefighters or police officers withdraw the
recognition. Such agents must be recognized
by a majority of the firefighters or police
officers of that department. Any vote or
ballot authorized by the agreed procedures
shall be accompanied by a copy of the
voter's driver license or other state
authorized identification card. If no parties
can agree on election procedures, either
party may request the American Arbitration
Association to conduct the election and
certify the results. Elections for bargaining
agents may only be held once per 12- month
period.
HB 2778 (Pfeiffer/Coleman) authorizes a
district attorney to destroy records and files
pertaining to felony, misdemeanor, traffic,
wildlife, or juvenile cases if they have been
digitized.
Public Finance
SB 75 (Simpson/Townley) exempts the
Social Security Disability Determination
Services Division of the Department of
Rehabilitation Services from the
requirement to obtain an information
security risk assessment identifying
vulnerabilities associated with the
information system.
SB 88 (Howard/Worthen) modifies voting
requirements for public trusts to waive
public bidding requirements. The measure
authorizes public trusts with fewer than 4
trustees to waive bidding requirements with
2/3’s of the vote instead of 3/4’s of the vote.
Additionally, the measure exempts public
trusts from auditing requirements provided
the trust does not possess any debt
obligations and has assets totaling less than
$50,000.00.
SB 91 (Hall/Boles) modifies the maximum
length of performance-based efficiency
contracts by specifying that the term shall be
the greater of 20 years or the useful life of
the project. Additionally, the measure
provides that a public entity may consider
capital cost avoidance and include additional
revenue that is directly attributed to the
performance-based efficiency contract when
calculating cost-savings.
SB 147 (Thompson/Wallace) directs the
Commissioners of the Land Office when
calculating the 5% cap on investments in
real property to not include the value of real
property under long-term lease to the state,
agencies of the state, or subdivisions thereof.
SB 281 (Quinn/O’Donnell) requires county
investments into bonds issued by the United
States to only be invested in bonds with a
rating of A+ or better by Standard and
Poor’s Corporation or A1 or better by
Moody’s Investor Service or an equivalent
investment grade by a securities ratings
41
organization accepted by the National
Association of Insurance Commissioners
including investment grade obligations of
state agencies.
SB 345 (Garvin/McEntire) clarifies that
awards made pursuant to the provisions of
the Oklahoma Dental Loan Repayment
Program shall be deposited into an
appropriate loan agency.
SB 382 (Standridge/Conley) exempts the
J.D. McCarty Center from the certain
provisions of the Oklahoma Central
Purchasing Act.
SB 606 (Rader/Pfeiffer) strikes the
designation for the Oklahoma Local
Development and Enterprise Zone Incentive
Leverage Act Incentive Payment Fund and
changes it from a special fund to an
Oklahoma Tax Commission special account.
The measure also removes language limiting
the liability of the state to the balance
contained in the fund.
SB 789 (Leewright/Wallace) authorizes the
Oklahoma Employment Security
Commission to claim 25% of the federal
relief funds made available to the state,
decease the surcharge to be charged to each
employer to a percentage rate that is
sufficient to bring the balance of the fund to
$25 million, borrow federal funds, and allow
the balance of the fund to drop to $10
million if needed during a state of
emergency declared by the Governor, the
Oklahoma Legislature, the United States
President, or the United States Congress.
SB 840 (Kidd/Boles) increases the cap for
county agents making purchases or lease
agreements without following bidding
procedures from $15,000.00 to $25,000.00.
The measure also provides for county
purchasing agents to purchase goods and
services from the next lowest bidder or the
best quote if the lowest bidder refuses to
provide such goods and services provided
the purchase amount is below $25,000.00.
SB 853 (J.J. Dossett/Burns) exempts the
Oklahoma Military Department from the
provisions of the Oklahoma Central
Purchasing Act as it applies to purchasing
heraldry items.
SB 867 (Pugh/Tommy Hardin) authorize the
Military Department to purchase products
which are available through a General
Services Administration contract. The
products do no need to be on a current state
contract before a purchase can be made.
SB 868 (Pugh/Tommy Hardin) provides for
federal programs administered by the
Military Department with a Certified
Procurement Officer making purchases on
behalf of the program to be regarded as an
individual purchasing entity.
SB 1051 (Thompson/Wallace) repeals the
authority for the Department of Mental
Health and Substance Abuse Services to
issue notes and bonds in an amount not to
exceed $6 million.
HB 1061 (Boles/Paxton) directs funds to the
Crime Victims Compensation Fund that
would otherwise be deposited to the credit
of the General Revenue Fund; for this
reason the measure will have a negative
revenue impact on the General Revenue
Fund.
HB 1376 (McCall/Pugh) subjects the
Oklahoma Aeronautics Commission to the
provisions of the Public Competitive
Bidding Act of 1974 as it relates to contracts
for airport and air navigation facility
construction and repair. The Department of
Transportation may administer the process.
42
HB 1990 (Trey Caldwell/Montgomery)
provides that monies from the Ad Valorem
Fund may be used to reimburse counties for
homestead exemptions granted to 100
percent disabled veterans and surviving
spouses if the number of exemptions granted
to veterans and surviving spouses for the
most recently concluded calendar year 0.8%
of the total county population according to
the latest Federal Decennial Census or most
recent annual population estimate. The
reimbursement provided in this paragraph
shall amount to 25% of the loss of revenue
claimed by the qualified county.
HB 2331 (Steagall/Newhouse) exempts the
Oklahoma Military Department from the
requirement to obtain an information
security risk assessment by the Information
Services Division of the Office of
Management and Enterprise Services.
HB 2365 (Burns/Coleman) creates the
Oklahoma Supplier Diversity Initiative. The
program shall provide convenience for
qualified and certified small business
enterprises and minority business enterprises
in contracting projects in underserved areas.
Qualified businesses, as defined in the
measure, shall register with the Office of
Management and Enterprise Services
(OMES). OMES is directed by the measure
to allow registered vendors to be
automatically notified of opportunities to do
business with the state for specific
commodities. The measure directs the State
Purchasing Director to submit an annual
report to the President Pro Tempore of the
Senate, Speaker of the House, and Governor
on or before September 1. The report shall
detail the status of the percentile of state
funds expended on contracts awarded to a
certified Oklahoma Department of
Transportation Disadvantaged Business
Enterprise and all of the entities certified by
the United States Small Business
Administration in the preceding fiscal year.
HB 2861 (Wallace/Rosino) provides that
only persons having a direct contractual
relationship with the party furnishing the
payment bond would have a right of action
upon a bond as it relates to at-risk
construction management contracts.
HB 2862 (Wallace/Pemberton) raises the
thresholds for completive bidding
requirements. For public construction
contracts, the amount is raised from
$50,000.00 to $100,000.00. The limit that
may be negotiated with a qualified
contractor is raised from $5,000.00 to
$10,000.00. The limit on contracts for right-
of-way clearance to not be considered
construction contracts and required to be
open for bidding is raised from $50,000.00
to $100,000.00. The limit on contracts for
projects of the Oklahoma Department of
Wildlife conservation relating to fish and
wildlife conservation is raised from
$25,000.00 to $50,000.00. The limit on
contracts under an emergency authority
declared by the governing body of a public
agency is raised from $75,000.00 to
$150,000.00.
State Government
SB 28 (Bergstrom/Josh West) broadens the
classification of “political subdivision”
within the Governmental Tort Claims Act to
include substate planning districts and
regional councils of government.
SB 62 (Montgomery/Luttrell) extends the
sunset date for the Oklahoma Strategic
Military Planning Commission from
December 31, 2020, to December 31, 2025.
SB 63 (Montgomery/Frix) removes the
requirement for a state employee who
departed an agency under a separation
43
agreement to repay the state agency if he or
she is employed within 1 year of the
execution of the separation agreement.
SB 76 (Simpson/Tommy Hardin) strikes the
requirement for the Military Department to
annually report to the President Pro
Tempore of the Senate, the Speaker of the
House, and the Secretary of Finance the
amount of savings realized from its authority
to purchase motor vehicles.
SB 118 (Hall/Osburn) authorizes the
Oklahoma Municipal Power Authority to
hold executive sessions closed to the public
when discussing security plans and
procedures including, but not limited to,
cybersecurity matters. Records pertaining to
security plans and cybersecurity may be kept
confidential.
SB 123 (Hall/Osburn) exempts the
Oklahoma Municipal Power Authority from
the provisions of the Information
Technology Consolidation and Coordination
Act.
SB 148 (Rader/Dills) increases the number
of members on the Oklahoma Uniform
Building Code Commission within the
Construction Industries Board from 11 to
13. The additional members must be a
licensed electrical engineer from a state-
recognized professional engineering firm
and a licensed mechanical engineer from a
state-recognized professional engineering
firm respectively. The measure requires
these members to be appointed within 90
days of the effective date.
SB 282 (Simpson/Tommy Hardin) provides
for annual leave cap placed on state
employees to temporarily increase and
carryover to the new fiscal year following an
emergency declaration.
SB 364 (David/Josh West) moves the
domicile of the district for the Grand River
Dam Authority from Craig County to Mayes
County.
SB 428 (Thompson/Hilbert) requires the
Director of the Office of Management and
Enterprise Services initiate a request for
proposal for the rationalization and
determination of which state applications
and databases can be immediately
transferred to a cloud-based data storage
platform.
SB 487 (Pugh/Nollan) modifies the
membership of the Oklahoma Science and
Technology Research and Development
Board. The measure provides for the
President Pro Tempore of the Senate,
Speaker of the House, and Governor to
appoint members to the Board for a term of
4 years. The Secretary of Science and
Innovation shall serve as Chair.
SB 492 (Taylor/Newton) authorizes the
Corporation Commission and its members to
utilize an electronic signature to satisfy
requirements in law requiring the signature
of a member, the Chair, or the Vice-Chair.
Additionally, the Corporation Commission
is authorized to utilize an electronic image
of the Commission’s seal.
SB 585 (Dahm/Sean Roberts) specifies that
constitutional neglect of duty shall include
giving false testimony to a committee of
either house of the Legislature, engaging in
operations beyond the constitutional or
statutory authority delegated to the agency
that the officer is employed by or serves, or
repeatedly refusing to provide information
to a committee or member in a timely
manner.
SB 758 (Pugh/Osburn) authorizes the Real
Estate Appraiser Board to employ a Director
44
to oversee the organization and activities of
the Board. Additionally, the measure
removes the Board’s authority to develop
guidelines relating to appraiser examinations
and the requirement to study the number of
appraisers licensed in the state. The measure
also provides for employees of the Board to
considered unclassified employees of the
Oklahoma Insurance Department. The
Director may employ temporary employees.
The Insurance Department is also required
to provide administrative support for the
Board.
SB 802 (Leewright/Phillips) modifies the
membership of the Rural Broadband
Expansion Council. The measure clarifies
that a current or past mayor may serve on
the Council and increases the maximum
population of the municipality a mayor
serves to remain eligible to serve on the
Council from 25,000 to 35,000. The
measure also increases the membership of
the Council by 2, adding a resident of this
state who is a Wireless Internet Service
Provider as well as a Tribal Leader of a tribe
recognized in this state.
SB 870 (Rader/Pfeiffer) removes the
requirement for the Oklahoma Tax
Commission (OTC) to prepare its audit
according to the standards established by the
Governmental Accounting Standards Board
and to submit the results of its audit to the
State Auditor and Inspector. The measure
also modifies the OTC’s audit by providing
for such audit to be an annual, operational
audit instead of a continuous audit.
Language requiring the OTC to furnish
necessary office space for employee of the
State Auditor is stricken by the measure.
SB 910 (Murdock/Newton) requires the
auction for the sale of land owned by the
Commissioners of the Land Office to be
held in the county in which the land is
situated.
SB 913 (Daniels/O’Donnell) provides for
the Legislature to repeal an agency rule by
joint resolution and removes the Governor’s
authority to repeal agency rules by
declaration. Agencies exempted from the
procedures of the Administrative Procedures
Act or pursuing a preemptive rule are
directed by the measure to publish exempt
rules on any website associated with the
agency. Every agency is also directed to
publish agency rules on the website
associated with the agency. Additionally, the
measure requires agencies to respond to
small businesses requesting a review of their
rules no later than 90 business days and to
the Legislature or Governor within 30 days
instead of the 90 days currently provided for
in law. The measure also directs the
President Pro Tempore of the Senate and
Speaker of the House to establish a Joint
Committee on Administrative Rules.
Membership shall be comprised of current
members. The chairs of the Joint Committee
shall be appointed by both the President and
Speaker. The Joint Committee shall consider
proposed rules, amending rules, and repeal
requests submitted by an agency. Those
rules approved by the Committee shall be
presented to the Legislature for final
approval for repeal. All Committee actions
on items for consideration require a majority
vote of both the Senate members and the
House members of the Committee.
Emergency rules must be sent to the chairs
of the Joint Committee in addition to the
other recipients outlined in current law. The
measure requires agencies providing notice
of a new rule to provide 1 electronic copy to
of the complete text of the proposed rule,
amendment, or revocation and a copy of the
notice to the Governor and to the
appropriate cabinet secretary. The Governor
or relevant cabinet secretary may disapprove
45
the rule within 30 days. If the Governor or
the cabinet secretary disapproves a rule, the
affected agency shall be notified in writing
of the reasons for disapproval. Agencies
may proceed with the rulemaking process if
the Governor or secretary does not expressly
disapprove the rule within 30 days of
receiving notice. The measure also creates a
new section of law in the Act by providing
for the expedited repeal of rules beginning
September 1, 2021. An agency may submit a
request for expedited repeal to the President
Pro Tempore of the Senate and the Speaker
of the House, whereupon they will assign
the request to the Joint Committee to
conduct the repeal process. Such a request
shall be accompanied by a statement of the
purpose for the repeal. Upon completion of
the comment period, the Joint Committee
may schedule a hearing on the agency repeal
request. If the Committee approves the
repeal, it shall be presented to the
Legislature for final approval.
SB 961 (Daniels/Lepak) prohibits any state
agency or official from imposing any filing
or reporting requirement on an organization
regulated or specifically exempted from
regulation under the Oklahoma Solicitation
of Charitable Contributions Act more
stringently that is otherwise required by
federal and state law. The provisions of this
measure shall only apply to private
foundations or charitable trusts, excluding
nonprofit hospitals.
SB 1015 (Daniels/Rick West) provides that
records received from risk pool participants
that can otherwise be obtained from risk
pool participants shall be considered
confidential.
SB 1031 (Treat/Echols) extends the sunset
date as it relates to authorizing public bodies
to meet via teleconference or
videoconference as modified for the
emergency conditions from November
15,2020, to February 15, 2022 or until 30
days after the Governor ends the declared
state of emergency relating to the threat of
COVID-19. The measure also requires
public bodies giving notice of meetings to
be conducted via videoconference to not
modify the method of meeting described in
the notice prior to the meeting and to include
the code or password to access the meeting
in the public notice when applicable.
SB 1064 (Daniels/Kannady) is the annual
Duplicates Section bill that conforms
multiple versions of statutes.
HB 1140 (Fetgatter/Taylor) transfers the
Oklahoma Chief International Protocol
Office from the Office of the Secretary of
State to the Department of Commerce.
HB 1146 (Osburn/Treat) places all state
employee positions under the administration
of the Human Capital Management Division
of the Office of Management and Enterprise
Services beginning January 1, 2022. Persons
employed by the Governor, Lt. Governor,
Speaker of the House, or President Pro
Tempore of the Senate, as well as elected
officials, political appointees, and up to 5%
of an agency’s executive management shall
not be placed under the Division’s
administration. The measure directs the
Division to establish and maintain a dispute
resolution system for state agencies and
employees, to promulgate rules necessary to
perform duties required by the measure,
receive and act on complaints arising from
disciplinary actions by state employees, use
administrative law judges as independent
contractors, submit quarterly reports on
workload statistics to the Legislature, and
create and administer a confidential
whistleblower program. The measure
sunsets the Oklahoma Merit Protection
Commission on December 31, 2022.
46
HB 1236 (McCall/Treat) expands the duties
of the Attorney General to include
monitoring and evaluating any action by the
federal government including executive
orders by the President of the United States,
rules or regulations promulgated by an
agency of the federal government or acts of
Congress. The Attorney General is directed
to determine whether any such action
violates the Tenth Amendment to the
Constitution of the United States. The
measure creates the State Reserved Powers
Protection Unit within the Office of the
Attorney General to carry out these duties. If
the Attorney General determines the action
constitutes a violation of the Tenth
Amendment, the Attorney General shall
determine whether the state should seek an
exemption from the application of the action
or seek to have the action declared
unconstitutional. The measure also creates
the State Reserved Powers Protection Unit
Revolving Fund, which shall consist of the
first $10 million of funds derived from the
corporate income tax beginning July 1,
2021, and ending July 1, 2025.
HB 1783 (Luttrell/Weaver) expands the
regulatory of the Oklahoma State Athletic
Commission to include amateur kickboxers
and amateur kickboxing events. This
measure also eliminates the exemption from
the provisions of the Oklahoma State
Athletic Commission Act for amateur
combative sports events conducted or
sponsored by amateur sanctioning bodies.
USA Boxing events and events sponsored or
conducted by the International Olympic
Committee are exempted from the
provisions of the Oklahoma State Athletic
Commission Act by the measure.
HB 1816 (McBride/Weaver) creates “Cali’s
Law.” The measure designates the rescue
animal as the state pet of Oklahoma.
HB 1876 (Tammy West/Stanley) extends an
exception to the Oklahoma Open Records
Act relating to public employee personal
information. The home addresses, home
telephone numbers, Social Security
numbers, private email addresses, and
private mobile phone numbers of current
and former public employees shall not be
open to public inspection or disclosure.
Public records created using a private email
address or private mobile phone are not to
be included within this exception.
HB 2296 (Dustin Roberts/Bullard) re-
creates the Red River Boundary
Commission. The Commission is directed to
confer and act in conjunction with
representatives from Texas to evaluate the
methods and other information used to
establish the Texas boundary in the Texoma
area as well as determine the location of the
south bank of the Red River as located and
marked by the US Army Corps of
Engineers. Additionally, the Commission is
charged with redrawing the boundary with
Texas on any real property for which the
Army Corps of Engineers was granted an
easement for construction and operation of a
water pipeline in the Texoma area. The
commission is required to report findings
and recommendations no later than January
15, 2022, and issue a final report no later
than January 30, 2025.
HB 2326 (Frix/Pemberton) provides that a
member of the Oklahoma Abstractors Board
that has served 2 consecutive terms may be
reappointed after the expiration of at least 1
full term. The measure provides that a
felony conviction that could result in the
loss of an abstract license must substantially
relate to the practice of abstracting and pose
a reasonable threat to public safety.

47
HB 2338 (Kendrix/Pugh) provides that the
Director, department heads, emergency
responders, and other essential employees of
the Department of Corrections may be
permitted to use a state-owned or state-
leased vehicle to provide transportation
between the residence of the employee and
the assigned place of employment and
between the residence and any location other
than the assigned place of employment to
which the employee travels in the
performance of the official duty of the
employee. Department heads, emergency
responders, and other essential employees
must obtain permission from the Director to
receive such transportation.
HB 2462 (Dick Lowe/Howard) authorizes
the State Department of Education to enter
into contracts and agreements for the
payment of food, lodging and other
expenses to host, conduct, sponsor or
participate in conferences, meetings or
training sessions.
HB 2648 (Hill/Bullard) deems any order or
rule issued by any governmental entity
pursuant to an emergency that requires
closure of any place of worship as a
substantial burden even if the order or rule is
one of general applicability.
HB 2863 (Wallace/Thompson) requires state
agencies to present to the Commissioners of
the Land Office a complete appraisal of real
property including the present fair value, the
value of improvements, and the actual
condition of the improvements on the
property before the property can be sold,
leased, disposed of, or exchanged.
Additionally, the agency must provide a 20-
day period to the CLO to provide a proposal
for acquisition or disposal of the property.
The CLO may decline the proposal.
HB 2965 (McCall/Treat) extends the sunset
date of the entities outlined in the measure to
2024.
OMES Funding
HB 2902 (Wallace/Thompson) directs
$1,920,000 of FY-2022 appropriations to the
Office of Management and Enterprise
Services for the Pay for Success program.
The measure requires the Office to expend
this amount according to certain population
criteria.
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Office of
Management and
Enterprise
Services
$113,886,169
$102,781,593
-9.75%
Health Measures
SB 4 (Garvin/Marti) authorizes pharmacists
to substitute an interchangeable biological
product for a prescribed biological product
under certain conditions. The product must
be approved by the U.S. Federal Drug
Administration as an interchangeable
product and the patient must be informed of
the change. Pharmacists must make an entry
into their records showing the name of the
product and the manufacturer after
dispensing the product. An entry into the
$0
$50,000,000
$100,000,000
$150,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Office of Management and
Enterprise Services
48
electronic records system is presumed to
provide notice to the prescriber. The
measure directs the State Board of Pharmacy
to maintain a link on its Internet website to
the current list of all biological products
determined by the FDA to be
interchangeable with a specific biological
product. If no electronic records system is in
use by the pharmacy, the pharmacist is
authorized to communicate the biological
product dispensed to the prescriber using
facsimile, telephone, electronic
transmission, or other prevailing means
when required.
SB 42 (Rader/Dills) exempts individuals
providing personal care services in the home
from the licensing provisions of the Home
Care Act. The measure also updates
statutory language relating to the regulation
of care homes by replacing the State Board
of Health with the State Commissioner of
Health as the oversight entity.
SB 57 (Rader/Echols) authorizes members
of the Opioid Overdose Fatality Review
Board to access information collected at the
central repository under the Anti-Drug
Diversion Act. The measure also adds a
reference to a definition for the term “opioid
use disorder” as used in the opioid
prescription limit law. The measure also
clarifies exemptions for hospice care and
palliative care, and removes the requirement
that a patient be in active treatment for
cancer to be exempted. The measure
removes language allowing the Oklahoma
State Bureau of Narcotics and Dangerous
Drugs Control to provide unsolicited
notification to the licensing board if a
pharmacist or practitioner has exhibited
prescriptive behavior consistent with
generally recognized standards indicating
potentially problematic prescribing patterns.
Additionally, the measure specifies that
opioid use disorder is to be defined by the
American Psychiatric Association and
clarifies exemptions for patients receiving
cancer or aftercare cancer treatment or
palliative care in conjunction with a serious
illness.
SB 58 (Rader/Echols) exempts practitioners
ordering a controlled dangerous substance to
be administered through a hospice program
from electronic prescription requirements.
SB 95 (Stanley/Miller) requires the medical
examiner to conduct a sudden unexplained
infant death investigation (SUIDI) when the
death of an infant occurs in this state and the
cause of death is considered undetermined.
Medical examiner is defined as the Chief
Medical Examiner, Deputy Medical
Examiner, or a designee of the Chief
Medical Examiner. The examiner must
interview the parent, legal guardian or
caregiver of, or person who last had contact
with, the deceased infant. The measure
directs the State Department of Health to
retain a copy of each completed SUIDI
reporting form as well as provide a copy of
each completed SUIDI reporting form to the
Child Death Review Board.
SB 96 (Hall/McEntire) requires the medical
examiner to conduct a sudden unexplained
infant death investigation (SUIDI) when the
death of an infant occurs in this state and the
cause of death is considered undetermined.
Medical examiner is defined as the Chief
Medical Examiner, Deputy Medical
Examiner, or a designee of the Chief
Medical Examiner. The examiner must
interview the parent, legal guardian or
caregiver of, or person who last had contact
with, the deceased infant. The measure
directs the State Department of Health to
retain a copy of each completed SUIDI
reporting form as well as provide a copy of
each completed SUIDI reporting form to the
Child Death Review Board.
49
SB 104 (Haste/McEntire) authorizes
physical therapy sessions to be provided
remotely via telehealth to individuals or
groups. The measure defines telehealth and
telecommunication.
SB 136 (Simpson/Roe) modifies the time
period of the annual report compiled by the
State Department of Health pursuant to the
Oklahoma Breast and Cervical Cancer Act.
The measure requires the Department to
submit the report once every 5 years instead
of annually.
SB 164 (Stanley/Roe) authorizes
participation in an experimental treatment
program in life-threatening emergencies
without informed consent, provided the
treatment is approved by an accredited
institutional review board as well as
approval and continuing review of the
research activity has approved both the
research activity and a waiver of informed
consent. In no case shall an experimental
treatment regimen be approved on a
pregnant patient.
SB 187 (Rosino/Josh West) removes the Bill
Willis Community Mental Health and
Substance Abuse Services Center Tahlequah
and the Norman Alcohol and Drug
Treatment Center from, and adds the
Oklahoma Crisis Recovery Unit in
Oklahoma City to, the list of maintained
facilities within the Department of Mental
Health and Substance Abuse Services. The
measure also removes references to the
Tahlequah and Norman facilities.
SB 207 (Garvin/McEntire) provides for
administrative judges to consider appeals by
any applicant or recipient of benefits
provided by the Oklahoma Health Care
Authority. The measure requires the
Administrator of the Authority to only
appoint administrative judges from another
state agency as established in the State
Medicaid Plan and approved by the Centers
for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
SB 208 (Garvin/Moore) modifies birth
certificates as it relates to naming the father
of the child. The measure removes the
requirement for the husband to be married to
the mother at the time of conception and
adds language providing for the husband to
be placed on the certificate as the father if
the mother and husband were married any
time during the 300 calendar days preceding
the birth. The measure also directs the State
Commissioner of Health to authorize the
secure electronic transmission of any birth,
death, paternity or adoption data and other
documents or information necessary to
comply with the Uniform Parentage Act or
for the purpose of assisting with programs
administered by the Department of Human
Services. The measure also directs the
Commissioner to amend birth certificates
involving a child born out of wedlock to
reflect the paternity of the child upon
receiving such documentation and an
acknowledgement of paternity from both
parents. The measure prohibits the
Department of Human Services from
releasing such documents and directs the
Department of Health and Department of
Human Services to enter into a data sharing
agreement.
SB 344 (Garvin/McEntire) exempts
ambulatory surgical centers that are not
certified by the Centers for Medicare and
Medicaid Services from the requirement to
submit data and information relating to
tumors to the Commissioner of Health.
SB 368 (Bullard/Hill) prohibits any
governmental entity from declaring or
deeming a religious institution and any
activity directly related to the institution’s
50
discharge of its mission and purpose to be
nonessential. Additionally, the measure
prohibits the closure of such institutions for
the purposes of health or security that is
greater than that imposed upon any private
entity facing the same or similar health or
security conditions.
SB 378 (Rosino/Bush) creates Everett’s
Law. The measure prohibits any covered
entity from considering any individual
ineligible to receive an anatomical gift
solely due to an individual’s disability, deny
any medical services relating to organ
transplants, refuse to refer an individual for
the purpose of being evaluated for or
receiving an organ transplant, refuse to place
an individual on the waiting list, place an
individual lower on the priority list due to
his or her disability, and refuse to accept
health insurance coverage. Covered entities
must also provide for reasonable
modifications to its policies, practices or
procedures to allow individuals with
disabilities access to transplantation-related
services. Covered entities violating the
provisions of this measure may be held
liable by affected individuals. The measure
also prohibits a health carrier from denying
coverage or limiting provider reimbursement
solely due to a disability.
SB 388 (Rosino/Josh West) provides for the
eligibility of a patient for home care services
to be certified by a healthcare provider and
care of the patient shall be overseen by the
healthcare provider. Healthcare provider, as
defined in the measure, includes physicians,
physician assistants, or Advanced Practice
Registered Nurses. Current law provides
physicians with the sole authority to
determine eligibility.
SB 398 (Rosino/Baker) authorizes
pharmacists to administer immunizations
that have been approved or authorized by
the Food and Drug Administration without a
patient-specific prescription or similar
arrangement.
SB 405 (Stanley/Roe) clarifies the
expiration term for each class of member on
the Advisory Committee on Midwifery. The
first class’s term shall expire on January 31,
2023, the second’s shall expire on January
31, 2025, and the third’s shall expire on
January 31, 2027. The measure authorizes
the Advisory Committee on Midwifery to
investigate all reported violations of
Shepherd’s Law and requires all information
obtained during investigations to be kept
confidential. Such record can be introduced
by the State Department of Health in
proceedings before the Committee. The
measure also prohibits confidential
investigative records to be subject to
discovery or subpoena in any civil or
criminal proceeding unless the Committee
decides to give such information to law
enforcement or other state agencies as
necessary and appropriate. Additionally, the
measure prohibits any data required to be
submitted to the Department of Health
pursuant to Shepherd’s Law to contain any
personally identifying information of the
client by the midwife and it considers the
records to be confidential and collected for
statistical information purposes only.
SB 406 (Garvin/Boles) authorizes the
Oklahoma Children’s Hospital to extend
services to persons over the age of 21.
Additionally, the measure authorizes the
University Hospitals Authority to designate
other names under which the Oklahoma
Medical Center may operate. The measure
allows the University Hospitals Authority to
assign its inpatient and outpatient hospital
and clinical facilities and office and research
buildings, facilities, or property under its
control to the Oklahoma Children’s
Hospital, University Hospital or another
51
division of University Hospitals. It also
updates the name of the “Children’s
Hospital of Oklahoma” to “Oklahoma
Children’s Hospital” and prohibits the use of
either term without permission. The measure
also modifies, deletes, and repeals obsolete
language and updates names of facilities
under the University Hospitals Authority.
SB 511 (Montgomery/Bush) defines harm-
reduction services in the Uniform Controlled
Dangerous Substances Act. Harm-reduction
services are programs established to reduce
the spread of infectious disease, reduce drug
dependency, and increase safe recovery and
disposal of used syringes and sharp waste.
Government entities or their partners,
religious institutions, nonprofits, tribal
governments, and for-profit companies may
establish a harm-reduction service. Such
services are authorized to possess certain
drug paraphernalia items to further the goals
of the service, refer patients to mental health
services, offer referrals for drug treatment
programs, and employ rapid testing for
sexually transmitted infections. Entities
seeking to establish a harm-reduction
service shall register with the State
Department of Health.
SB 574 (McCortney/McEntire) directs the
Oklahoma Health Care Authority to
establish a health information exchange
certification with input from stakeholders.
Certification shall be required for a health
information exchange organization to
qualify as an Oklahoma Statewide Health
Information Exchange (OKHIE). Until such
time as the health information exchange
certification is established by OHCA, an
OKHIE shall mean either Oklahoma State
Health Information Network and Exchange
(OKSHINE) or a health information
exchange organization that was previously
certified by the Oklahoma Health
Information Exchange Trust. OKSHINE is a
unit of the Oklahoma Health Care Authority
charged with facilitating the exchange of
health information to and from authorized
individuals and healthcare organizations.
Individuals and entities using the system
shall not be held liable in any action for
damages or costs of any nature that result
solely from the person’s use or failure to use
OKSHINE information or data. The measure
also specifies that users providing data to the
network shall retain the ownership rights of
such information. Additionally, the measure
repeals provisions of law relating to the
study of creating such a network.
SB 584 (Dahm/Olsen) extends the
prohibition on providers receiving funding
from the state to include political
subdivision funding if such providers are
found to have transferred any human fetal
tissue for valuable consideration if the
transfer affects interstate commerce.
SB 647 (Pugh/Stark) creates Lily’s Law and
defines fetal death and stillbirth.
Additionally, the measure subjects birthing
centers and medical facilities to the same
requirement to maintain a written policy for
the disposition of the remains of a child
from a stillbirth or fetal death event as
licensed hospitals.
SB 673 (McCortney/Newton) modifies the
definition of the term telemedicine
throughout statute to be uniform. The
measure defines telemedicine to include
synchronous mechanisms such as
videoconference, asynchronous mechanisms
such as exchanging health information,
patient monitoring, mHealth, and other
electronic means that support clinical health
care.
SB 674 (McCortney/McEntire) requires
every health benefit plan offered in the state
to provide coverage of telemedicine. No
52
insurer may exclude a service for coverage
solely because the service is provided
through telemedicine and is not provided
through in-person consultation or contact
between a health care professional and a
patient for services. Reimbursements for
telemedicine services may not exceed the
copayment or coinsurance applied.
Additionally, any benefit restrictions
imposed on telemedicine treatments must be
equally applied to in-person treatments.
Additionally, no insurer may prohibit the
prescription of medicine through
telemedicine that are more restrictive that
applicable state and federal law.
Additionally, the State Department of Health
is directed to request a report from the
Statewide Health Information Exchange that
will provide the data outlined in the
measure.
SB 689 (Pugh/Miller) modifies the
membership requirements for the Advisory
Committee on Medical Care for Public
Assistance Recipients. The measure caps the
total membership to 15 members and
requires the board to include a member
representing individuals with developmental
disabilities, a member representing nursing
homes, and a member representing 1 or
more behavioral health professions.
Additionally, the Committee must include
the Commissioner of Mental Health and
Substance Abuse Services or a designee as
well as a member of a federally recognized
American Indian tribe. Appointments shall
be for a term of 4 consecutive years after
January 1, 2022. The chair shall serve for a
term of 1 year.
SB 718 (McCortney/McEntire) authorizes
facilities without a pharmacy license to
distribute or dispense dialysate or peritoneal
dialysis devices necessary to perform home
peritoneal dialysis to patients with end stage
renal disease (ESRD) provided certain
conditions are met.
SB 778 (Daniels/Lepak) requires physicians
to, prior to administering an abortion-
inducing drug, to follow procedures outlined
in the measure. The physicians must
determine the woman’s blood type and
administer RhoGAM at the time of the
abortion if the woman is Rh negative.
Additionally, the physician must inform the
woman that she may see the remains of her
unborn child after the procedure. The
physician must also document the
gestational age and intrauterine location of
the pregnancy and whether the patient
received treatment for Rh negativity. The
physician must then schedule a follow-up
exam 7-14 days after the procedure.
Informed consent must be obtained 72 hours
prior to administering the drug. The consent
form shall be published by the State Board
of Medical Licensure and Supervision and
must be filled in the manner prescribed by
the measure. Additionally, the State
Department of Health shall receive a report
from each facility providing abortions using
the consent forms to promote maternal
health. Using these reports, the Department
shall compile a comprehensive annual
statistical report for the Legislature. The
measure provides for the confidentiality of
each patient to be maintained. Physicians
shall report any adverse health event relating
to the administration of an abortion-inducing
drug to the Department. No abortion-
inducing drug may be provided on state
grounds. Any person found to have violated
the provisions of this measure shall be guilty
of a misdemeanor or a felony if the person
fraudulently used an abortion-inducing drug.
Persons found to have violated the
provisions of this measure shall be subject to
professional and civil penalties. The
Legislature may also appoint 1 or more
members who sponsored or cosponsored this
53
measure to intervene as a matter of right in
any case in which the constitutionality of
this act is challenged. The measure provides
for severability of its provisions.
SB 779 (Daniels/Lepak) directs the State
Board of Pharmacy, State Board of Medical
Licensure, and Supervision, and the State
Board of Osteopathic Examiners to
promulgate rules to create a certification
program to oversee and regulate the
provision of abortion-inducing drugs, which
shall be known as the Oklahoma Abortion-
Inducing Drug Certification Program. The
State Board of Pharmacy shall promulgate
rules to create a certification program to
oversee and regulate the manufacture and
distribution of abortion-inducing drugs by
manufacturers and distributors licensed by
the State Board of Pharmacy. The State
Board of Medical Licensure and Supervision
and the State Board of Osteopathic
Examiners shall promulgate rules to create a
certification program to oversee and regulate
the provision of abortion-inducing drugs by
physicians licensed by the respective state
licensing board. Such drugs shall only be
distributed and provided in this state only by
manufacturers or distributors certified to do
so under this program. The measure outlines
the process for certification, and states that
any physician found to be in violation of
these provisions shall be suspended from
practice until such time that the physician
demonstrates full compliance. Individuals in
another state shall be required to follow
certification procedures outlined in this
measure. The State Board of Pharmacy is
required to adopt an electronically based
reporting system for certified physicians to
annually report the demographics,
medication used, complicating events,
unresolved cases, and number of patients
served. Physicians shall be prohibited from
administering abortion-inducing drugs to
women with certain risk factors and any
woman with a pregnancy 10 weeks into their
pregnancy. Physicians shall also be required
to report certain information relating to
complications, deaths, and other health
events to the State Department of Health as
it relates to the administration of abortion
inducing drugs. Any physician
administering abortion-inducing drugs shall
be required to maintain hospital admitting
privileges or enter into a written agreement
with an associated physician in the county or
contiguous county where the abortion-
inducing drug was provided. Any person
found to have distributed an abortion-
inducing drug to persons not qualified to
administer such drugs shall be guilty of a
misdemeanor or a felony if a drug is
provided to a pregnant woman without her
knowledge. Persons found to have violated
the provisions of this measure shall be
subject to professional and civil penalties.
Additionally, the State Board of Pharmacy
shall levy a fine of not less than $5 million
on manufacturers and $250,000.00 for
physicians who violate the provisions of this
measure. The Board must also create a
website a complaint portal for patients,
pharmacy, nursing, and medical
professionals and the public to submit
information about potential violations. The
Board must review each complaint and
determine a disposition including referral to
another appropriate state agency, within 30
days. The Legislature may also appoint 1 or
more members who sponsored or
cosponsored this measure to intervene as a
matter of right in any case in which the
constitutionality of this act is challenged.
The measure provides for severability of its
provisions.
SB 782 (Garvin/McEntire) directs any
pharmacy maintaining an emergency
medication kit to establish a policy and
procedures governing the maintenance and
dispensation of emergency medication. The
54
measure also authorizes pharmacies to
designate a person who shall be responsible
for transmitting required information for
dispensation of controlled dangerous
substances to the central repository of the
Oklahoma State Bureau of Narcotics and
Dangerous Drugs Control. Pharmacies are
required to register emergency medication
kits as a pharmacy location with the
Oklahoma State Bureau of Narcotics and
Dangerous Drugs Control. The total volume
of controlled dangerous substances in each
kit shall be limited to 3 doses per licensed
bed or sixty individual doses.
HB 1006 (Bush/Pugh) creates the
Transparency in Health Care Prices Act. The
measure requires each health care provider
and facility to publicize the most common
health care services electronically or via
their website. Health care facilities are also
required to make common diagnosis and
outpatient CPT codes public. The price list
must be updated annually.
HB 1014 (Roe/Simpson) provides that all
information created, received, investigated,
held, or maintained by the State Department
of Health concerning any person who has
participated in a public health investigation
are exempt from the provisions of the
Oklahoma Open Records Act. The measure
also prohibits the attendance of students
having or suspected of having a
communicable disease in public or private
schools. The responsibility of removing such
students is transferred from teachers to
schools.
HB 1071 (Boatman/Stanley) expands the list
of entities exempted from the provisions of
the Oklahoma Alcohol and Drug Abuse
Services Act by including services provided
by a health center as defined in the Public
Health Service Act.
HB 1638 (Lepak/Bergstrom) requires the
funeral director or person acting in such
capacity to give notification to the person
providing personal data for a death
certificate that knowingly providing false
information or misrepresentation is a felony.
The measure prohibits knowingly providing
false personal data to a certifier of a death
certificate or misrepresenting any person's
relationship to the decedent.
HB 1690 (Newton/Jech) removes the
requirement that the board of directors of a
Federally Qualified Health Center be
considered a public body and subject to the
provisions of the Oklahoma Meeting Act.
The measure removes penalties and
reporting requirements for non-compliance
with the Oklahoma Open Meeting Act. The
measure modifies the definition of “public
body,” and further requires the Oklahoma
Health Care Authority to ensure that
Federally Qualified Health Centers receive
at minimum, payment for services in
accordance with U.S. law.
HB 1784 (Pae/Paxton) requires food
vendors utilizing kratom as an ingredient to
disclose on the product label, or a quick
response (QR) code on the product label
linked to a website, the factual basis on
which that representation is made. Vendors
must provide test results to confirm items
listed on the product label upon request by
the State Department of Health. Any failure
to disclose this information shall proscribe
any effort by the vendor to sell the item
based on containing kratom. Vendors are
prohibited from adulterating kratom
products and may not sell kratom products
containing at least 2% of the alkaloid
composition of the product. No kratom
product may be sold if it contains any
synthetic alkaloid including synthetic
mitragynine, synthetic 7-
hydroxymitragynine or any other
55
synthetically derived compounds. Persons
convicted of violating the provisions of this
measure shall be guilty of a misdemeanor
and subject to a $500.00 fine for a first
offense and a fine of not more than
$1,000.00 fine for second and subsequent
offenses. Such persons shall also be
prohibited from selling kratom products for
3 years.
HB 1794 (Miller/Pugh) defines dementia as
it relates to the renamed Alzheimer's
Dementia and Other Forms of Dementia
Special Care Disclosure Act. The measure
requires the State Department of Health to
develop the disclosure form for certain
recipients. Additionally, the measure
requires the facility to submit the disclosure
form to the Department prior to entering into
any agreement to provide care or services.
The State Department of Health must
examine and review each disclosure at the
time the disclosure is submitted to the
Department. The measure requires certain
information to be included in the
disclosures. Additionally, the measure
creates the Alzheimer-Dementia Disclosure
Act Advisory Council. The Council is
directed to make recommendations State
Commissioner of Health regarding the
disclosure form and rules promulgated in the
measure. The Council shall be comprised of
9 members. Members on the Council shall
serve without compensation and shall
receive staff assistance from the State
Department of Health. The Department shall
also establish a website with a list of those
facilities that have filed a disclosure form.
HB 1877 (Tammy West/Coleman) creates
new procedure for an assisted living center
when a resident is prescribed an
antipsychotic drug. The center will ensure a
resident is assessed at least quarterly for
effectiveness and possible side effects and
the results shall be documented and
provided to the resident or their
representative. The center will also ensure
the resident care staff understand potential
benefits and side effects of the medication.
Additionally, the assisted living center will
document the rationale for use and describe
the condition that indicates administration,
monitor the use of the drugs for potential
harm to the resident, and document the
results of the monitoring when prescribed on
an as-needed basis.
HB 1904 (Roe/Garvin) requires persons
performing abortions in the state to be board
certified in obstetrics and gynecology.
HB 2006 (Townley/Stanley) requires the
Board of Mental Health and Substance
Abuse Services to promulgate rules and
standards for certification of Problem
Gambling Treatment Counselors. The
measure requires the rules to include criteria
for certification and renewal outlines the
criteria for application of certification as a
Problem Gambling Treatment Counselor.
The Board may also establish an application
and renewal fee. The measure allows limited
use of the title of Problem Gambling
Treatment Counselor and prohibits
practicing other professions unless licensed
to do so. Failure to comply with the rules
and standards declared by the Board are
grounds for revocation, suspension, or
nonrenewal of certification.
HB 2009 (Townley/Coleman) authorizes an
advanced practice registered nurse to sign a
death certificate. The measure clarifies how
“suicide” is recorded as the manner of death
on a death certificate.
HB 2120 (McEntire/Montgomery) provides
that if there is substantial evidence that an
insurer is insolvent and the condition of that
insurer renders the continuance of its
business hazardous to the public or to
56
holders of its policies or certificates of
insurance or if an insurer has exceeded its
powers or fails to comply with the laws of
this state, the Insurance Commissioner must
require said insurers to file a written plan of
action within 30 days of notification of
insolvency. Additionally, the Commissioner
may require the insurer to take additional
action within 90 days of notification. The
Commissioner may determine at any time
during or after the 90-day period that
judicial or administrative proceedings
should be initiated to place the insurer in
conservation, rehabilitation, or liquidation
proceedings. The Commissioner may also
assess a $500.00 fine per day for failure to
timely file a written plan of action.
HB 2441 (Russ/Daniels) requires persons
performing or inducing an abortion to first
attempt to determine whether her unborn
child has a heartbeat. Upon detecting a
heartbeat, an abortion may not be performed
unless the mother has a condition that so
complicates her medical condition that it
necessitates the abortion of her pregnancy to
avert her death or to avert serious risk of
substantial and irreversible physical
impairment of a major bodily function. No
such condition may be determined to exist if
it is based on a claim or diagnosis that the
woman will engage in conduct which she
intends to result in her death or in substantial
and irreversible physical impairment of a
major bodily function. Persons found to
have violated the provisions of this measure
shall be guilty of homicide.
HB 2566 (Chad Caldwell/McCortney)
requires every long-term care facility in the
state to provide reasonable access to a
resident through family, compassionate
caregivers, or the Oklahoma Long Term
Care Ombudsman to withdraw consent at
any time. Such facilities must also provide
reasonable access to a resident by health
care providers who are contracted with the
facility to withdraw such consent. The
measure directs long-term care facilities to
include and submit to the State Department
of Health in their emergency-preparedness
plan procedures for visitation during an
emergency. The visitation plan shall be
made available by the facility to contracted
health care providers, family members,
essential support persons, and
compassionate caregivers upon request.
Long-term care facilities are prohibited from
unilaterally eliminating visitation for any
reason. The measure provides that visitation
may be suspended for a period not to exceed
72 hours based upon the emergency-
preparedness plan provided to the State
Department of Health.
HB 2676 (Marti/Weaver) allows controlled
dangerous substances issued by a
practitioner to be dispensed with an
electronic prescription if certain conditions
apply. The measure also allows electronic
prescriptions to be utilized for compounded
prescriptions, compounded infusion
prescriptions, and prescriptions issued under
approved research protocols.
HB 2687 (Hasenbeck/Bergstrom) creates the
“No Patient Left Alone Act. The measure
provides that each minor or adult admitted
to a hospital has the right to have a parent,
guardian or person standing in loco parentis
who shall have the ability to be present
while the minor patient is receiving hospital
care. The measure authorizes hospitals to
establish visitation policies that limit or
restrict visitation under certain
circumstances outlined in the measure.
Hospitals may require visitors to wear
personal protective equipment, provided that
any such required equipment shall be
provided by the hospital. The measure also
prohibits the termination of visitation rights
by the hospital, the State Department of
57
Health or any governmental entity,
notwithstanding declarations of emergency
declared by the Governor or the Legislature.
Health Funding
SB 131 (McCortney/McEntire) creates the
Ensuring Access to Medicaid Act. The
measure specifies which Medicaid
populations may be required to enroll in
managed care plans by the Oklahoma Health
Care Authority, which populations may
voluntarily enroll in managed care plans,
and which populations the Authority is
prohibited from requiring managed care
enrollment for or offering enrollment to. The
measure directs the Authority to develop
network adequacy standards for all managed
care organizations and dental benefit
managers. Managed care organizations and
dental benefits managers are required by the
measure to contract to the extent possible
and practicable with all essential community
providers, all providers who receive directed
payments, and other providers the Authority
may specify. Additionally, managed care
organizations and dental benefits managers
are required to notify the Authority of all
changes materially affecting the delivery of
care or the administration of its program and
must meet certain medical loss ratios. Such
organizations are prohibited from requiring
providers to contract for all products that are
currently offered or that may be offered in
the future by the managed care organization
or dental benefit manager or subcontractor.
Managed care organizations are required by
the measure to make a determination on a
request for an authorization of the transfer of
a hospital inpatient to a post-acute care or
long-term acute care facility within 24 hours
of receipt of the request. The measure also
establishes deadlines for managed care
organizations and dental benefit managers to
determine prior authorization for care
ordered by primary care or specialist
providers. Denials of prior authorization
requests shall be subject to peer-to-peer
review unless such requests are for services
not covered by the state Medicaid program.
Managed care organizations and dental
benefit managers are required to comply
with certain requirements outlined in the
measure as it relates to processing and
adjudication of claims for payment
submitted in good faith by providers for
health care items and services furnished by
such providers to enrollees. Such
requirements include processing clean
claims within 14 days, establishing a process
a provider may provide such additional
information as may be necessary to
substantiate a claim, conducting
postpayment audits in accordance with the
requirements of the measure, and applying
readmission penalties in compliance with
rules and regulations promulgated by the
Authority. The Authority is directed by the
measure to establish procedures for
enrollees or providers to seek review by the
managed care organization or dental benefit
manager of any adverse determination made
by the managed care organization or dental
benefit manager. Providers shall have 6
months from the receipt of a claim denial to
file an appeal. Additionally, the Authority
shall require managed care organizations
and dental benefit managers to participate in
readiness reviews. Such reviews shall assess
the criteria outlined in the measure. A
managed care organization or dental benefit
manager found to be in violation of the
provisions of this measure shall be subject to
1 or more non-compliance remedies of the
Authority. The Oklahoma Health Care
Authority may only execute the transition of
the delivery system of the state Medicaid
program to the capitated managed care
delivery model 90 days after the Centers for
Medicare and Medicaid Services has
approved all contracts entered into between
the Authority and all managed care
organizations and dental benefit managers
58
following submission of the readiness
reviews to the Centers for Medicare and
Medicaid Services. The Authority is also
directed to create a scorecard that compares
managed care organizations and dental
benefit managers within 1 year of
transitioning to the delivery model.
Additionally, the Authority is directed to
establish minimum rates of reimbursement
from managed care organizations and dental
benefit managers to providers who elect not
to enter into value-based payment
arrangements and fixes the rates until July 1,
2026 at percentages of the fee schedule of
the Authority. Managed care organizations
are required to offer value-based payment
arrangements to providers, but may not
require such arrangements. The measure
also creates the MC Quality Advisory
Committee to make recommendations to the
Administrator of the Oklahoma Health Care
Authority and the Oklahoma Health Care
Authority Board on quality measures used
by managed care organizations and dental
benefit managers in the capitated managed
care delivery model of the state Medicaid
program. A majority of the members shall
be providers participating in the capitated
managed care delivery model of the state
Medicaid program.
SB 434 (McCortney/McEntire) creates the
I/T/U Shared Savings Program. The
Program provides for non-I/T/U services to
receive 100% of the federal matching rate if
such services are rendered to an American
Indian or Alaska Native (AI/AN) Medicaid
beneficiary as a result of a referral from an
I/T/U facility provider. The Health Care
Authority is also directed by the measure to
distribute 50% of any savings that result
from the I/T/U Shared Savings Program.
Any savings not distributed to I/T/U
facilities or spent on administrative costs
shall be deposited in the I/T/U Shared
Savings Revolving Fund. The Authority is
directed to provide an annual report on the
Revolving Fund to the Governor, President
Pro Tempore of the Senate, and Speaker of
the House.
SB 918 (Treat/Echols) repeals regulations
relating to the performance of abortions in
the state. The measure does not repeal 21
O.S. Section 861, which states that a person
convicted of inducing a woman to take any
medicine, drug, or substance with the intent
of inducing a miscarriage is guilty of a
felony unless such measures were taken to
preserve the life of the woman. A person
may be imprisoned for no less than two
years and no more than five years if
convicted. The measure also does not repeal
the Choosing Childbirth Act, which provides
grants to non-profit organizations that help
women carry their children to term. The
measure will only take effect if the Attorney
General certifies that the United States
Supreme Court overruled the central holding
of Roe v. Wade or an amendment to the
United States Constitution is adopted that
restores to the State of Oklahoma the
authority to prohibit abortion.
SB 1045 (Thompson/Wallace) modifies the
Supplemental Hospital Offset Payment
Program (SHOPP). The measure defines
“directed payments” as specific payments
made by managed care plans to providers
under certain circumstances that assist states
in furthering the goals and priorities of their
Medicaid programs. The measure provides
that funds from SHOPP may be used to fund
supplemental or directed payments.
Additionally, the measure modifies the
assessment calculation methodology from a
rate needed to generate an amount up to the
sum of certain expenses to a fixed rate. The
measure fixes the assessment rate at 3% for
the calendar year ending December 31,
2022, and 3.5% for the calendar year ending
December 31, 2023. The rate will be fixed at

59
4% for the calendar year ending December
31, 2024, and each year thereafter. The
measure provides that the base year for
assessment shall be determined annually by
the Oklahoma Health Care Authority Board.
Additionally, the measure renders the
portion of the SHOPP fee attributable to
certain expenses null and void if federal
matching funds for the program become
unavailable. The measure also eliminates the
termination date of the program and
removes a cap on quarterly transfers of
funds. The measure extends the time period
the Authority has to make quarterly hospital
access payments from 10 days to 14 days.
SB 1046 (Thompson/Wallace) provides that
of the funds appropriated to the Oklahoma
Health Care Authority, $28,844,877.00 shall
be used for program growth. Additionally,
the measure provides that $16,733,682.00
shall be used to expand the dental benefit of
the state’s Medicaid enrollees and
$7,555,287.00 shall be used for alternative
treatments for pain management of the
state’s Medicaid enrollees. The measure also
authorizes the Administrator of the
Authority to make a request for exemption
to the Office of Management and Enterprise
Services in writing and file a revised budget
program unless both the Chair and Vice
Chair of the Joint Legislative Committee on
Budget and Program Oversight provide
written notification to the Office of
Management and Enterprise Services within
12 calendar days of the Committee’s receipt
of the exemption request that the exemption
subverts the intention and objectives of the
Legislature in establishing the original limit.
Additionally, the Administrator may request
the Director of the Office of Management
and Enterprise Services an early transfer of
tax collections to the General Revenue Fund
for the purpose of early allocation to the
agency’s disbursing funds to alleviate cash-
flow problems.
HB 2904 (Wallace/Thompson) increases the
funding for the Oklahoma Athletic
Commission by $100,000 as well as the
continuation of the Choosing Childbirth Act,
both within the Oklahoma State Department
Health. The PCS also maintains funding for
sickle cell outreach ($50,000) and
Uncompensated Care fund at $1.9 million.
The measure requires the State Department
of Health to utilize an amount necessary to
hire and employ, in addition to current
staffing, certain positions at the Oklahoma
Medical Marijuana Authority. The Medical
Marijuana Authority is required to establish
the qualifications and salary for each
position and hire such persons no later than
December 1, 2021.
HB 2950 (Wallace/Thompson) creates the
Ambulance Service Provider Access
Payment Program Act, which directs the
Oklahoma Health Care Authority to, upon
recommendation of the Oklahoma
Ambulance Alliance, to assess Oklahoma-
licensed ambulance service providers a fee.
Monies received pursuant to this fee shall be
deposited in the newly created Ambulance
Service Provider Access Payment Fund. The
measure specifies how the monies in the
fund are to be used, provides for
implementation, and lists exempt entities.
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Department of
Health
$58,337,964
$59,337,964
1.71%
$50,000,000
$52,000,000
$54,000,000
$56,000,000
$58,000,000
$60,000,000
$62,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Department of Health

60
Health Care Authority Funding
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Health Care
Authority
$1,000,039,368
$1,194,337,303
19.43%
Mental Health & Substance Abuse
Funding
SB 1047 (Thompson/Wallace) provides that
$1,541,252.00 appropriated to the
Department of Mental Health and Substance
Abuse Services in HB 2900 shall be used to
supplement program growth. Additionally,
the measure apportions the appropriations
made to the Department in HB 2900 in the
following manner:
1) $500,000.00 shall be used to carry out the
provisions of SB 848
2) $2,000,000.00 shall be used to carry out
the provisions of HB 2877
3) An increase in funding shall be provided
for crisis intervention training sessions
4) $2,034,000.00 shall be used to expand
connectivity programs between law
enforcement officers, mental health
providers and Oklahomans in a mental
health crisis
5) $7,500,000.00 shall be used to expand the
number of mental health crisis centers and
urgent care centers
6) $2,966,000.00 shall be used for additional
mobile crisis teams to respond and diffuse
crisis situations in communities
7) $500,000.00 hall be used to maintain 5
pilot programs to provide offenders
incarcerated in county jails in the State of
Oklahoma access to United States Food and
Drug Administration-approved, evidence-
based, medication assisted treatment for
opioid and alcohol dependence.
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Department of
Health &
Substance Abuse
$334,915,240
$321,489,597
-4.01%
Human Services
SB 27 (Stanley/Moore) directs the
Department of Human Services to forward
fingerprints to the Federal Bureau of
Investigation Interstate Identification Index
as it relates to conducting fingerprint-based
criminal records of placement homes. In the
event a person in the placement home does
not submit to the check within 5 business
days immediately after emergency
placement of the child, the child shall be
immediately removed from the emergency
placement home.
SB 45 (Stanley/Talley) requires the
Department of Human Services to include in
the background check for applicants a
fingerprint-based national criminal history
record check. The measure authorizes the
Department to directly request a national
criminal history record check from the
Oklahoma State Bureau of Investigation.
$900,000,000
$1,000,000,000
$1,100,000,000
$1,200,000,000
$1,300,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Oklahoma Health Care
Authority
$300,000,000
$320,000,000
$340,000,000
$360,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Department of Mental
Health & Substance Abuse
61
SB 65 (Montgomery/Dustin Roberts)
modifies the term “deployment” as it relates
to the Deployed Parents Custody and
Visitation Act by adding any transfer
pursuant to military orders requiring
presence in a foreign country.
SB 93 (Hicks/McBride) replaces the term
“retarded person” with “an individual with
intellectual disability” as it relates to funeral
expenses for children in the custody of the
Department of Human Services.
SB 134 (Daniels/Kannady) adds the
requirement for the Judiciary Committees of
the Senate and House to review the schedule
of basic child support obligations every 4
years. The review must include economic
data from the Title IV-D Child Support
Program in the Department of Human
Services and provide opportunity for public
input. Information relating to the report, as
well as the current membership of the
Committees, must be published on both the
Senate and House websites. Current law
only requires the Committees to review
child support guidelines.
SB 198 (Rosino/Lawson) modifies “least
restrictive alternative” in the Oklahoma
Guardianship and Conservatorship Act to
mean an approach to meeting the needs of
an individual that restricts fewer rights of
the individual than would the appointment
of a guardian or conservator. The measure
also adds “supported decision making” to
the Act and defines it as assistance from 1 or
more persons chosen by an individual in
understanding the nature and consequences
of potential personal and financial decisions.
Additionally, the measure requires court
orders appointing a guardian for a person to
include a specific finding that it was
established by clear and convincing
evidence that the identified needs of the
subject of the proceeding cannot be met by a
protective arrangement instead of
guardianship or other less restrictive
alternatives. The FS provides for the court to
dismiss the action if the court finds that less
restrictive alternatives to guardianship are
feasible and adequate to meet the needs of
the child. The measure also requires such
guardianships to be used only as is
necessary to promote and protect the
wellbeing of the person and to promote the
self-reliance of the person.
SB 199 (Rosino/Lawson) prohibits the
disclosure of agency records to Department
of Human Services employees whose
official duties include the audit or
investigation of programs, services,
administrative, or employment matters
involving the Department or the Medicaid
program unless such access is limited to the
purposes for which the disclosure is
authorized.
SB 300 (Rosino/Kannady) requires the court
that issued a temporary guardianship for
vulnerable adults as it relates to involuntary
protective orders to dismiss the temporary
guardianship when the underlying
conditions that created the emergency have
been removed. The measure also requires
the Department of Human Services limit
provided services in temporary
guardianships to protective services or the
establishment of eligibility for protective
services for the person and estate. The
measure also directs the Department to
request dismissal of a temporary
guardianship when certain conditions are
met.
SB 340 (Paxton/Boatman) removes the
requirement for prospective adoptive parents
to sign a release of information allowing the
release of the results of any search to the
agency or person conducting the home study
62
or home study update. The measure also
strikes language requiring such the
Oklahoma State Bureau of Investigation and
the Department of Human Services to
conduct a home study investigation on such
parents.
SB 421 (Rosino/Echols) provides for the
calculation of gross income as it relates to
child support to be calculated on the basis of
current income if a parent is incarcerated for
more than 180 days, provided, the
incarceration is a result of indirect contempt
of court for failure to pay child support or
crime of omission to provide child support
or for any offense for which the obligee’s
dependent child or the oblige was a victim.
Upon release, child support obligations shall
revert to the preincarceration order amount
beginning the first day of the month 90 days
after release. The measure also modifies the
calculation used to determine income if
evidence of current income is not available
or equitable by adding the average wages
and hours worked in the parent’s particular
industry and geographic area and the
parent’s education, training, work
experience, and ability to work. Such
calculation shall also include wages the
parent could earn consistent with the
minimum wage rate of not less than 25
hours a week. Veteran benefits received by a
child are also treated in a manner similar to
Social Security Title II benefits by the
measure.
SB 433 (Rosino/Lawson) requires any
investigation of a community-based service
provider conducted by the Department of
Human Services to notify the provider of
areas of concern and administrative
information. Areas of concern and
administrative information are not
considered to be final investigative findings
and will not be included in the final
investigative report.
SB 960 (Treat/McCall) extends the age at
which a child may be relinquished to
medical services providers or child rescuers
from 7 days to 30 days of age. Such
relinquishments are to be considered an
affirmative defense in child abandonment
cases. The measure provides for such
relinquishments to be effectuated by an in-
person transfer of the child to the medical
services provider or child rescuer or by
leaving the child in a newborn safety device
that meets certain criteria. Providers or
rescuers that install such a device shall be
responsible for the cost of installation and
maintenance. directs the State Department of
Health to award grants to organizations that
provide healthcare services to mothers and
infants for the purpose of reducing the rates
of maternal mortality and infant mortality by
3% within the 5 years of the measure’s
effective date.
SB 987 (Weaver/Bush) authorizes the court
to order a child to be transported to a
location approved by the court for an
interview or examination as it relates to
child abuse investigations. The court may
also designate a person to transport the
child. The measure directs the court to
consider safety protocols based on the
gender of the child when determining who
shall transport the child.
HB 1085 (Boatman/Daniels) authorizes the
court to waive e requirement for a child
abuse and neglect information system
(CANIS) search if it cannot be obtained in a
reasonable time and the court determines
that it is in the minor's best interest that the
CANIS search be waived in emergency
placement proceedings.
HB 1086 (Boatman/Daniels) authorizes a
guardian to petition a court to transfer or
convey ward-owned property deemed a
63
resource by federal or state authority into a
protective arrangement. A protective
arrangement shall not modify any state or
federal authorized rules regarding exemption
or transfer of assets or resources for
determination of Medicaid or Social
Security eligibility and is not considered a
sale of property. Additionally, a court order
authorizing a protective arrangement will
not have any impact on the protective
arrangement’s consideration in the actual
Medicaid eligibility determination decision.
HB 1151 (Osburn/Howard) modifies the
child custody hearing process to give courts
the option to consider evidence of the ability
of parents to communicate on issues related
to their children in addition to evidence of
harassment, domestic violence and stalking.
The measure provides that if equal access is
not granted to both parents, the court shall
issue findings and conclusion of law to
support its decision.
HB 1709 (Hill/Rosino) changes a
qualification for continuation of successful
adulthood services. The services may
continue until 21 years of age provided the
individual is in the custody of the
Department of Human Services or a
federally recognized Indian tribe and in an
out-of-home placement at the time of their
sixteenth birthday. Previous law stipulated
that this must occur at the time of their
eighteenth birthday.
HB 1797 (Miller/Garvin) prohibits any
individual who is under investigation for
heinous and shocking abuse while
responsible for a child to work with children
or reside in a childcare facility while the
investigation is pending. Employers are also
prohibited from contracting with such
persons while the investigation is pending.
measure also states that if the Department
determines a substantiated finding of
heinous and shocking abuse by a person
responsible for a child, the Department shall
notify the childcare facility owner and the
childcare resource and referral agency
within 1 business day after the finding. The
facility shall also notify parents or guardians
within 72 hours of the finding. The
Department will also develop a process
prohibiting the perpetrator from future
childcare employment. Any person who is
the perpetrator of a substantiated finding by
the Department of heinous and shocking
abuse may not o work with children, reside
in a childcare facility, or be hired by an
employer who offers or provides services to
children.
HB 1902 (Roe/Garvin) provides that the
safety plan monitor of a child who is in a
safety plan with the Department of Human
Services may, if the parent of the child is
unavailable, authorize medical or dental
treatment or examinations which are
necessary for the well-being of the child.
HB 1992 (Trey Caldwell/Kidd) requires the
Office of Juvenile Affairs (OJA) to provide
a report to the President Pro Tempore of the
Senate, Speaker of the House, and Governor
on the feasibility of entering into a contract
for or operating group homes of any level at
the Southwest Oklahoma Juvenile Center
campus located in Manitou, Oklahoma no
later than October 1, 2021. The measure
provides that the OJA may enter into other
contracts with state agencies, the federal
government, and tribes to allow for the
placement of children or young adults in the
custody of such an entity to reside and
participate in any identified OJA contracted
or operated program or facility.
HB 2311 (Lawson/Haste) defines “fixed
wireless broadband Internet service
provider” as an entity that offers Internet
access through a stationary fixed point-to-
64
point connection, often requiring direct line
of sight between the provider’s wireless
transmitter and its end-user consumer’s
receiver as it relates to the Ad Valorem Tax
Code. The measure clarifies that fixed
wireless broadband Internet service
providers are not included in the definitions
of transmission company and public service
corporation.
HB 2312 (Lawson/Haste) modifies the
competency evaluation process to include
youthful offenders in addition to
delinquency. The measure also adds
language that a copy of the child’s petition
or information is presented to the court. The
measure also modifies who may file a
motion for determination of competency to
state that the district attorney or the child’s
attorney shill file this motion under a
reasonable basis. At any time prior to or
during delinquency or youthful offender
proceedings, the Office of Juvenile Affairs
may file a Motion to Intervene to raise
issues of competency.
HB 2317 (Lawson/Haste) establishes a
grievance process for children detained in an
adult facility and provides that the Office of
Juvenile System Oversight shall receive
grievances for investigation, resolution, and
referrals. Each facility in which children is
directed to create grievance policies and
procedures available upon public request
and to make resources readily accessible to
children in the facility. The provisions of
this measure do not apply to children housed
in a Department of Corrections facility or
housed under a Department of Corrections
contract.
HB 2318 (Lawson/Garvin) modifies rules
on the termination of parental rights to
include any findings of child abuse or
neglect or failing to protect any child from
abuse or neglect as legal grounds for the
termination of parental rights.
HB 2327 (Bashore/Stanley) creates a
procedure to provide notice and an
opportunity to review to the individual and
to the facility if the individual is employed
with an Office of Juvenile Affairs affiliated
facility as it relates to the Restricted
Registry.
HB 2352 (Lawson/Garvin) provides that the
Director of the Department of Human
Services and the Executive Director of the
Office of Juvenile Affairs may enter into
agreements on behalf of the state with
Indian tribes in Oklahoma regarding care
and custody of Indian relating to the care of
Indian children. Such agreements may
transfer the jurisdiction of over child
custody proceedings and may be done on a
case-by-case basis. Additionally, the
measure clarifies that the State ratifies all
agreements in conformity with the Federal
Indian Child Welfare Act executed prior to
the enactment of the measure and provides
that the provisions of the measure shall
apply retroactively to any case filed or
pending at the time that an agreement
vesting concurrent jurisdiction is entered
into between the state and an Indian tribe.
The measure also removes the requirement
for the Administrative Director of the Courts
(ADC) to develop a form used to collect
data related to the adoption of each child.
HB 2367 (Burns/Coleman) provides that a
child 16 years of age or older may enter into
contracts to obtain housing if he or she
receives a certification of unaccompanied
status from a youth services provider with
the Department of Human Services. The
certification shall show that they determined
the child is homeless or a victim of domestic
violence or abuse. The provider is required
to notify the parent or guardian that the child
65
is seeking unaccompanied child status.
Certification of this status does not
discharge the parent or guardian of parental
or legal authority.
HB 2565 (Chad Caldwell/McCortney)
provides that evidence of material,
educational, or cultural disadvantage as
compared to other children shall not be
sufficient to prove that a child is deprived as
it relates to the Oklahoma Children’s Code.
The measure also modifies “neglect” to
include the failure to protect the child from
harm or threatened harm of which any
reasonable and prudent person responsible
for the child's health, safety or welfare
would be aware. Neglect shall not include a
child who engages in independent activities,
except if the person responsible for the
child's health, safety or welfare willfully
disregards any harm or threatened harm to
the child, given the child's level of maturity,
physical condition or mental abilities.
HB 2899 (Wallace/Thompson) states that
applications for Home and Community
Based Medicaid Water Services for the
Community Waiver, In-Home Supports
Waiver for Adults, and In-Home Supports
Waiver for Children operated by the
Department of Human Services cannot be
made until the applicant has been an
Oklahoma resident for 5 years prior to the
application date.
Human Services Funding
SB 1044 (Thompson/Wallace) transfers the
Support Service Providers Grant Program
and from the Department of Rehabilitation
Services to the Department of Human
Services and reduces the total amount of
grants awarded annually from $300,000.000
to $250,000.00.
SB 1073 (Thompson/Wallace) states that
portions of the appropriations made to the
Department of Human Services in HB 2900
be used in the following manner:
1) $2,000,000.00 shall be used for providing
services for persons with developmental
disabilities
2) $250,000.00 shall be used to implement
the provisions of SB 1044
3) $1,004,344.00 shall be used to fund debt
service obligations for the renovation and
construction of the Robert M. Greer Center
located in Enid, Oklahoma
4) $2,800,000.00 shall be transferred to the
Child Abuse Multidisciplinary Account
It also states that all federal monies received
by the state during the fiscal year ending
June 30, 2022, from the Temporary
Assistance to Needy Families Block Grant
and the Child Care and Development Fund
Block Grant to meet the provisions of
federal law relating to such grants. As well
as stating targeted priorities for increased
FMAP funds not related to COVID-19.
HB 2905 (Wallace/Thompson) provides that
$1.5 million of the funds appropriated to the
Office of Juvenile Affairs shall be used to
increase the funding of the Community
Based Youth Services Division of the Office
of Juvenile Affairs. This funding shall be
used to supplement existing funding.
Appropriations made in the 1st session of
the 58th Oklahoma Legislature may be
budgeted for fiscal year 2022 or fiscal year
2023. Funds remaining after each fiscal year
deadline for expending funds, if not
budgeted for the next year, shall lapse to the
credit of the proper fund. These
appropriations may not be budgeted in both
fiscal years simultaneously. Funds budgeted
for fiscal year 2022 and not required to pay
of obligations in that fiscal year may be
budgeted for fiscal year 2023 after the
agency to which the funds have been
appropriated has prepared and submitted a
budget work program revision removing the

66
funds from the previous fiscal year and have
it approved by the Office of Management
and Enterprise Services.
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Department of
Human Services
$713,831,158
$717,585,502
0.53%
Insurance Measures
SB 66 (Haste/Sims) exempts surplus line
policies sold to school districts from the
surplus lines premium tax.
SB 122 (Montgomery/Sims) authorizes
credit as either an asset or a reduction from
liability on account of reinsurance if an
insurer is domiciled or has its head office in
a reciprocal jurisdiction. A reciprocal
jurisdiction is a jurisdiction that is subject to
a covered agreement with the United States,
is a member state of the European Union, a
jurisdiction within the United States that
meets the standards of the National
Association of Insurance Commissioners, or
a jurisdiction that meets all previous
requirements as determined by the Insurance
Commissioner. The Insurance
Commissioner is directed by the measure to
publish a list of assuming insurers that have
satisfied these conditions. The
Commissioner may add an assuming insurer
to the list if a National Association of
Insurance Commissioners accredited
jurisdiction has added the assuming insurer
to a list of such assuming insurers. Should
the Commissioner determine that an insurer
no longer meets the requirements, the
Commissioner may revoke or suspend
eligibility of the insurer in accordance with
the procedures outlined in the measure.
Credit may only be assumed after the
effective date of this measure.
SB 137 (Taylor/ODonnell) creates the Act
Concerning Interpretation of Oklahoma
Insurance Laws. The measure clarifies that
any legal treatise, scholarly publication,
textbook, or other explanatory text does not
constitute the law or public policy of the
State if such a statement conflicts with the
Constitution of the United States, a statute of
the state, case law, or other common law
adopted in the State.
SB 287 (Quinn/Sims) modifies various
regulations relating to the Travel Insurance
Act. Travel assistance services is amended
to include all noninsurance services offered
to consumers and removes language
requiring such services to be offered by a
limited lines travel insurance producer.
Additionally, the measure specifies that
travel insurance may not include pre-paid
funeral contracts. The measure also
authorizes limited lines producers to sell,
solicit, and negotiate travel insurance
without an appointment by an insurer. The
measure specifies that that travel insurance
shall be classified and filed for purposes of
rates and forms under an inland marine line
of insurance. Cancellation requirements are
modified by the measure by allowing
policyholders to cancel a policy provided the
primary policyholder is not on a trip and
other conditions outlined in the measure are
met. Unfair trade practices are also modified
by the measure by excluding certain
practices requiring the consumer to choose
between purchasing the coverage required
by the destination jurisdiction through the
travel retailer or limited lines travel
$700,000,000
$710,000,000
$720,000,000
$730,000,000
$740,000,000
$750,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Department of Human
Services
67
insurance producer supplying the trip or
travel package or agreeing to obtain and
provide proof of coverage that meets the
requirements of the destination jurisdiction
prior to departure. Insurers are held
responsible for the acts of a travel
administrator managing travel insurance
underwritten by the insurer.
SB 288 (Quinn/O’Donnell) lowers the
percentage of an insurance company’s
admitted assets that a single mortgage loan
issued to any individual to 3% and
authorizes insurers to invest 45% of the
company’s admitted assets invested in total
aggregate amount in mortgage loans if the
portfolio average loan to value is 75% or
less of fair market value.
SB 330 (Rader/Pfeiffer) removes the
requirement for the Oklahoma Tax
Commission to verify the balance of the
Self-insurance Guaranty Fund and to inform
the Workers’ Compensation Commission of
the balance.
SB 392 (Standridge/McEntire) directs health
insurers to provide direct payment or
reimbursement to a licensed pharmacist for
providing a health care service to an
individual if said pharmacist provided care
for which he or she is licensed to practice
and the health benefit policy, contract, or
agreement of the individual that received
care provides for payment or reimbursement
of the service.
SB 472 (Daniels/Kannady) provides for an
annual $1.75 million payment to be made to
the credit of the Workers' Compensation
Administrative Fund derived from premiums
on employers.
SB 490 (Quinn/Hill) includes home
warranties within the legal framework of the
Oklahoma Home Service Contract Act.
Warranties and home service contracts are
also not classified as insurance by the
measure.
SB 529 (Quinn/Mize) modifies an interest
rate used in calculating minimum
nonforfeiture amounts relating to life
insurance annuities from 1% to 1/15 of 1%.
SB 550 (Newhouse/Pae) requires insurers
denying a clean claim to notify the insured,
enrollee or subscriber, assignee of the
insured, enrollee or subscriber, and health
care provider within 30 days after receipt of
the claim by the insurer. The notification
must state the reason for the denial and
include instructions on where a person or
entity that received notification may
respond. Recipients may submit a detailed
appeal in writing explaining why the claim
should be approved.
SB 738 (Montgomery/McEntire) modifies
conditions that consider an entity an insurer.
The measure specifies that an entity
organized for the purpose of transacting
insurance that ensures an Oklahoma
educational institution will be considered an
insurer for all kinds of insurance that the
entity transacts. The measure removes the
requirement that the entity must within a
twelve-month period receive aggregate
premiums of $1,000,000.00. Additionally,
the measure requires the Insurance
Commissioner to serve notice to an
insolvent insurer. The insurer must file a
written plan of action within thirty days of
notification. If the Insurance Commissioner
further determines that supervision is
necessary, the Commissioner is required to
serve notice to the insurer that supervision is
required. Insurers must comply with the
requirements of the Insurance Commissioner
and will have 90 days from the date of
notice to comply unless the Commissioner
determines otherwise. The Commissioner is
68
authorized to initiate judicial or
administrative proceedings against
noncompliant insurers. Additionally, the
measure authorizes the Insurance
Commissioner to assess a fine for failure to
timely file a written plan of action required
by this act in an amount not to exceed
$500.00.
SB 887 (Quinn/Sneed), otherwise known as
the Insurance Omnibus Bill, authorizes the
Insurance Commissioner to fine insurance
carriers for failing to file a market conduct
statement for up to $1,000.00 for each
occurrence. The measure also provides for a
Business Character Report to contain data
that is up to 6 months old instead of 1 year.
Insurance carriers are also authorized to
provide reasonable exceptions to the rate of
the insurer, rating classifications, company
or tier placement, or underwriting rules or
guidelines for a consumer who has
experienced and whose credit information
has been directly influenced by certain
catastrophic events outlined in the measure.
Applicants for the exception must request
the exception in writing. The measure
additionally authorizes the Oklahoma
Automobile Insurance Plan to issue policies
of insurance in the name of the plan for the
applicants as it relates to equitable
apportionment. Participating members shall
be liable to the plan for all costs, expenses,
and liabilities in proportion to its share of
voluntary market premium and must file an
annual audited financial statement with the
Commissioner. The measure provides for
surplus line licensees to be fined $25.00 per
policy for failing to remit the surplus line
tax. Additionally, the measure requires
insurers to reimburse clean claims filed
electronically within 1 year and provides for
notices of expiration for claims to be given
not more than 1 year after the date of the
loss. The measure also creates the Motor
Service Club limited lines category for
limited line insurance. Nonresident
administrators shall also be required to
notify the Commission of any termination of
employment within 30 days instead of 15.
Any entity making application to the
Oklahoma Insurance Department as a third-
party administrator (TPA) or within 30 days
of a change for a licensed TPA shall provide
current National Association of Insurance
Commissioners Biographical Affidavits and
independent third-party background reports
from a NAIC-approved vendor on behalf of
all officers. The measure increases the
licensing fee for limited line producers to
$40.00. The measure modifies the
membership of the Oklahoma Property and
Casualty Insurance Guaranty Association
and authorizes each insurer to appoint an
alternate representative. Any person serving
as an alternate representative shall, while
serving, have all the powers and
responsibilities of the appointed insurer
representative. Additionally, the Association
may use legal postings on its website to
satisfy notification requirements. The
measure provides for insurance policies
issued by members and later transferred to
another insurer to be considered to have
been issued by a member insurer which is an
insolvent insurer in the event that the insurer
to which the policy has been transferred.
Prepaid funeral benefit permit holders are
prohibited from changing the name under
which the permit holder operates unless they
receive permission to do so from the
Commissioner. The permit holder must first
obtain permission for such a change from
the Commissioner 30 days prior to the
change. The Commissioner may deny or
approve any request to change the name.
Certificates of dormancy, as defined by the
measure, may be issued by the
Commissioner. Dormant captive insurance
companies are companies that ceased
transacting the business of insurance and
have no remaining liabilities. Such
69
companies shall not be liable for any
insurance taxes and may possess a total of
$25,000.00 in unimpaired, paid-in capital,
and surplus funds. Dormant companies shall
be subject to examination by the
Commissioner. The measure also modifies
the date by which the Insurance
Commissioner must make certain reports
provided to the Commissioner available to
the public from June 1 to December 31 of
each year. Additionally, the measure
clarifies in the event an insurance company
cancels any personal residential insurance
coverage, notice of the cancellation is
required to be provided by the insured to the
insurer. The measure also requires the
cancellation notice to provide the date of
cancellation of the policy and the insurance
company is required to reimburse the
insured for any premiums paid for coverage
beyond the date of cancellation. The
measure provides that in the event an
insured cancels a homeowner’s policy or
any other personal residential insurance
coverage, a notice is required to be provided
by the insured to the prior insurer. An
insurer canceling any personal residential
coverage is required to make the
cancellation of coverage effective as of the
date of the inception of the new coverage
and the insurer will not be liable for claims
arising after the date of inception.
SB 1030 (Quinn/Mize) provides for the
Insurance Commissioner to levy a civil
penalty of up to $1,000.00 per violation.
Additionally, the measure requires insurers
to pay the $200.00 filing fee relating to
market conduct statements at the time of
filing.
SB 1035 (Quinn/Sneed) updates definition
for risk retention group. A risk retention
group seeking to be chartered for domicile
in this state is required to be chartered and
licensed to only write liability insurance
pursuit to the insurance laws of Oklahoma.
The measure requires all risk retention
groups chartered in the state to file with the
Insurance Department and the National
Association of Insurance Commissioners
(NAIC) an annual statement in a form
prescribed by the Association and in
electronic form if required by the Insurance
Commissioner. The measure requires the
risk retention group or purchasing group to
submit an appropriate revision of changes in
any item of the plan of operation or
feasibility study within ten (10) days of the
change to the Insurance Commissioner for
approval. Once the plan is approved, a copy
of the approved revision plan must be
submitted to the Commissioner within thirty
(30) days of the date of approval. The
measure prohibits the risk retention group or
purchasing group from offering additional
kinds of liability insurance in this state or
any other state until a revision of the plan is
approved by the Commissioner. The
measure requires the risk retention group to
provide the Commissioner a summary of
specific information. The information is
required to then be transmitted to the
National Association of Insurance
Commissioners. Existing risk retention
groups are required to comply with certain
governance standards within one year of the
effective date of this act. Risk retention
groups licensed after the effective date are in
compliance at the time of licensure. The
measure provides the requirements and
conditions for the Board of Directors of risk
retention groups. The measure also requires
the risk retention group to have an audit
committee with certain conditions. The risk
retention group or purchasing group is
required to pay a filing fee determined by
the Commissioner for application of charter.
At the time of application for charter, the
risk retention group is required to provide
the Commissioner a summary of certain
information which will then be forwarded to
70
the National Association of Insurance
Commissioners. This will satisfy the
requirements of Oklahoma law. The
measure requires each risk retention group
to pay premium taxes and taxes on
premiums of direct business for risk and
report premiums for direct business for risks
to the Commissioner. The measure removes
the requirement of risk retention groups to
pay the tax for risks insured within the state
and the mandatory reporting of all premiums
paid to it for risks insured within the state.
The measure adds “claimants against its
insureds” to the list of entities prohibited
from receiving any from any insurance
insolvency guaranty fund or similar
mechanism. The measure also specifies that
when insurance is bought from insurers not
authorized in the state, such risks will not be
covered by any insurance guaranty fund or
similar mechanism in the state. The measure
removes the exemption of a purchasing
group being exempt from state law and
modifies the provision to include a
purchasing group and its insurer or insurers
to be subject to all applicable laws of
Oklahoma with the exception of any law of
this state that would prohibit the
establishment of a purchasing group in
regards to liability insurance. Additionally,
the measure prohibits an insurer from
providing advantages to a purchasing group
or its members based on the loss and
expense experience of the group such as
advantages on rates, policy forms and
coverage that is not afforded to other
persons or entities. A purchasing group
which intends to do business in the state is
required to list all other states in which the
group intends to do business with to the
Insurance Commissioner. The measure also
clarifies that individuals, firms, associations,
or corporations are prohibited from
soliciting, negotiating or procuring liability
insurance from an insurer not authorized to
do business in the state of Oklahoma. The
measure requires a special purpose captive
insurance company to pay the Department of
Insurance a non-refundable fee of three-
hundred dollars ($300.00) for reviewing its
application to determine whether it is
complete. The measure requires the
Insurance Commissioner to specify the
amount relating to the minimum capital and
surplus of a series captive insurance
company. Certain papers relating to
mergers, consolidation, conversion,
mutualization and change of control are
confidential and not subject to subpoena or
distribution with an exception relating to the
authority of the Commissioner under
Oklahoma law. The measure requires
modifications, assets and liabilities by use of
GAAP accounting principles to be reported
with certain requirements. The measure
requires modifications, assets and liabilities
to be reported with certain conditions. Each
series captive insurance company is required
to pay a minimum aggregate tax of three-
thousand five-hundred dollars ($3,500.00).
Lastly, the measure provides conditions for
annual maximum tax premiums.
HB 1019 (Worthen/Simpson) modifies the
cap amounts for a 30-day and 90-day supply
of insulin to an amount not to exceed $30.00
for a 30-day supply and $90.00 for a 90-day
supply for each covered prescription.
HB 2123 (McEntire/McCortney) directs the
Insurance Commissioner to determine the
duties assigned to the Patient’s Right to
Pharmacy Choice Commission.
Additionally, the Commissioner may
employ actuaries, statisticians, accountants,
and attorneys on behalf of the Commission.
The measure authorizes the Commission to
approve, disapprove, or approve with
modifications any filings submitted to it.
The Commission may also conduct
examinations and investigations of insurance
matters within the scope of its authority. The
71
authority to investigate pharmacy benefits
managers is transferred from the Insurance
Commissioner to the Pharmacy Choice
Commission. Other duties transferred to the
Pharmacy Choice Commission include
reviewing complaints, and requiring
restitution from pharmacy benefits managers
who have violated the law.
HB 2180 (Johns/McCortney) directs state
agencies to make payroll deductions for the
payment of any insurance premiums due a
private insurance organization or service
company upon the request of a state
employee. The measure strikes the
requirement for such organizations or
companies to be regulated by the State
Insurance Commissioner and have a
minimum participation of 500 state
employees for legal services.
HB 2323 (Frix/Pemberton) prohibits
insurers and preferred provider
organizations from unilaterally removing a
provider from the network solely because
the provider informs an enrollee of the full
range of physicians and providers available
to the enrollee. Provider agreements may not
prohibit, penalize, terminate, or otherwise
restrict a preferred provider from referring to
an out-of-network provider, provided the
insured signs an acknowledgement of
referral that the insured may incur certain
charges, deductibles, and higher
coinsurance.
HB 2403 (Russ/Quinn) requires the
Insurance Department to only terminate a
license that failed to renew after a 12-month
inactive period upon notification 90 days
prior to termination of the license.
HB 2678 (Marti/McCortney) expands the
list of practices constituting an unfair claim
settlement practice to include failing to
include any amount paid by an enrollee or
on behalf of an enrollee by another person
when calculating the enrollee's total
contribution to an out-of-pocket maximum,
deductible, copayment, coinsurance or other
cost-sharing requirement as it relates to a
health insurer that provides pharmacy
benefits or a pharmacy benefits manager that
administers pharmacy benefits for a health
plan.
Liquor, Smoking, & Tobacco
SB 85 (Coleman/Strom) authorizes the
holder of multiple small brewer licenses to
sell beer produced at any brewery for which
the licensee has a license, at any other
brewery for which the licensee has a license,
or on premises located contiguous to such
properties.
SB 262 (Thompson/Echols) provides for the
excise tax on wine shipped directly to a
consumer by a winery maintaining a
Winemaker Self-Distribution License be
collected and remitted by the winery. The
wholesaler who purchases the alcoholic
beverages for sale shall collect the excise tax
on all other wine and spirits sales.
SB 315 (Coleman/McDugle) authorizes
distiller licensees to sell spirits produced by
the licensee for either on-premises or off-
premises consumption to consumers on the
licensed distillery premises or in an area
controlled by the licensee located
contiguous to the licensed distillery
premises as well as sell spirits at public
events such as trade shows or festivals. The
measure provides that such products sold
must have been sold to and shipped to an
Oklahoma licensed wine and spirits
wholesaler and then made available for
purchase by the Oklahoma licensed distiller.
These sales shall be capped at 15,000
gallons per year.
72
SB 385 (Coleman/Strom) authorizes a retail
spirits licensee to host alcoholic beverage
tastings for consumers on its licensed
premises provided the conditions outlined in
the measure are met. Servings shall be
limited, on the licensee’s premises, poured
from original containers, supervised by the
licensee, and served only to persons 21 years
of age or older. Licensees are directed to
maintain records of any samples served. The
licensee shall not permit any alcoholic
beverages content or retail container
unsealed in connection with sampling to
remain on the licensed premises at the close
of the business on that day.
SB 499 (Coleman/McEntire) requires stores
selling alcoholic beverages to customers to
present the 13.5% gross tax on alcohol as a
separate item on the receipt. This
requirement shall not apply to catered,
public, and special events.
SB 760 (Pugh/Osburn) authorizes persons to
transport alcoholic beverages from one
licensed premises to the common use area if
the facility contains multiple licensed
premises. The ABLE Commission shall
designate common drinking area for the
consumption of alcoholic beverages in such
facilities.
SB 1078 (Thompson/Wallace) modifies
several definitions, including “tobacco
products” and adds several definitions which
include “smokeless tobacco,” “snuff,”
“chewing tobacco,” “smoking tobacco,”
“pipe tobacco,” and “roll-your-own
tobacco.” The following sections conform
statutory language to the new definitions.
HB 1096 (Strom/Coleman) authorizes a
retail, mixed beverage, on-premises beer and
wine, public event, special event, charitable
auction, charitable alcoholic beverage event,
or complimentary beverage licensee to
communicate with a brewer, beer
distributor, small brewer, small brewer self-
distributor, or brewpub self-distributor on
social media. Licensees may request free
social media advertising from such persons.
Such persons may share social media posts
provided the post does not contain the retail
price of any alcoholic beverage.
HB 2122 (McEntire/Coleman) creates the
Oklahoma Cocktails To Go Act of 2021.
The measure allows establishments holding
a caterer’s or a mixed beverage license to
sell single-serve wine and cocktails to-go as
long as they are in a sealed tamper-proof
container. The sealed container must be
properly labeled as outlined in the measure.
Deliveries must be made by employees of
the establishment and must be at least 21
years of age. The employee must be able to
verify the age of the customer as well. If
delivered or picked up, the beverage must be
placed in the trunk of the vehicle, or in the
rear compartment of the vehicle if there is
no trunk. Third-party deliveries of cocktails
are prohibited. Entities holding a license to
manufacture alcoholic liquors or beverages
are prohibited from being able to sell
cocktails to-go.
HB 2277 (Bashore/Leewright) clarifies that
mixed beverage licensees permitted to offer
drink specials are not required to offer such
drink specials at all venues operating under
the same license.
HB 2380 (Marti/Coleman) authorizes
alcoholic beverage licensees to provide self-
pour automated devices for dispensing beer
and wine. Such licensees must use an ABLE
approved device to dispense the alcoholic
beverages and may only dispense 10 ounces
of wine or 32 ounces of beer per serving.
Licensees are required to provide constant
video monitoring at all times during which
the licensee is open, keep such footage for at
73
least 60 days, and provide the footage upon
request to any ABLE Commission agent or
other authorized law enforcement.
HB 2511 (Kannady/Howard) requires every
manufacturer of a vapor product sold or
intended to be sold in the state to deliver to
the ABLE Commission an attestation
certifying that the product was available for
purchase in the United States as of August 8,
2016, and the manufacturer has applied for a
marketing order from the FDA on or before
September 9, 2020, or that the manufacturer
has received a marketing order or other
authorization from the FDA. The measure
further requires manufacturers to notify the
ABLE Commission within 30 days of any
material change to the attestation, and
directs the ABLE Commission to develop a
directory listing of all manufacturers and
their vapor products that have provided
attestations. Any vapor product not in the
directory is prohibited from being
manufactured, distributed, sold, bartered or
furnished in the state.
HB 2665 (Echols/Coleman) separates the
alcoholic beverage manufacturer license
from the nonresident seller license and sets
its fees based on the number of cases sold
per year. For 50 cases or less, the licensing
fee is set at $50.00 with a $100.00 annual
fee. If the licensee sells between 51 and 500
cases, the licensing fee is set at $75.00 with
a $225.00 annual fee. For licensees sealing
over 501 cases per year, there shall be a
$150.00 licensing fee and an additional
$450.00 annual fee.
HB 2674 (Marti/Howard) clarifies that a
person must be 21 years of age to purchase
nicotine products. Nicotine products include
any product that contains nicotine extracted
or isolated from plants, vegetables, fruit,
herbs, weeds, genetically modified organic
matter, or that is synthetic in origin and is
intended for human consumption.
HB 2726 (Pittman/Coleman) defines “bottle
service” and “club suite” in the Oklahoma
Alcoholic Beverage Control Act. A bottle
service is defined as the sale and provision
of spirits in their original packages by a
mixed beverage licensee to be consumed in
that licensee’s club suite. A club suite is
defined as a designated area within the
premises of a mixed beverage licensee that
is exclusive to patrons specifically granted
access by the licensee. Spirits in the original
packages must be consumed in the club suite
of a mixed beverage licensee and cannot be
removed if not consumed in their entirety or
before the period a club suite was made
available ends. Spirits in their original
packages consumed in the club suite must be
provided exclusively by the mixed beverage
licensee.
Judiciary/Court Measures
SB 16 (Floyd/Bush) provides access to the
Crime Victims Compensation Board written
documentation included with a sexual
assault forensic evidence kit tested by an
accredited forensic lab if such
documentation is essential to determine
eligibility for compensation. Additionally,
the measure modifies the time period by
which the Board may examine sexual assault
forensic evidence kits involving an adult 18
years of age or older. The measure also
specifies that victims who undergo forensic
medical examination within 120 hours of the
assault shall be found to have fully
cooperated.
SB 31 (Daniels/Moore) requires the court to
enter an order dismissing a plaintiff’s case
against a defendant if the defendant
demonstrates that he or she was not timely
served. The court is directed by the measure
to dismiss the action 200 days after the filing
74
of the action in which no service has been
made on any defendant.
SB 38 (Thompson/Echols) places oversight
of the drug court programs established by
the Oklahoma Drug Court Act under the
Administrative Office of the Courts. The
measure also establishes a county Drug
Court Fund under the county treasurer’s
management. All monies received by the
county drug court shall accrue to the Drug
Court Fund. Additionally, the measure
extends judicial immunity to include any
duty required by law to be performed by a
judge of a drug court.
SB 44 (Hicks/Strom) requires any charges or
warrants issued for failure to appear in court
to be dismissed upon the defendant showing
the court that he or she was incarcerated or
otherwise detained by law enforcement at
the time of the failure to appear.
SB 50 (Howard/Worthen) requires each
criminal case filed in the traditional manner
to also be cross-referenced to a mental
health court case file by the court clerk if the
case is subsequently assigned to a mental
health court program. The measure provides
for the originating case to remain open to the
public and requires the court to determine
what information or pleadings are to be
retained in the mental health case court file.
The mental health case court file is closed to
the public.
SB 90 (Howard/Chad Caldwell) provides
that an affidavit of publication provided by a
publisher or authorized employee shall
constitute conclusive proof that the
newspaper has published the notice,
advertisement, or publication.
SB 97 (Brooks/Miller) trikes the prohibition
on videoconference technology as it relates
to using such technology in a jury trial or a
trial before a judge in a district court.
SB 140 (Brooks/Newton) modifies the
definition of “offender” as used in the
Delayed Sentencing Program for Young
Adults. The measure increases the maximum
age from 21 to 25 to participate in the
program for those who have not been
sentenced for a nonviolent felony offense.
SB 153 (Howard/Moore) authorizes the use
of a trust created by the court on behalf of
person under 18 years of age when
depositing recovered monies.
SB 155 (Howard/Kendrix) directs the
Oklahoma Supreme Court to maintain a
calendar of cases pending before the court
and to publish the calendar on its website.
Entries on the calendar shall include dates
the court shall hear oral arguments, cases
challenging the constitutionality of an act of
the Legislature, dates of court conferences,
dates the court is closed, and any
information that will assist the public in
monitoring cases. Entries noting oral
arguments must include the case number,
names, counsel of record, and a summary of
the case. The Supreme Court must also
weekly publish a list of cases for which it
has granted review.
SB 162 (Howard/McEntire) creates the
Oklahoma Decanting Act. The measure
provides for the authorized trustee with full
discretion to distribute the principal of the
trust to distribute all or part of the principal
of that trust in favor of a trustee of a second
trust for the benefit of the current trust.
Authorized trustees may grant a power of
appointment in the second trust to one or
more of the current beneficiaries of the first
trust who is eligible to receive the principal
outright under the terms of the first trust.
The measure also authorizes petitioners to
75
petition a court to order a distribution.
Authorized trustees with limited discretion
to distribute the trust may distribute all or
part of the principal of that trust in favor of a
trustee of a second trust, provided the
beneficiaries of the second trust are
substantially the same as the members of the
current trust. The measure authorizes
special-needs fiduciaries to exercise similar
distribution powers as authorized trustees
with full discretion. The measure authorizes
the interest of a special-needs trust to have
an interest in additional financial tools, such
as a pooled trust as defined by Medicaid law
for the benefit of the beneficiary with a
disability. The measure describes various
notification requirements associated with
“decanting” a trust.
SB 171 (Daniels/Moore) prohibits the court
clerk from publishing court records on its
website if the cases involve rape, sodomy,
sex crimes, sexual images, lewd or indecent
conduct, pornography, child abuse or
neglect, domestic abuse, kidnapping,
extortion of a vulnerable victim, human
trafficking, or similar offenses.
SB 310 (Murdock/Josh West) requires the
court to give consideration to the statements
of the victim or victims of a juvenile crime
when ruling on any motions for certification
as a youthful offender or an alleged juvenile
delinquent. The measure also removes rape
in the 1st degree from the list of crimes
designating an offender aged 15-17 as a
youthful offender. Additionally, the measure
provides that any person aged 15-17 who is
charged with rape in the first degree or
attempted rape in the first degree may be
held accountable for his or her act as if the
person was an adult.
SB 578 (Floyd/Munson) clarifies the
requirements for statements made under
penalty of perjury.
SB 677 (Kidd/Osburn) removes the
requirement for the court clerk to first offer
all or part of the records subject to
destruction to the Archives and Records
Division of the Oklahoma Department of
Libraries for preservation. The measure also
authorizes destruction of court records
related to a domestic relations case in which
a minor child is involved after 20 years, and
records related to a domestic relations case
that does not involve a minor child after 10
years. Records pertaining to protective
orders may be destroyed 1 year after the
case was dismissed and no further action
taken in the case, or 10 years after the order
was issued.
SB 1002 (Weaver/Moore) removes the term
cases involving misdemeanors from
“signature” as it relates to criminal
procedure.
HB 1022 (Worthen/Weaver) provides that
the payment of the fine and costs not
accompanied by a written plea of guilty or
nolo contendere is deemed to be a plea of
nolo contendere and is to function as a
written, dated and signed citation form
acceptable to the court.
HB 1024 (Worthen/Daniels) prohibits any
person who has been convicted of a violent
crime or a crime that requires the person to
register as a sex offender in this state or
another state from applying for or obtaining
a license to serve process. Currently licensed
persons subject to this prohibition shall not
have their license renewed. The measure
strikes language which required a person
applying to be a process server to publish
notice of the hearing for a license. The
measure requires notice of the application to
be sent to the Administrative Office of the
Courts. Any person who knowingly and
willfully serves process in Oklahoma
76
without a process server license or who
holds himself or herself out to be a process
server licensed by the State of Oklahoma
when the person is not licensed shall be
guilty of a misdemeanor. The measure
provides that assault of a process server is a
misdemeanor punishable by imprisonment
for up to 1 year in the county jail, a fine of
not more than $1,000, or both such fine and
imprisonment. The measure states that it is a
crime to fail to control an animal at the time
a legal process is being served.
HB 1152 (Osburn/Garvin) removes the
requirement to possess a minimum level of
court reporting proficiency for applicants
seeking to be examined for enrollment as a
certified shorthand reporter.
HB 1632 (David Hardin/Weaver) modifies
the writ of execution form used in actions of
forcible entry and detainer by providing that
physical possession of the property is to be
restored to the plaintiff.
HB 1776 (Conley/Weaver) provides that an
attorney employed by the Oklahoma State
Bureau of Investigation may enter an
appearance in court if requested to do so by
another prosecuting authority as it relates to
quashing subpoenas, other discovery
matters, expungement applications,
evidentiary hearings, and forfeiture
proceedings. The measure also expands the
requirement for a person convicted of a drug
crime to provide a blood or saliva sample to
law enforcement to include any person
convicted under the provisions of the
Uniform Controlled Dangerous Substances
Act.
HB 1799 (Miller/Rosino) modifies the
process for expunging a juvenile court
record. The petition for expungement may
be filed orally or as a written petition and
must be presented at the time the case is
before the court for a final review or any
time after an informal adjustment agreement
has been successfully completed and the
court dismissed the case or is closing it due
to a lack of jurisdiction or the child reaching
the age of 18 or 19 years of age if
jurisdiction of the court was previously
extended. A person who reaches the age of
18 can file for their own expungement
provided they meet all the requirements. A
written petition for the expungement of the
juvenile court records must be allowed if the
state objected to oral written or written
petition. If expungement is granted, the
measure provides that an attorney will
prepare a written order of expungement and
send it to all relevant parties. Landlords shall
not require an applicant to disclose any
information contained in any expunged
juvenile court records.
HB 1980 (Lepak/Daniels) directs the
Judicial Nominating Commission to
promulgate rules to promote transparency in
the Judicial Nominating Commission’s
selection process. The rules must be
published on the Commission’s website.
HB 2229 (Moore/Howard) creates the
Uniform Interstate Depositions and
Discovery Act. The measure creates uniform
procedures for the issuance of subpoenas.
HB 2548 (Stinson/Howard) creates the
Uniform Power of Attorney Act. The model
legislation adopted in approximately 30
states brings uniformity to the power of
attorney in the various states in probate
procedures. The measure provides
definitions and procedures used in the act
regarding the use of power of attorney. The
measure also repeals various existing
Oklahoma statutes regarding power of
attorney that are now addressed in the
measure.

77
HB 2746 (Ford/Newhouse) exempts
municipal or state law enforcement officers
employed in a county with a population of
more than 255,000 and federal law
enforcement officers from jury duty. The
measure provides that municipal or state law
enforcement officers in counties with a
population of less than 255,000 may serve
on noncriminal actions only.
HB 2913 (Wallace/Thompson) provides that
the Administrative Director of the Courts is
responsible for and has control over matters
concerning the budget, personnel,
technology, purchases and other
administrative operations over all courts of
this state, including the Court of Civil
Appeals and the Court of Criminal Appeals,
and performing such additional duties as
may be assigned by the Chief Justice.
Judiciary Funding
SB 343 (Paxton/Boles) clarifies the
authority of courts to collect court fines and
fees through tax warrant intercepts.
HB 2689 (Hasenbeck/Taylor) provides that
on October 1, 2021, each court reporter shall
receive a one-time stipend of $1,250.00.
HB 2869 (Wallace/Howard) provides a
salary increase to members of the Judiciary.
HB 2889 (Wallace/Thompson) appropriates
$7,500,000 from the General Revenue
Cashflow Reserve Fund to the Supreme
Court for the support of the District Courts.
HB 2912 (Wallace/Thompson) extends the
apportionment of $10 collected from district
court civil case filings to the Court Clerk’s
Records Management and Preservation Fund
until 2027.
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
District
Courts
$75,480,361
$68,241,076
-9.59%
District
Attorneys
and District
Attorney
Council
$56,642,149
$58,779,782
3.77%
Supreme
Court
$16,212,078
$16,223,855
0.07%
Oklahoma
Indigent
Defense
System
$17,508,363
$20,537,878
17.30%
$0
$20,000,000
$40,000,000
$60,000,000
$80,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
District Courts
$0
$20,000,000
$40,000,000
$60,000,000
$80,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
District Attorneys and
District Attorneys Council

78
Professions & Occupations
SB 49 (Floyd/Osburn) increases the initial
application fee for a chiropractic license
from $175.00 to $300.00 and removes the
examination fee of $175. The measure also
lowers the fee for an original license by
relocation of practice from $350 to $300.
Additionally, the measure allows applicants
to take an examination given by the National
Board of Chiropractic Examiners.
SB 100 (Stanley/Davis) modifies
requirements for applicants to take the
licensing examination administered by the
Board of Podiatric Medical Examiners. The
measure specifies applicants may fill out an
electronic application online and removes
the requirement for applicants to be free
from contagious or infectious diseases. The
measure also changes the requirement for
applicants to demonstrate loyalty to the
United States and states that such persons
must instead legally reside in the United
States.
SB 270 (Murdock/Hasenbeck) modifies
various provisions relating to veterinarians.
The measure defines telemedicine and
provides for veterinarians and clients to
interact in real-time via digital means. The
measure also creates the Probable Cause
Committee, which shall consist members
from the State Board of Veterinary Medical
Examiners as outlined in the measure. The
newly created Committee shall negotiate
and settle disputes. The measure also
extends the prohibition on the Veterinary
Center from entering into any program
agreements from 2018 to 2025. The measure
also creates a new duty for the State Board
to grant scholarships to an individual
advancing toward obtaining a degree in
veterinary medicine from an Oklahoma
higher education institution. The State Board
is authorized by the measure to contract with
third-party entities as necessary to carry out
this new duty. Additionally, the measure
provides for any member of the military or
their spouse licensed in another recognized
jurisdiction but residing in the state to
submit a completed application for licensure
or registration in Oklahoma.
SB 317 (Daniels/Sims) defines “student
electrical intern” and “listed electrical
apprentice” within the Electrical License
Act. The measure directs the Construction
Industries Board to issue a license as a listed
electrical apprentice to any person who has
been certified by the Committee of
Electrical Examiners as having 10,000 hours
of experience or more as an electrical
apprentice. Associated fees for the license
are set at the same rate as the registration for
electrical apprentices. The fee for an
electrical intern registration is set at half the
amount of the fee for the registration of
electrical apprentices. The measure also
prohibits electrical apprentices from
supervising the work of a registered
electrical intern. Only one intern may work
$13,500,000
$14,000,000
$14,500,000
$15,000,000
$15,500,000
$16,000,000
$16,500,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Supreme Court
$14,000,000
$16,000,000
$18,000,000
$20,000,000
$22,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Oklahoma Indigent Defense
System
79
on a job site under a single journeyman or
electrical contractor; however, the intern
shall not be counted against the maximum
number of apprentices who are allowed to
work under a journeyman. Up to 2 electrical
apprentices may work on a job site under a
single journeyman or electrical contractor.
SB 408 (Garvin/Miller) defines
“teledentistry” as the remote delivery of
dental patient care via telecommunications
and other technology for the exchange of
clinical information and images for dental
consultation, preliminary treatment planning
and patient monitoring. The measure also
adds the Commission on Dental
Competency Assessments to the list of
entities the Oklahoma Board of Dentistry
may accept examinations from and provides
that the Board may make allowances in
requirements of all candidates for licensure
and issue temporary licenses for extended
periods of time or as needed if government
officials declared a health pandemic through
a resolution. The resolution shall have a
beginning and an end date and shall
automatically expire no less than 30 days
after the end of the disaster is declared by
governmental officials. The measure
modifies the continuing education hours
required for oral maxillofacial surgery
assistants from 12 hours to 8 hours of
continuing education and requires such
courses to be taken every 2 years instead of
every 3 years. Publishing papers, presenting
clinics, and lecturing shall also qualify as 6
credited hours. The measure provides that
Residents and Fellows with a valid permit
may supervise student dental clinics under
the authority of the Dean or Associate Dean
of the University of Oklahoma College of
Dentistry. The measure adds the practices of
dental anesthesiology, oral medicine, and
orofacial pain as specialties that may be
licensed by the Board. The measure
consolidates the unprofessional conduct
sections for dental hygienists. SB 408
requires the patient record to include
documentation of any medications
prescribed, administered, or dispensed to the
patient. Additionally, the measure
establishes the required content of
continuing education courses provided to
dentists and dental hygienists and provides
for such courses to be taken online. The
measure also extends the period a laboratory
prescription may remain active from 3 years
to 7 years and authorizes dentists to refer
patients to a lab in order for the patient to
select the shading or matching shades of a
prosthetic device being prepared for the
dentist to deliver to the patient.
SB 654 (Standridge/Chad Caldwell) creates
a $25.00 annual renewal license fee for
resident care homes to replace the current
two-year renewal license fee of $50.00.
Renewal licenses may be issued for a period
24-36 months for the license period
immediately following November 1, 2021.
The measure also extends the maximum
licensure period for adult day care centers to
36 months. The measure also establishes a
$10.00 renewal fee per bed for a continuum
of care facility or assisted living center. This
renewal license shall expire 3 years from the
date of issuance. The initial license shall
expire 180 days from the date of issuance.
SB 748 (Jech/Martinez) provides for the
reports, proceedings, and other records
submitted to or generated by any peer
review committee or peer reviewer to be
privileged and not subject to discovery,
subpoena, or other means of legal
compulsion for their release. The design
professional who retains or employs the peer
reviewer or peer review committee is the
holder of the privilege. A peer review
committee or peer reviewer may report to
and discuss activities, information, and
findings with other peer review committees
80
or peer reviewers or the design professional
who retains or employs such reviewers. The
members of a peer review committee are
also exempt from any civil liability for
reporting activities and findings to another
reviewer or committee.
SB 850 (Dahm/Stark) authorizes licensees in
the fields of cosmetology and barbering to
provide services to customers in the
customer’s home. Such services shall not be
subject to inspection or rules promulgated
by the State Board of Cosmetology and
Barbering. Customers shall assume the
liability for the services and any home
equipment utilized by the licensee or
certificate holder and may review the
person’s license or certificate for validity
and authority to perform the services
requested.
HB 1102 (Olsen/Daniels) modifies the
categories of “unprofessional conduct” to
include the performance of an abortion
unless the procedure is performed to prevent
the death or significant physical impairment
of the mother. An abortion may not be
performed based solely on the mental or
emotional health of the mother,
notwithstanding a claim or diagnosis that the
woman may engage in conduct which she
intends to result in her death. The State
Board of Health shall impose penalties on
persons violating the provisions of this
measure which may include suspension of
the license for a period of not less than 1
year. The measure also directs the Attorney
General to calculate costs paid for by the
state or local entities in court challenges to
this act. The office of the Attorney General
is also required to report such amounts for
each calendar quarter to all members of the
Legislature.
HB 1147 (Osburn/Pugh) redesignates the
State Architectural and Registered Interior
Designers Act as the State Architectural and
Registered Commercial Interior Designers
Act and designates interior designers as
commercial interior designers. The measure
adds definitions for commercial interior
designer, nonstructural commercial interior
construction, and fire and life safety
systems. Additionally, the measure requires
each registered commercial interior possess
a seal showing certain information outlined
in the measure. All technical submissions
prepared by such registered commercial
interior designer, or under the responsible
control of the registered commercial interior
designer, shall be sealed, signed and dated.
The measure prohibits a registered
commercial interior designer from accepting
or receiving compensation from an
individual other than their client in
connection with reparation or construction
of a building interior in which they are
employed and from bidding or holding
interest in an entity bidding for a contract for
reparation or erection of a structure for
which they have prepared plans or
specifications, unless the contract is a
design/build contract.
HB 1148 (Osburn/Rosino) provides that
only a real estate licensee may market for
sale an equitable interest in a contract for the
purchase of real property between the
property owner and a prospective purchaser.
HB 1150 (Osburn/Rogers) gives the
Construction Industries Board rulemaking
authority to implement the provisions of the
Plumbing License Law of 1955, including
categories and limitations for licensure.
HB 1742 (Dills/Newhouse) adds a definition
for alkaline hydrolysis as it relates to
cremation as well as defines crematory as a
structure containing a furnace or alkaline
hydrolysis vessel. The measure eliminates
the $25.00 fee for funeral directors applying
81
for a license after failing to renew said
license within a 3-year period.
HB 1817 (Dempsey/Rader) 7 exempts
501(c)(3) organizations that meet certain
conditions from the provisions of the
Oklahoma Secure and Fair Enforcement for
Mortgage Licensing Act.
HB 1934 (Martinez/Paxton) provides that
any provision in a design professional
services agreement which requires an entity
or its insurer to indemnify or otherwise hold
harmless another entity against liability
arising from death or bodily injury, or
damage to property, due to negligence or
fault of the entity or its agents is void and
unenforceable.
HB 2072 (McCall/Bullard) authorizes the
Oklahoma Funeral Board to issue a
temporary funeral director or embalmer
license in the event a statewide emergency is
declared by the Governor. The authorization
ends 1 year from the effective date of the
act.
HB 2680 (Marti/Rosino) specifies that the
practice of optometry shall include the
dispensing of medications to treat ocular
abnormalities.
HB 2741 (Ford/Howard) allows a tow
operator or wrecker yard operator to release
a motor vehicle to a legal representative or
an immediate family member who is within
the first or second degree of consanguinity
or affinity if the owner of the vehicle is dead
or incapacitated. The measure increases the
license application fee for a wrecker license
from $100.00 to $500.00. The measure
apportions $90.00 to the General Revenue
Fund and $410.00 to the Department of
Public Safety Restricted Revolving Fund to
administer the Wrecker Services Division
and modernize computer programs. The
measure increases the wrecker license
renewal fee from $50.00 to $250.00 and
apportions $200.00 to the Department of
Public Safety Restricted Revolving Fund to
administer the Wrecker Services Division
and modernize computer programs. The
measure removes a requirement that the
Tow Request and Authorization Form be
completed in quadruplicate. Allows the
Department to notify the owner of a towed
vehicle the vehicles location by first-class
mail. The measure allows for the release of
personal property in a towed vehicle when
the registered owner or representative of the
owner provides proof of identity.
HB 2770 (Randleman/Standridge) modifies
the court in which appeals, or legal actions
are brought as it relates to the Psychology
Interjurisdictional Compact. The court is
changed from the U.S. District court for the
state of Oklahoma to the U.S. District court
for the state of Georgia.
HB 2873 (Wallace/Leewright) creates the
Universal Licensing Recognition Act. The
measure provides that a person moving to
Oklahoma would be able to apply for
licensing or certification for an occupation
with a similar scope of practice, and the
applicant supplies verifiable proof of
physical residency in the state or is married
to and accompanying an active-duty
member of the Armed Forces to an official
permanent change of station to a military
installation located in the state. The
Oklahoma regulatory entity would apply all
similar and verifiable work experience in the
manner most favorable to the applicant.
Certain examination requirements and fees
would still apply to the applicant. The
applicant must also demonstrate that they
are free of any complaint, investigation,
suspension, revocation or discipline by any
other regulatory entity or jurisdiction for
unprofessional conduct.
82
Public Safety
SB 3 (Bullard/Humphrey) authorizes
sheriffs and peace officers to utilize
telemedicine to assess a person whom the
officer reasonably believes needs treatment
by a mental health professional.
Additionally, the measure requires officers
to transport such individuals in need of
treatment or subject to an emergency
detention or protective custody order to the
nearest facility within a 30- mile radius. The
law enforcement agency that transported
such an individual to an urgent recovery
clinic shall be responsible for any
subsequent transportation of such individual
pending completion of the initial
assessment, emergency detention, protective
custody, or inpatient services. If no such
facility is available, transportation to a
facility shall be completed by either the
Department of Mental Health and Substance
Abuse Services or an entity contracted by
the Department for alternative
transportation.
SB 10 (Taylor/Dick Lowe) eliminates the
November 1, 2022, sunset date as it relates
to the $10.00 fine applied to persons
convicted of a speeding violation 1-10 miles
per hour over the speeding limit.
SB 17 (Floyd/Bush) specifies that an officer
conducting a lethality assessment on a
potential domestic abuse victim must
implement the protocol referral process to a
domestic violence advocate from a certified
or tribal program in a manner outlined in the
measure. Regardless of the results of the
lethality assessment, referral information for
shelters, domestic violence programs and
other social services must be provided to the
victim.
SB 87 (Haste/Bush) authorizes persons in
possession of a controlled dangerous
substance who appear to be in need of help
to, in lieu of arrest, be taken to an approved
drug treatment center or approved center for
substance abuse evaluation by a law
enforcement officer. Such centers shall be
subject to the appropriate county, municipal,
or tribal authority. The Department of
Mental Health and Substance Abuse
Services may approve or disapprove
individual treatment centers. Additionally,
the treatment center must receive annual
approval from the county’s district attorney.
SB 94 (Hall/Mize) adds the President of the
Association of Oklahoma Narcotic
Enforcers and the Executive Director of the
State Board of Pharmacy or their designees
as members to the Opioid Overdose Fatality
Review Board.
SB 106 (Allen/ODonnell) modifies various
provisions of the Oklahoma Self-Defense
Act. The measure defines completed
application to mean all fields are completed,
questions answered and contains all required
signatures on the Application for Self-
Defense Act License and all required
documents. The 90-day renewal grace
period provided to license holders is
removed from the Act and requires renewal
applications to be denied if a current license
is pending suspension or revocation or has
been suspended or revoked. Additionally,
the measure removes the preclusive period
for holders that have 2 or more convictions
of public intoxication provided the holder
has a certified statement from a licensed
physician stating that the person is not in
need of substance abuse treatment. The
measure establishes a preclusive period of 5
years for persons whose license was
suspended or revoked. The measure requires
the Oklahoma State Bureau of Investigation
to utilize the Immigration Alien Query
database for non-United States citizens in
the course of its background check and
83
authorizes the Oklahoma State Bureau of
Investigation OSBI to conduct a National
Instant Criminal Background Check (NICS)
as part of the license background check.
SB 172 (Rosino/Walke) directs the
Oklahoma State Bureau of Investigation
(OSBI) to coordinate with the United States
Attorney’s Office and the United States
Department of Justice to obtain federal
funding no later than January 1, 2022, for
the purpose of gathering data to address the
issue of missing and murdered indigenous
persons. The measure creates the Office of
Liaison for Missing and Murdered
Indigenous Persons under the OSBI. The
newly created Office shall work with tribal,
state, and federal authorities on missing
persons and homicide cases, provide
guidance to victims’ families, facilitate
training and promote best practices, and
consult with community organizations to
promote community relations.
SB 242 (Thompson/Dustin Roberts)
modifies the membership of the Council on
Law Enforcement and Education Training
(CLEET) by requiring the appointee from
the Oklahoma Department of Career and
Technology to have experience in the
creation and review of curriculum as well as
experience in teaching criminal justice or
law enforcement courses. The measure
further requires CLEET’s application form
to not exceed 20 pages.
SB 272 (Weaver/Worthen) creates the
Kelsey Smith Act. The measure authorizes a
law enforcement agency, as defined in the
measure, to request and receive the call
location of a user’s communication device
from a telecommunication company in order
to respond to a call for emergency services
or in an emergency situation that involves
risk of death or serious physical harm. The
measure requires notice to be provided to
the user whose information was provided to
law enforcement 30 days after the call for
emergency services or the emergency
situation. Every telecommunication
company registered to do business in the
state must annually submit emergency
contact information to the Oklahoma State
Bureau of Investigation (OSBI) to facilitate
requests from a law enforcement agency.
Carriers are not required to submit
emergency contact information for
individual.
SB 283 (Brooks/Ford) requires persons
convicted of giving alcohol to a minor to
attend a victims impact panel program in
addition to other fines levied for such
violations.
SB 304 (Jech/Gann) amends the judgment
and sentence form used to transfer a prisoner
to the custody of the Department of
Corrections. The measure clarifies the role
of jail trust administrators as it relates to
such transfers.
SB 312 (Burn/Dempsey) provides for
persons convicted of identity theft from a
victim less than 18 years of age shall be
guilty of a felony and face a term of
imprisonment of not less than 2 years and
not more than 10 years as well as a fine of
not more than $100,000.00.
SB 319 (Standridge/Pae) exempts research
institutions conducting a scientific study on
tobacco use and cessation from the
provisions prohibiting the distribution of
tobacco products to persons under 21 years
of age.
SB 320 (Garvin/McEntire) provides for the
“medically frail” and “medically vulnerable”
as defined in the measure to receive
consideration in compassionate parole
proceedings. The measure defines medically
84
frail as it relates to medical parole to mean
an individual with a medical condition
which precludes the individual from
performing 2 or more activities of daily
living on their own. The measure also
defines medically vulnerable as an
individual with 1 or more medical
conditions which makes the individual more
likely to contract an illness or disease while
incarcerated that could lead to death or
cause an individual to become medically
frail. The measure specifies the medical
conditions that place an individual in the
medically vulnerable category. The measure
also requires victim notification to be
provided.
SB 348 (Paxton/Worthen) creates a statute
of limitations for first- and second-degree
manslaughter. The statute of limitations is
set at 10 years after the crime is reported to a
law enforcement agency.
SB 361 (David/Wallace) allows immediate
family members to participate in peer
support counseling sessions provided to
emergency and public safety personnel and
provides for said participation to be kept
confidential.
SB 365 (David/Steagall) creates the
Oklahoma Distinguished Meritorious
Service Medal for extended exemplary
service to the state and provides for the
award to be granted posthumously.
SB 367 (David/Kannady) authorizes
Intermediate Emergency Medical
Technicians, Advanced Emergency Medical
Technicians, or paramedics to withdraw
blood for the purpose of testing a person’s
blood alcohol content. The measure also
removes tests involving a person’s breath,
saliva, or urine from the list of tests whose
costs are borne by law enforcement.
Additionally, the measure outlines standards
for any breathalyzer test to be considered
admissible as evidence in court proceedings.
Such tests must use a device that is
accredited by the U.S. Department of
Transportation in the Federal Register and
calibrated by a device from a list of
approved devices published by the U.S.
Department of Transportation. The test must
also be administered by a person properly
licensed by the Board of Tests for Alcohol
and Drug Influence. The FS provides that
analysis of a person’s blood to be considered
valid and admissible in evidence must be
performed by a properly accredited
laboratory.
SB 371 (David/O’Donnell) creates the
Unified State Law Enforcement
Commission. The Commission is tasked
with studying and evaluating the feasibility
of unifying the Oklahoma State Bureau of
Investigation, the Oklahoma Bureau of
Narcotics and Dangerous Drugs, and the
Department of Public Safety into a single
law enforcement agency. The Commission
is also directed to submit its findings to the
Governor, President Pro Tempore of the
Senate, Speaker of the House, and minority
leaders of the Senate and House no later
than December 1, 2021. The Commission
will be comprised of 10 members. Members
will not receive compensation but shall be
eligible to receive travel reimbursements.
Members are directed to meet at least once a
month.
SB 403 (Stanley/Manger) modifies
provisions of law barring any person from
interfering with or disrupting business. The
measure adds political subdivisions and
clarifies that disrupting business shall
include publicly posted meetings.
SB 456 (Coleman/Mize) adds inmates
convicted on counts relating to child abuse
or neglect as well as inmates convicted of
85
exploitation of a vulnerable adult to the list
of persons deemed ineligible to be placed in
the Electronic Monitoring Program.
SB 631 (Hamilton/Sean Roberts) creates the
Second Amendment Sanctuary State Act.
The measure occupies and preempts the
entire field of legislation by any agency of
this state or political subdivision in this state
to infringe upon the rights of a citizen of the
State of Oklahoma the unalienable right to
keep and bear arms. The preemption shall
include the provisions of the National
Firearms Act of 1934 and the Gun Control
Act of 1968.
SB 646 (Bergstrom/Steagall) authorizes
employees and owners of an establishment
serving alcohol to carry a firearm. The
employee must receive permission from the
owner to carry a firearm. Additionally, the
measure caps the fine for persons convicted
of violating the prohibition on carrying
firearms in a bar, refusing to leave an
establishment, or refusing to leave the bar at
$250.00.
SB 672 (Murdock/Patzkowsky) clarifies that
a person who is member or veteran of the
United States Armed Forces, Reserves or
National Guard or was discharged under
honorable conditions from the United States
Armed Forces, Reserves, or National Guard
between the ages of 18 to 21 to transport a
firearm on a public highway in his or her
vehicle. The measure also clarifies that any
person between the ages of 18 to 20 may
transport an unloaded firearm on a public
highway in or on his or her vehicle.
SB 801 (Weaver/Kevin West) requires
supervising agencies or contracted providers
as it relates to community sentencing to file
a statement with the court defining the
provision which has been successfully
completed instead of the administrator of the
local system.
SB 848 (David/Wallace) direct the
Department of Mental Health and Substance
Abuse Services to contract with public and
private entities to provide peer support crisis
intervention, counseling, and wellness for
the law enforcement, firefighter, emergency
medical, and corrections communities
impacted by trauma, anxiety, or addiction.
Such entities must be qualified shall be
required to be derived from the International
Critical Incident Stress Foundation (ICISF)
and shall employ the Critical Incident Stress
Management (CISM) crisis intervention
process. The measure outlines the content of
the training that must be provided.
SB 889 (Weaver/Josh West) modifies
retirement disbursement language to comply
with recent revisions to the Internal Revenue
Service and Treasury Regulations.
SB 926 (Jett/Eric Roberts) authorizes
municipalities to issue citations for
discharging an air powered pistol or rifle
when the projectile leaves the premises in an
intentional or negligent manner to the
individual or guardian of the individual who
discharged the air powered pistol or rifle.
SB 980 (Weaver/Worthen) adds the offenses
of child sexual exploitation or permitting
child sexual exploitation and soliciting
sexual conduct or communication with a
minor by use of technology to the list of
crimes allowing the court to authorize wire
the interception of wire, oral, or electronic
communications by law enforcement.
HB 1023 (Worthen/Weaver) provides that
any contraband item seized in a prison by
any agency may be forfeited by said agency
and sold in the manner governing the sale of
seized property by a peace officer.
86
HB 1026 (Worthen/Montgomery) provides
that the Council on Law Enforcement
Education and Training may establish and
certify additional law enforcement and
criminal justice programs at institutions
operating under the State Board of Career
and Technology Education for teaching
students between 16 and 19 years of age.
The tuition or fees for law enforcement and
criminal justice-related programs shall be
similar in cost as other vocational and
technical education courses and subjects
offered at technology center schools.
HB 1029 (Kerbs/Weaver) expands the
category of “security guard” to include
active reserve certified peace officers as it
relates to the Oklahoma Security Guard and
Private Investigator Act.
HB 1095 (Strom/Daniels) allows the court
to prohibit a defendant from entering,
visiting or residing within the judicial
district in which the defendant was
convicted until after completion of his or her
sentence. The court must ensure the
defendant has access to services or programs
which the defendant is required to
participate as a condition of probation. The
measure provides that when seeking to enter
the prohibited judicial district for personal
business not related to his or her criminal
case, the defendant shall be required to
obtain approval by the court.
HB 1135 (Fetgatter/Taylor) modifies
provides that a peace officer, government
employee engaged in the performance of
their duties, firefighters, emergency medical
personnel, or public utility employees
engaged in addressing an emergency, and
parties engaged in oil and gas operations
may enter garden, yard, pasture, or field of a
landowner without their express permission.
The measure also permits railroad
employees and emergency equipment from
entering such land to restore rail service, the
entrance of utility employees or contractors
while acting in the scope of their
employment, and employees or contractors
of valid easement or license holders while
acting in the scope of their employment to
enter the land. The measure also provides
for several persons of certain occupations to
enter the land of the owner unless expressly
prohibited from doing so. The measure
provides that a person convicted of entering
another’s land to commit waste, theft, or
damage shall be guilty of a misdemeanor
punishable by imprisonment in the county
jail for a term of not less than 30 days and
not more than 6 months as well as a fine of
not less than $50.00 and not more than
$500.00.
HB 1246 (McCall/Treat) would allow an
individual’s Social Security number to be
sufficient documentation when securing a
prescription that requires state-issued
identification, if the individual’s state-issued
identification card has been expired for less
than 1 year and they have no other form of
identification that complies with the
requirements.
HB 1567 (Boatman/Weaver) provides that
possessing 28 grams or more of heroin shall
constitute aggravated trafficking.
Additionally, persons found to traffic at least
1 gram of Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)
or Phencyclidine (PCP) shall be subject to a
maximum term of imprisonment of 20 years
and imposes a minimum of 2 years and
maximum of life in prison for persons
trafficking more than 10 grams of LSD or
PCP. Persons found to have trafficked 1
gram of fentanyl shall be subject to a
maximum term of imprisonment of 20 years
and a fine of not less than $100,000.00 and
not more than $250,000.00. Persons found
to have trafficked 5 grams of fentanyl shall
87
be subject to a minimum term of 2 years and
a maximum term of imprisonment for life
and a fine of not less than $250,000.00 and
not more than $500,000.00.
HB 1630 (David Hardin/Pemberton) amends
various sections of the Oklahoma Self-
Defense Act. The measure provides that
renewal applications are to be denied if the
current license is subject to suspension or
revocation or if the license has previously
been suspended or revoked by the Bureau
and removes the ability of the Bureau to
examine medical or other records during a
renewal application. Additionally, a person
who has been precluded from obtaining a
carry license due to convictions for public
intoxication may obtain a certified statement
from a licensed physician stating that the
person is not in need of substance abuse
treatment to remove the preclusion. A 5-year
preclusion period is also created if a
previously issued handgun license has been
revoked. The measure requires the OSBI to
conduct a search of the Immigration Alien
Query for non-United States citizens as part
of its background check and requires
applicants to include a declaration of
citizenship or admission number for a non-
United-States citizen. The measure requires
the applicant to acknowledge that the
applicant has reviewed the Federal Bureau
of Investigation Privacy Act Statement. The
measure requires that the license card
contain the date of issuance of the handgun
license.
HB 1643 (Humphrey/Bullard) prohibits any
individual from publishing identifying
information of a law enforcement officer
with the intent to threaten, intimidate,
harass, or stalk law enforcement officials.
Individuals convicted of violating the
provisions of this measure are subject to a
misdemeanor punishable by up to 6 months
in the county jail, a fine of up to $1,000.00
or both fine and imprisonment. Punishment
for a second or subsequent offense is up to 1
year in the county jail, a fine of up to
$2,000.00 or both fine and imprisonment.
The measure allows elected county officials
and peace officers to request that the county
assessor not make information available on
the internet.
HB 1651 (Humphrey/Bullard) repeals the
requirement for persons convicted after
November 1, 2012, to be subject to post-
imprisonment supervision for a period of not
less than 9 months nor more than 1 year
following confinement of the person.
HB 1674 (Kevin West/Standridge) provides
that any person who unlawfully obstructs the
normal use of any public street, highway, or
road within by restraining motor vehicle
traffic, by approaching motor vehicles, or by
endangering the safe movement of motor
vehicles or pedestrians are guilty of a
misdemeanor punishable by up to 1 year in
the county jail, a fine on not less than
$100.00 nor more than $5,000.00, or both
such fine and imprisonment. Additionally,
the person is liable for all damages to person
or property. The measure provides that a
motor vehicle operator who unintentionally
causes injury or death while fleeing a riot is
not to be held criminally or civilly liable.
The measure provides that if an organization
is found to be a conspirator with persons
committing riot related crimes, the
organization may be punished by a fine that
is ten times the amount of said fine
authorized by the appropriate provision.
HB 1679 (Stark/Weaver) creates the Sarah
Stitt Act. The measure directs the
Department Corrections to provide inmates
released from its custody with relevant
documentation to assist the inmate in
obtaining post-release employment and to
coordinate with the Department of Public
88
Safety to provide a REAL ID Noncompliant
Identification Card if the inmate does not
have a current state-issued identification
card or driver license. The measure provides
that if no other form of identification is
available, the Department of Public Safety
shall allow the use of a Department of
Corrections consolidated record cards to
serve as a valid identification document to
obtain a REAL ID Noncompliant
Identification Card. REAL ID Noncompliant
Identification Cards issued with a
consolidated record card from the
Department of Corrections for inmates shall
be valid for a period of 4 years from the
month of issuance. The fee charged for the
issuance or replacement of a REAL ID
Noncompliant Identification Card shall be
deposited in the Department of Public Safety
Revolving Fund.
HB 1684 (Grego/Coleman) allows a peace
officer to file a report with the district
attorney to see if an arrest is warranted as it
relates to investigations involving certain
gambling offenses.
HB 1753 (CrosswhiteHader/Haste) removes
the requirement for the Carl Albert Mental
Health and Substance Abuse Services
Center to provide a psychiatrist to the
Department of Corrections.
HB 1759 (Ranson/Taylor) prohibits the use
of malicious computer programs on a
computer or computer network as defined in
the measure and provides that is it unlawful
to willfully solicit another of any acts
prohibited by the Oklahoma Computer
Crimes Act.
HB 1770 (Dobrinski/Weaver) provides that
it shall be unlawful for any person to
maliciously throw an object at or in the
direction of any person riding a bicycle,
equine, or animal drawn vehicle. Persons
convicted of violating this provision shall be
subject to a term of imprisonment not more
than 1 year and/or a fine of $500.00.
Additionally, no driver of any vehicle shall
use a horn when passing a person riding a
bicycle, equine or animal-drawn vehicle
under normal conditions if no imminent
danger of a collision exists. The measure
also provides that bicyclists may extend
their arm horizontally to the right to signal a
right turn and may extend their right hand
and arm downward to their right side to
signal a stop or decrease in speed.
HB 1777 (Conley/Weaver) requires
toxicology laboratories collecting and
analyzing blood, breath, saliva, or urine for
law enforcement to be accredited by the
American Board of Forensic Toxicology or
by an accrediting body with an independent
system based upon ISO/IEC 17025
standards.
HB 1880 (Tammy West/Jech) authorizes
district attorneys to create restorative justice
programs for nonviolent offenders who
qualify for a deferred prosecution
agreement. The measure authorizes the
District Attorneys Council to develop and
administer a 5-year restorative justice pilot
program utilizing citizen-led mediation
panels. The measure defines the term
“restorative justice” as an alternative means
to the traditional criminal justice model for
qualifying nonviolent offenses. The measure
provides that the pilot program is to expire
November 1, 2026.
HB 1892 (Boatman/Weaver) creates the
Advisory Task Force on Prevention of
Human Trafficking and Child Exploitation.
The Task Force shall be comprised of 13
members and is directed to study human
trafficking, prostitution, and child
exploitation in the state. The Task Force is
directed to create and provide a report of
89
such studies to the President Pro Tempore of
the State Senate, the Speaker of the House,
and the Governor by February 1, 2022. A
Senate member of the Task Force is required
to call the first meeting to order by
September 1, 2021. Staff of the Oklahoma
State Senate and Oklahoma House of
Representatives shall jointly assist in
staffing the Advisory Task Force.
HB 1948 (Cruz/Floyd) broadens the term
family or household members as it relates to
the Protection from Domestic Abuse Act
and in the Domestic Abuse Reporting Act to
include persons otherwise related by blood
or marriage.
HB 1967 (Nollan/Pemberton) requires
school bus drivers to report a violation of
passing a loading or unloading school bus
on or before the end of the next business day
following the alleged offense instead of
within 24 hours of the alleged offense.
HB 2053 (McCall/Standridge) requires law
enforcement officers issuing a citation for
unsafe tire tread depth to include the tread
depth of the offending tire on the citation.
HB 2054 (McCall/Standridge) authorizes
motorists to drive in the left lane while not
attempting to pass another motorist if the
left lane is on a county road and if the
roadway is not part of the Interstate or
turnpike system.
HB 2056 (McCall/Rader) provides that
when there is an active lien from a
commercial lender in place on a vehicle,
motor license agents shall be prohibited
from transferring the certificate of title on
that vehicle until the lien is satisfied.
HB 2095 (Lepak/Daniels) modifies
racketeering as relates to the Oklahoma
Racketeer-Influenced and Corrupt
Organizations Act to include unlawful
assemblies.
HB 2236 (May/Weaver) creates a new
felony for failing to report to an employer,
insurance carrier, or thirdparty administrator
any earned income while receiving
temporary total disability benefits. The
measure also changes the qualification
requirements for personnel assigned to the
Workers’ Compensation Fraud Investigation
Unit by requiring personnel to be certified as
a peace officer by the Oklahoma Council on
Law Enforcement Education and Training in
lieu of a minimum of 3 years of certified law
enforcement experience.
HB 2275 (Josh West/Pemberton) directs the
Community Sentencing Division of the
Department of Corrections to submit
statistical information relating to community
sentencing participation by county, the total
number of qualifying and non-qualifying
community sentences per month for each
local community sentencing system, total
number of community sentences ordered per
month, program participation, and the
annual average cost per offender. The
measure provides that a copy of the report
must be submitted to the Oklahoma
Statistical Analysis Center for publication
on the Oklahoma State Bureau of
Investigation’s website.
HB 2295 (Dustin Roberts/Leewright)
provides that a person arrested for the
violation of a protective order, an act of
domestic violence, domestic abuse, stalking
or harassment shall not be eligible for a
personal recognizance bond.
HB 2316 (Lawson/Rader) modifies the
competency evaluation process to include
youthful offenders in addition to
delinquency. The measure also adds
language that a copy of the child’s petition
90
or information is presented to the court. The
measure also modifies who may file a
motion for determination of competency to
state that the district attorney or the child’s
attorney shill file this motion under a
reasonable basis. At any time prior to or
during delinquency or youthful offender
proceedings, the Office of Juvenile Affairs
may file a Motion to Intervene to raise
issues of competency.
HB 2515 (Stinson/Daniels) clarifies that
child abuse and neglect may apply to any
person responsible for the health of the child
instead of merely the child’s parents.
HB 2544 (Stinson/Jech) redefines the
definition of vulnerable adult to remove the
requirement to have to be in a nursing home.
HB 2546 (Munson/Floyd) creates the
“Sexual Assault Victims’ Right to
Information Act. The measure provides that
a sexual assault victim retains the rights
provided in the measure regardless of
whether the victim agrees to participate in
the criminal justice system at any time and
regardless of whether the victim agrees to
receive a medical evidentiary examination to
collect sexual assault forensic evidence.
Such rights include the right to
confidentially consult, either in person
virtually or telephonically, with a sexual
assault victims’ advocate before the
commencement of any medical evidentiary
or physical examination and the right to
request and receive the results and status of
the analysis of the sexual assault forensic
evidence relating to the victim. Additionally,
if the victim retains counsel, such counsel
may be present during all stages of the
investigation or other interaction with
representatives from the legal or criminal
justice systems within the state.
HB 2645 (Echols/Bergstrom) prohibits any
person from carrying a firearm on property
set aside by a county, city, town, public trust
with a county, city or town as a beneficiary,
or state governmental authority for an event
that is secured with minimum-security
provisions. Such events must meet the
criteria outlined in the measure. A person
may carry a firearm on such property if the
property does not meet the minimum-
security provisions outlined in the measure.
HB 2656 (Echols/Taylor) modifies
definition of marijuana to strike the
reference to cannabidiol as it relates to a
federally approved drug or substance. The
measure provides that any prescription drug
approved by the federal Food and Drug
Administration that is designated,
rescheduled, or deleted as a controlled
substance under federal law is to be
excluded from Schedule I and must be
prescribed, distributed, dispensed, or used in
accordance with federal law unless the
Board of Pharmacy acts. If the Board of
Pharmacy does not act, the drug is deemed
to be designated, rescheduled, or deleted as
a controlled substance.
HB 2666 (Echols/Garvin) clarifies the
definition of rape to include acts within or
without the bonds of matrimony.
HB 2773 (Pfeiffer/Weaver) requires
members of the Pardon and Parole Board to
uphold and promote the independence,
impartiality, fairness, and integrity of the
Board and to avoid impropriety or the
appearance of impropriety. A member of the
Board who determines that circumstances
would cause a reasonable person with
knowledge of all the relevant facts would
question the board members impartiality the
board member must disclose any potential
conflict of interest and withdraw from
participation in the matter.
91
HB 2774 (Pfeiffer/Bullard) requires all law
enforcement agencies, sheriffs, jailers,
prison keepers, and their deputies who have
custody of a person who is the subject of an
immigration detainer request to comply with
any request made in the immigration
detainer request provided by the federal
government and to inform persons identified
in the immigration detainer request that they
are being held because of the request. If a
person provides proof of citizenship,
sheriffs, jailers, and prison keepers are not
required to hold the person. The measure
also requires all sheriffs, jailers, prison
keepers, and their deputies to allow
reasonable access to their detention facilities
to the United States Immigration and
Customs Enforcement for the purpose of
identifying inmates.
HB 2877 (Wallace/Taylor) authorizes
sheriffs and peace officers to utilize
telemedicine to assess a person whom the
officer reasonably believes needs treatment
by a mental health professional.
Additionally, the measure requires officers
to transport such individuals in need of
treatment or subject to an emergency
detention or protective custody order to the
nearest facility within a 30- mile radius. The
law enforcement agency that transported
such an individual to an urgent recovery
clinic shall be responsible for any
subsequent transportation of such individual
pending completion of the initial
assessment, emergency detention, protective
custody, or inpatient services. If no such
facility is available, transportation to a
facility shall be completed by either the
Department of Mental Health and Substance
Abuse Services or an entity contracted by
the Department for alternative
transportation.
Public Safety and Law Enforcement
Funding
SB 1054 (Thompson/Wallace) directs
monies from the General Appropriations
Bill (HB 2900) provided to the Department
of Public Safety to be spent in the following
manner:
1) $439,120.00 for any necessary
expenditures related to interoperable
communications inside the State Capitol
Building
2) $4,000,000.00 to hold a trooper academy
or additionally academies, subject to
available funding.
SB 1082 (Thompson/Wallace) apportions
the appropriations made to the Oklahoma
Department of Commerce in HB 2900 in the
following manner:
1) $1,460,000.00) to implement the
provisions of Aerospace Commerce
Economic Services Act
2) $15,000,000.00 shall be used to fund and
implement the Oklahoma Accelerator
Program
HB 1015 (Roe/McCortney) strikes obsolete
language as it relates to reimbursing county
jails for medical care provided to inmates.
HB 2908 (Wallace/Thompson) requires the
Department of Corrections to direct funds in
the following manner:
1) $8 million to improve the correctional
officer to inmate ratio at correctional
facilities
2) $9.24 million for hepatitis C treatment;
3) $1.8 million for a contractual per diem
increase at the Lawton Correctional and
Rehabilitation Facility; and
4) $9,235,258 for transfer to the Department
of Corrections Offender Management
System Revolving Fund.
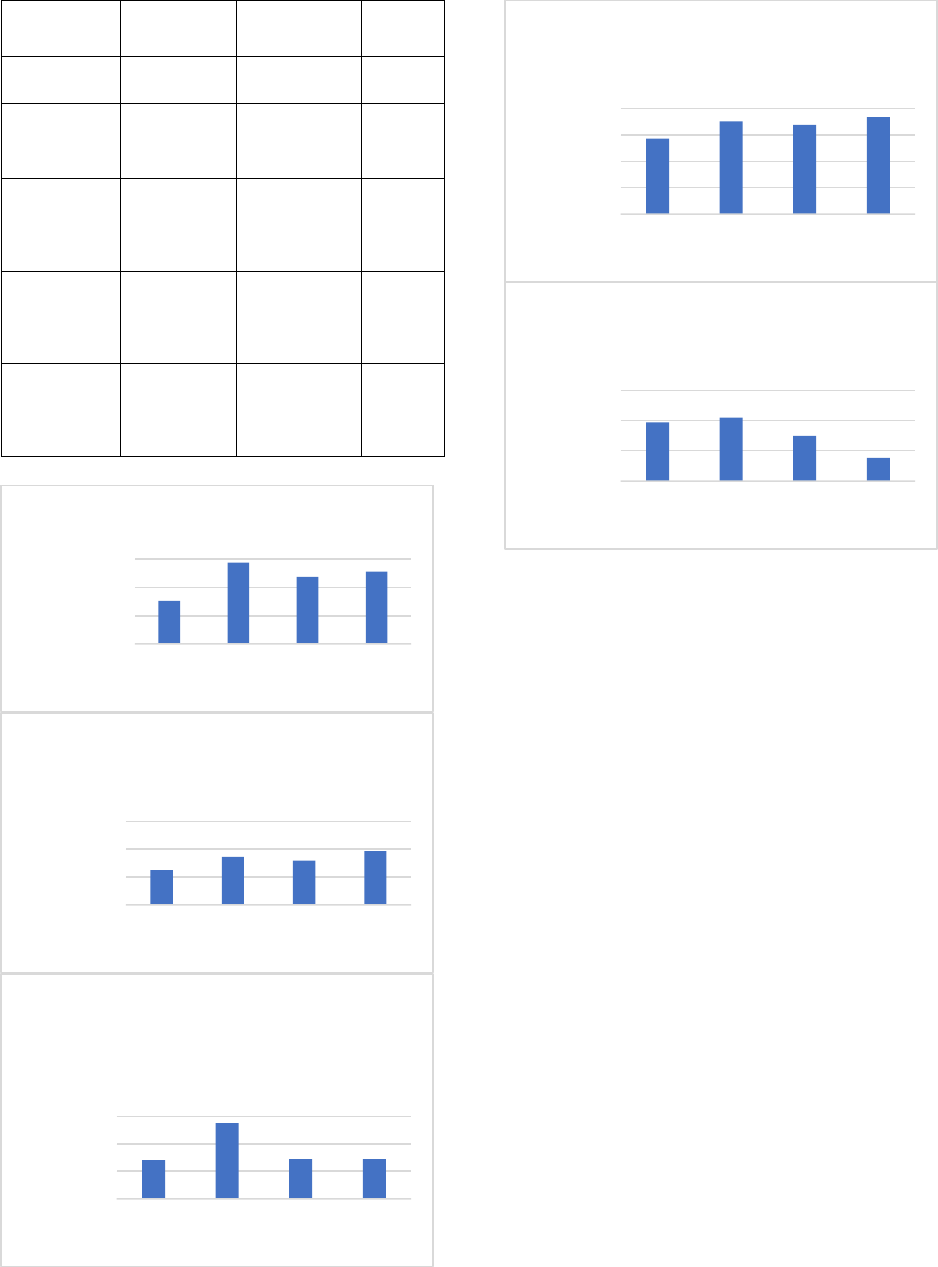
92
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Department of
Public Safety
$101,824,395
$102,827,246
0.98%
Oklahoma
State Bureau
of
Investigation
$75,480,361
$68,241,076
-9.59%
Oklahoma
Bureau of
Narcotics and
Dangerous
Drugs
$3,145,330
$3,145,330
0.00%
Council on
Law
Enforcement
Education and
Training
$3,370,833
$3,661,579
8.63%
Alcoholic
Beverage
Laws
Enforcement
Commission
$2,898,589
$2,753,659
-5.00%
Public Employees-
Retirement/Insurance/Pay/Benefits
SB 107 (Montgomery/Russ) authorizes the
Office of Management and Enterprise
Services to renew vision plan contracts with
plan providers for succeeding 1-year terms if
the provider had a contract for the
immediately preceding year. The Office may
require the provider to submit rate
schedules, contact information for the plan,
policy limits and applicable deductibles, and
billing practices of the plan prior to the
renewal.
SB 267 (Pemberton/Nichols) provides for
members of the Teacher Retirement System
that retired as of July 1, 2020, who received
benefits for at least 1 year to be reemployed
by a school district with no limitations on
earnings, provided the teacher was not
employed in a school district during the 1-
year period.
$90,000,000
$95,000,000
$100,000,000
$105,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Department of Public Safety
$0
$10,000,000
$20,000,000
$30,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Oklahoma State Bureau of
Investigation
$3,000,000
$3,100,000
$3,200,000
$3,300,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Oklahoma Bureau of
Narcotics and Dangerous
Drugs
$0
$1,000,000
$2,000,000
$3,000,000
$4,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Council on Law Enforcement
Education and Training
$2,600,000
$2,800,000
$3,000,000
$3,200,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Alcoholic Beverage Laws
Enforcement Commission
93
SB 333 (Simpson/Townley) extends the
time limit within which accrued
compensatory time may be used by state
employees and provides for such accrued
time to be carried over into the new fiscal
year after the Governor declares an
emergency.
SB 650 (David/Echols) modifies the
statutory minimum benefit allowance
amount for employee benefit plans
beginning with Plan Year 2022. The act
requires that the allowance amount for Plan
Year 2022 be increased by 2% from the
previous year’s amount and provides for an
additional 2% increase in the allowance
amount for Plan Year 2023 from the
previous year’s amount. It then establishes
the allowance amount in Plan 2023 as the
statutory minimum benefit allowance
amount.
SB 683 (Kidd/Lepak) removes the
requirement for full-time nonclassified
optional personnel to have been regularly
employed for a full year before joining the
Teachers’ Retirement System. The measure
also provides for all nonclassified optional
personnel regularly employed for 20 hours
or more per week to be enrolled in the
System upon hiring. Such persons may opt
out of the System within 30 days of hiring.
The opt out shall be irrevocable, unless the
person is later hired into a classified
position.
SB 684 (Weaver/Moore) authorizes the
Oklahoma State Bureau of Investigation, the
Oklahoma Bureau of Narcotics and
Dangerous Drugs, the Oklahoma Highway
Patrol, and the Oklahoma Alcoholic
Beverage Laws Enforcement to enter into
bilateral interagency transfers among
commissioned law enforcement officers.
The measure specifies that such transfers
must be for a period between 2-5 years.
SB 687 (Weaver/Humphrey) directs the 9-1-
1 Management Authority to begin
implementing the Next Generation 9-1- 1
program, which shall provide for
connectivity and interoperability between
state, regional, and local next-generation
systems. Training program standards must
include instruction on recognizing the need
for and delivery of HighQuality
Telecommunicator CPR (T-CPR) following
evidence-based, nationally recognized
guidelines that can be delivered by 9-1-1
call takers. Additionally, the measure directs
the Oklahoma Tax Commission to provide
the Authority a monthly report showing the
9-1-1 wireless fee deposits including the
name of the provider and the amount of each
deposit.
SB 745 (Weaver/Dobrinski) modifies the
annual retirement pay of retired police
officers to the annual salary limit of the
Economic Growth and Tax Relief
Reconciliation Act of 2001 multiplied by
2.5% multiplied by the number of years of
credited service. The measure provides for
members who retire as a result of a disability
to have such payments multiplied by 20
years of credited service, regardless of
whether the member served 20 years or not,
or the actual years of credited service if the
member served more than 20 years. At no
time shall a member receiving benefits
receive less than the amount the member
was receiving as of June 30, 2002.
SB 809 (Weaver/Ford) authorizes campus
police officers to retain the sidearm and
badge issued to them prior to retirement.
The measure provides that compensatory
time that accrued or expired during
emergency declarations issued in response
to the novel coronavirus shall carry over to
the end of the fiscal year following the year
in which the emergency declaration ended.
94
HB 2278 (Josh West/Rosino) measure
provides that, as it relates to distributions in
the Oklahoma Firefighters Pension and
Retirement System required to be made after
December 31, 2019, for individuals who are
70 ½ years old after that date, such
distributions shall take into account that age
70 ½ was stricken from the Code and
replaced by age 72.
HB 2293 (Dustin Roberts/Paxton) excludes
compensation paid to teachers if the sole
source of such compensation was paid for in
whole by federal funds or an externally
sponsored agreement such as a grant,
contract, or cooperative agreement and
received by a teacher for teaching during a
summer school program that is outside the
scope of employment of the teacher as it
relates to matching contributions from
employer retirement contribution
calculations. Additionally, the measure
provides that a teacher shall not receive
service credit for teaching during a summer
school program as defined in the measure.
HB 2457 (Dobrinski/Quinn) provides that,
as it relates to distributions in the Oklahoma
Police Pension and Retirement System
required to be made after December 31,
2019, for individuals who are 70 ½ years old
after that date, such distributions shall take
into account that age 70 ½ was stricken from
the Code and replaced by age 72.
HB 2458 (Lepak/Montgomery) authorizes
the Uniform Retirement System for Justices
and Judges (URSJJ) and the Oklahoma
Public Employees Retirement System
(OPERS) to release tax information of a
deceased member to a person acting in a
fiduciary capacity on their behalf for
purposes of filing a tax return. The measure
also provides that any actively participating
member of URSJJ or OPERS who’s first
participating service occurred on or after
July 1, 2013, and who works less than
fulltime but has had at least 5 years of full-
time employment during the 10 years
immediately preceding retirement is not
eligible to have their final average
compensation.
HB 2499 (Cornwell/Bergstrom) provides
that if an active member of the Oklahoma
Police Pension and Retirement System
(OPPRS) dies and does not leave a surviving
beneficiary, the member’s contributions to
the system may be paid to, if properly
designated by the member, a trust. The
measure also allows the benefit payment for
the month in which the member dies, if not
already paid, to be made to a trust upon the
death of a retired member with no surviving
beneficiary. The measure allows the same in
the event of the death of a beneficiary.
Finally, the measure allows OPPRS to pay a
death benefit to a trust.
HB 2824 (Sneed/Quinn) adds qualified
benefits administrator to the list of entities
that receive payments from the Oklahoma
Public Employees Retirement System as it
relates to the health insurance premium of
certain individuals receiving benefits from
the public retirement system.
Taxation and Tax Exemptions
SB 79 (Thompson/Wallace) exempts the
sale of property or services to or by the
University Hospital Trust as well as
nonprofit entities that are in a joint operating
agreement with the University Hospitals
Trust from the sales tax.
SB 181 (Taylor/Boles) modifies the formula
for payments made to the Oklahoma Tax
Commission for delinquent taxes. The
measure strikes language requiring the
payments be made in 2 equal installments
95
and instead requires the payments be made
in 2 installments.
SB 265 (Matthews/Nichols) exempts the
sale of tangible property to a city-county
library system from the sales tax.
SB 379 (David/Hasenbeck) reauthorizes the
income tax checkoff for the Court
Appointed Special Advocate program,
extending its authorization through the end
of tax year 2026.
SB 415 (Simpson/Tommy Hardin)
authorizes the Oklahoma Tax Commission
to disclose information relating to the name
and basis for eligibility of each individual
who qualifies for the sales tax exemption
granted to registered veterans to the
Oklahoma Department of Veteran Affairs.
The measure requires qualifying disabled
veterans to register with the veterans registry
in order to receive or continue receiving the
sales tax exemption.
SB 422 (Simpson/Kerbs) specifies the
documents the Oklahoma Tax Commission
shall accept as proof of eligibility to receive
the agricultural sales tax exemption.
SB 436 (Paxton/Pae) reauthorizes the
income tax checkoff for donations to the
Oklahoma chapter of the Y.M.C.A. Youth
and Government program.
SB 600 (Rader/Hilbert) exempts charging
stations with a charging capacity of less than
50 kilowatts and charging stations that do
not require payment for use from the $0.03
per kilowatt tax. The measure The measure
also directs the Oklahoma Tax Commission
to promulgate rules for the purpose of
determining a percentage basis equivalent
tax, which shall be recalculated annually.
The provisions of the measure shall become
effective upon the enactment of the
provisions of Enrolled House Bill No. 2234
of the 1st Session of the 58th Oklahoma
Legislature.
SB 601 (Rader/Pfeiffer) requires the
Oklahoma Tax Commission to pay interest
on tax refunds not paid within 45 days for
returns filed electronically and 90 days for
all other returns after the return is filed or
due, whichever is later. The measure also
allows the Commission to provide a later
due date for the returns of individuals and
certain entities if a state of emergency is
declared by the Governor or upon
declaration by the Internal Revenue Service
to postpone deadlines in disaster areas.
Lastly, the measure modifies the period of
underpayment for corporations to be 30 days
after the due date for returns established
under the Internal Revenue Code.
SB 770 (Stephens/Eric Roberts) extends the
income tax checkoff for the Oklahoma
Wildlife Diversity Program to January 1,
2022.
SB 825 (Standridge/Kevin West) provides
that any municipality levying a tax for the
purpose of funding public safety or any
other governmental purpose may not
redirect all or a portion of the dedicated tax
revenue to another purpose without a vote of
the people authorizing such an action.
SB 905 (Bullard/Davis) provides an income
tax credit of $20.00 per employee donating
blood to employers. The credit is not
refundable and shall sunset after tax year
2027. The total state-wide cap for the credit
is set at $500,000.00.
SB 909 (Pugh/Trey Caldwell) creates a sales
tax exemption for sales of tangible personal
property or services to a museum that
operates as part of a 501(c)(3) organization,
is not accredited by the American Alliance
96
of Museums, and operates on an annual
budget of less than $1 million until
December 31, 2024.
SB 915 (Howard/Trey Caldwell) creates an
income tax deduction based on an accredited
investor’s qualified equity investment in an
eligible Oklahoma venture capital entity.
The amount of the deduction shall be equal
to the actual investment. A qualified equity
investment shall not exceed $25 million for
any taxable year. Records of the equity
interest acquired by an accredited investor
shall be maintained by the accredited
investor and the eligible Oklahoma venture
capital company for a period of at least 5
years from the date the equity investment is
made by an accredited investor. Investments
made by investors into a company with
persons relating to the investor shall not
qualify for the deduction unless certain
conditions are met as outlined in the
measure. Additionally, such investments
shall not qualify for the deduction if the
investor owns 51% of the voting equity
interest. The deduction may not be used to
reduce the Oklahoma taxable income
amount or the Oklahoma adjusted gross
income amount to less than 0. The
Oklahoma Tax Commission shall be
required to notify claimants of the deduction
if the Commission denies the claim.
HB 1009 (Sims/Montgomery) 9 increases
the maximum gross household income to
qualify for an additional homestead
exemption of $1,000.00 from $20,000.00 to
$25,000.00. The measure excludes the
amount of any federal stimulus or relief
payments related to the COVID-19 virus
from the calculation.
HB 1060 (Boles/Paxton) provides a sales tax
exemption for the transfer of tangible
personal property between wholly owned
subsidiaries of a parent company and
between a parent company and its wholly
owned subsidiary.
HB 1062 (Boles/Garvin) extends the
homestead tax exemption for 100% disabled
veterans, their surviving spouses, or the
surviving spouse of a person who died while
in the line of duty to include those who own
homes located on land owned by a city or
town.
HB 1121 (Boatman/Thompson) extends the
sunset date for the Oklahoma Quality Events
Incentive Act from June 30, 2021, to June
30, 2026. The measure also requires the host
community to submit an economic impact
study of the quality event, as defined in the
measure, to the Oklahoma Tax Commission
within 60 days. The measure also modifies
the deadline for designating the date the
event will be hosted and the types of
expenses from 6 months to 30 days.
HB 1566 (Sims/Rader) requires that any
state tax generated from sales for admission
to a 501(c)(3) aquarium, or an aquarium
owned by a public trust or political
subdivision of Oklahoma, to be collected
and disbursed to the nonprofit, public trust,
or political subdivision responsible for the
operation of the aquarium. The disbursed
funds must be used for servicing debt
incurred by the aquarium or to promote
visitation for out-of-state residents.
HB 1588 (Dempsey/Burns) provides a sales
tax exemption relating to the sale of
commercial forestry service equipment
outlined in the measure to businesses
engages in logging, timber, and tree farming
from sales tax until January 2027.
HB 1935 (Martinez/Montgomery) exempts
the sales of tangible property to a nonprofit
entity organized prior to January 1, 2022,
that provides assistance to natural persons
97
following a disaster as defined in the
measure. Such assistance must emphasize
repair or restoration to single-family
residential dwellings, or the construction of
a replacement single-family residential
dwelling. The entity must expend at least
75% of its funds on the restoration to single-
family housing following a disaster to be
eligible for the program.
HB 2178 (Hilbert/Montgomery) creates a
tax deduction for taxpayers contributing to
accounts relating to the Achieving a Better
Life Experience (ABLE) Program. The
deduction shall not exceed $10,000.00 for an
individual taxpayer or $20,000.00 for
taxpayers filing a joint return in any tax
year.
HB 2292 (creates the Tobacco Products Tax
Enforcement Act of 2021. The measure
authorizes the Oklahoma Tax Commission
(OTC) to establish a Tobacco Products Tax
Enforcement Unit for the purpose of
enforcing tobacco tax laws through
investigations, audits, and inspections. The
provides that the excise tax on tobacco
products shall be due and payable on the 1 st
day of each month by the wholesaler.
Wholesalers are required by the measure to
file electronically with the OTC to
determine the amount owed on or before the
12th of each month. If the taxes are not
collected by the 1 st day of each month, the
tax shall be collected as a backup tax upon
the 1 st receipt of tobacco products by any
retailer or end user when received from a
source outside of the state or upon the first
sale or use when the product is
manufactured in this state. All purchase
invoices shall contain the license number of
the wholesaler and shall be made available
for inspection by the Tax Commission. Any
purchases of tobacco products from a person
who is not holding a current Oklahoma
wholesale tobacco license shall be
punishable by a fine of the greater $1,000.00
or five times the unpaid tax on such
products. Funds collected from the Unit
shall be deposited in the Tobacco Products
Tax Enforcement Unit Revolving Fund. Any
amount in excess of $2 million shall be
transferred to the General Revenue Fund.
HB 2297 (Dustin Roberts/Hall) defines
“fixed wireless broadband Internet service
provider” as an entity that offers Internet
access through a stationary fixed point-to-
point connection, often requiring direct line
of sight between the provider’s wireless
transmitter and its end-user consumer’s
receiver as it relates to the Ad Valorem Tax
Code. The measure clarifies that fixed
wireless broadband Internet service
providers are not included in the definitions
of transmission company and public service
corporation.
HB 2362 (Burns/Dugger) extinguishes any
claims for taxes or other liens or
encumbrances that the state and/or
municipality may have had on real estate
with respect to any deed conveying title to
the board of county commissioners where
such property was bid off in the name of the
county.
HB 2684 (Echols/Thompson) provides that
the excise tax on all wine and spirits shall be
collected and remitted by the wholesaler
who purchases the beverages for sale within
the state, unless the wine is shipped directly
to the consumer, where the excise tax shall
be collected and remitted by the winery
maintaining the direct wine shipper’s permit.
HB 2775 (Pfeiffer/Montgomery) amends the
definition of cost approach as related to the
Ad Valorem Tax Code to mean a method of
establishing the fair cash value of property
involving an estimate of current construction
cost of improvements, subtracting accrued
98
depreciation including any loss in value that
may be caused by physical deterioration, or
functional or economic obsolescence and
adding the value of the land. The measure
also requires the Ad Valorem Division of
the Oklahoma Tax Commission to provide
schedules of values of personal property in
accordance with Uniform Standards of
Professional Appraisal Practice (USPAP)
and International Association of Assessing
Officers (IAAO) requirements.
HB 2805 (Pfeiffer/Paxton) strikes the
requirement that livestock owned by a
general partnership, limited partnership,
corporation, limited liability corporation,
estate, trust, or other lawfully recognized
entity must have the primary purpose of
conferring economic benefits of such
ownership on 2 or more members of the
same family in order to qualify for an ad
valorem tax exemption.
HB 2866 (Wallace/Thompson) modifies the
banking privilege tax credit period to apply
to guaranty fees paid on or after January 1,
2022, and before January 1, 2025.
HB 2930 (Rick West/Simpson) expands the
Oklahoma Agriculture Enhancement and
Diversification Program to include grant
programs for agritourism, value-added
agriculture, as well as young and veteran
farmers. The measure also prohibits
awarding grants for growing, or any other
aspect of medical marijuana. The measure
eliminates the Agriculture Department’s
authority to allocate funds on a matching
basis as well as cooperative marketing loans
for entities that intend to work together. The
measure also exempts certain information
submitted to the Agriculture Department
from the Open Records Act.
HB 2946 (Wallace/Thompson) provides a
sales tax exemption for the sale, lease,
rental, storage, use or other consumption of
qualifying broadband equipment by Internet
providers or subsidiaries if the property is
directly used or consumed by the provider or
subsidiary for the purpose of establishing or
expanding broadband services in
underserved or unserved areas. The
exemption would be administered as a
rebate and the broadband equipment
provider would pay sales tax at the time of
the equipment purchase and then obtain a
rebate from the Tax Commission. The bill
requires the Department of Commerce to
prepare a report regarding the utilization of
the sales tax exemption/rebate process.
HB 2949 (Wallace/Thompson) provides
sales tax exemptions as it applies to the
transfer of tangible personal property by the
University Hospitals Trust, the transfer of
tangible personal property or services by or
to the University Hospitals Trust or
nonprofit entities in a joint operating
agreement with the University Hospitals
Trust, and the sales of personal property or
services for use in a clinical practice or
medical facility that is in a joint operating
agreement with the University Hospitals
Trust and is acquired or leased by the
organization for the University Hospitals
Authority, University Hospitals Trust or
University of Oklahoma on or after June 1,
2021.
HB 2960 (McCall/Treat) reduces the
corporate income tax from 6% to 4% for all
taxable years beginning after December 31,
2021.
HB 2961 (Wallace/Thompson) reduces the
bank privilege tax from 6% to 4% for all
taxable years beginning after December 31,
2021.
HB 2962 (McCall/Treat) reduces the
individual income tax by 0.25% for all

99
taxable years beginning on or after January
1, 2022. The measure also restores the
refundability of the earned income tax credit
and provides that it shall be computed using
the same requirements for computing the
earned income tax credit for federal income
tax purposes in effect for the 2020 income
tax year, other than the 5%amount already
provided for, which shall remain constant.
HB 2963 (Wallace/Thompson) reduces the
income tax for both corporations that are
equity owners in a pass-through entity and
the tax rate for pass-through entities such as
general partnerships, limited partnerships
and limited liability companies, from 6% to
4%.
HB 2964 (McCall/Treat) exempts
commercial trailers and semitrailers from
the 1.25% motor vehicle tax.
Tax Commission Funding
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Oklahoma Tax
Commission
$43,177,267
$43,844,417
1.55%
Transportation, Vehicle, and License
Measures
SB 8 (Bergstrom/Frix) designates State
Highway 69 from the Kansas border to the
Texas border as the Historic Jefferson
Highway Route. The cost associated with
signage required by this measure shall be
provided from private sources or other
categories of funding and shall include the
cost of the initial erection of signs as well as
the cost of potential replacement or
reconstruction of signs.
SB 61 (Bergstrom/Frix) specifies the
location of various highway intersections
designated as high-wide corridors. The
measure also removes the high-wide
corridor designation from the intersection of
US-177 and US-64, proceeding east on US-
64 to SH-108 as well as the intersection of
US-64 and SH108, proceeding south on SH-
108 and ending at SH-51.
SB 184 (Hick/Bush) authorizes the use of
Class 3 electric-assisted bicycles on multi-
use paths.
SB 263 (Daniels/Stearman) authorizes
individuals to reclaim the license plate of a
car when repossessing a vehicle that has not
had its license plate removed. The measure
also authorizes a person to obtain a 30- day
temporary permit on a vehicle in their
possession if said vehicle is subject to a lien.
SB 355 (Rosino/Sims) creates the Peer-to-
Peer Car Sharing Program Act. A peer-to-
peer car sharing program is defined as
business platform that connects vehicle
owners with drivers to enable the sharing of
vehicles for financial consideration. Such a
program may not offer renting motor
vehicles without a driver except as
specifically provided for in the measure. The
program is required by the measure to
assume liability of a shared vehicle owner
for bodily injury or property damage to third
parties or uninsured and underinsured
motorist or personal injury protection losses
during the car sharing period. The program
is exempted from this provision, provided
the car owner makes an intentional or
fraudulent material representation or
omission to the program or acts in concert
with a shared vehicle driver who fails to
$40,000,000
$42,000,000
$44,000,000
$46,000,000
$48,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Oklahoma Tax Commission
100
return the shared vehicle. The measure
further requires such programs to disclose to
shared vehicle owners or drivers certain
facts pertaining to the insured vehicle and
liability. The program may own the named
insured one or more policies of motor
vehicle liability insurance. The program is
required to ensure each of its drivers and
vehicle owners are insured under a motor
vehicle liability insurance policy that meets
certain requirements outlined in the
measure. The program’s, driver’s, or
owner’s insurer shall indemnify the car
sharing program if it is determined that the
shared motor vehicle's owner was in control
of the shared motor vehicle at the time of the
loss. Coverage under an automobile
insurance policy maintained by the peer-
topeer car sharing program shall not be
dependent on another automobile insurer
first denying a claim. The measure also
requires the program to notify the driver of a
vehicle with a lien on it may the terms of the
contract with the lienholder.
SB 463 (Hall/Kannady) modifies the
authority of the Oklahoma Tax Commission
(OTC) to remove motor license agents from
their position. The measure changes the at-
will termination of such agents to “for
cause” as defined in the measure. The
measure also requires the OTC to comply
with the provisions of the Administrative
Procedures Act as it relates to removing tag
agents. The FS strikes language requiring
the OTC to discharge motor vehicle agents
who fail to file timely accounting reports.
SB 607 (Rader/Pfeiffer) changes “shall” to
“may” as it relates to the Oklahoma Tax
Commission establishing another tag agency
in counties with a population in excess of
25,000.
SB 624 (Standridge/Frix) designates certain
sections of the highway system as the
William Charles "Charley" Coen Memorial
Highway, the Speaker Pro Tempore Jim R.
Glover Memorial Highway, the Medal of
Honor Recipient Sergeant John R. Crews
Memorial Bridge, the Trooper J.C. Magar
Memorial Highway, the Congressional
Medal of Honor Recipient Edward A.
DeVore, Jr. Memorial Bridge, the Navy
Cross Recipient CPL Russell Keck
Memorial Highway, the Sweetwater
Veterans Memorial Highway, the SSGT
Cecil Wellman Memorial Bridge, the
Officer Michael Bruce Keen Memorial
Bridge, the Tommy Wayne Haley Memorial
Bridge, the MSGT Michael Werdehoff
Vietnam MIA Memorial Bridge, the James
Amos Callins Memorial Bridge, the
Lieutenant Eugene Smith Memorial
Highway, the SP4 Alfred Dean Hildebrand
Memorial Highway the Bud Martin
Memorial Bridge, the Private Robert "Bob"
Clark Memorial Bridge, and the President
Donald J. Trump Highway. The measure
also strikes the requirement for persons
proposed to be so honored to have been
deceased not less than 3 years, received the
Medal of Honor, or been a member of the
armed forces or emergency personnel that
fell in the line of duty.
SB 706 (Rosino/Echols) authorizes any
personal delivery device to operate on any
sidewalk, crosswalk, road or street of any
county or municipality, notwithstanding any
other law. The measure requires each device
to have a unique identifying device number
providing contact information to the owner.
The measure prohibits any device from
interfering with traffic and obstructing rights
of way. Such devices must also travel under
10 miles per hour, be equipped with a
controlled stop system, be equipped with
lights on the front and back, and obey all
relevant traffic laws. Such devices are
prohibited from transporting hazardous
material. Owners are required to maintain
101
certain insurance requirements on such
devices. The measure also preempts any
municipal ordinance or law that would
otherwise govern the manufacture and
contents of personal delivery devices.
SB 787 (Weaver/Sterling) authorizes road-
service vehicles to equip flashing yellow and
white lights when providing road services
and repairs to disabled passenger vehicles.
Such lights must be visible from 500 feet to
the rear of the vehicle and may only be used
to warn operators of other vehicles to
exercise care in approaching, overtaking or
passing such vehicle.
SB 899 (Leewright/Hilbert) exempts
kiteboards from the registration
requirements provided for in the Oklahoma
Vessel and Motor Registration Act.
SB 967 (Pugh/Martinez) expands “political
subdivision” as it relates to the
Governmental Tort Claims Act to include a
regional transportation authority, its contract
operator, and railroads operating in interstate
commerce that sell a property interest or
provides services to a regional transportation
authority or allow the authority to use the
property or tracks of the railroad for the
provision of public passenger rail service.
The measure authorizes political
subdivisions to enter into a contract with
such entities to acquire commercial liability
insurance.
SB 998 (Standridge/Osburn) directs the
Oklahoma Tax Commission (OTC) to
implement a program providing for the
electronic storage of and filing of motor
vehicle certificates of title and allow a
lienholder to perfect, assign and release a
lien on a motor vehicle in lieu of submission
and maintenance of paper documents. The
OTC shall enter into competitive contracts
with qualified third-party service providers
to provide the necessary infrastructure for
such a program.to provide the necessary
infrastructure for such a program. The
measure provides for participating tag
agents to receive all fees provided by the
Oklahoma Vehicle License and Registration
Act notwithstanding current law. The OTC
is also authorized to expend monies from the
Oklahoma Tax Commission and Office of
Management and Enterprise Services Joint
Computer Enhancement Fund to implement
the provisions of the measure. Additionally,
the OTC is directed by the measure to
consult interested parties including, but not
limited to, representatives of the Oklahoma
Automobile Dealers Association, the
Oklahoma Bankers Association, the
Oklahoma Credit Union Association, and
the Oklahoma Tag Agent Coalition.
SB 999 (Bergstrom/Frix) creates the
Oklahoma Courier Application Services
Act. A courier application service (CAS) is a
business entity operating in Oklahoma that
uses a digital network to connect business
entities including itself, its affiliates, or
people to CAS drivers for the purpose of
providing courier services on an on-demand
basis. Additionally, such services shall not
be considered motor carriers nor shall a
CAS driver be considered a for-hire motor
carrier. Such services must adopt a zero-
tolerance policy against CAS drivers
operating under the influence of drugs or
alcohol while providing courier services.
CAS networks must require drivers to
submit information regarding his or her
address, age, driver license, and other
information required by the CAS prior to
admitting them into the network as a driver.
HB 1044 (Luttrell/Standridge) provides that
Killed in Action License Plates shall be
designed to honor members of the United
States Armed Forces who were killed in
action while engaged in combat with a
102
hostile force. The parents, siblings, half-
siblings, grandparents or spouse of the
deceased person, if the spouse has not
remarried, or if remarried, the remarriage is
terminated by death, divorce or annulment,
may apply for a killed in action license plate
upon presenting proper certification that the
person was killed in action and that the
person making the application is the
qualifying spouse or family member of the
deceased person. The Killed in Action
License Plate shall be exempt from any
minimum issuance criteria related to license
plate applications. Additionally, the measure
expands eligibility to apply for a Gold Star
Families License Plates to include siblings,
half-siblings, or grandparents. The
Oklahoma Aquarium License Plate is
reauthorized by the measure. The measure
also authorizes members of the Oklahoma
Veterans of Foreign Wars organization to
apply for the Oklahoma Veterans of Foreign
Wars License Plate. The Oklahoma City
Barons, Oklahoma City Redhawks, and
Tulsa Shock License Plates are stricken by
the measure. The measure directs the
Oklahoma Tax Commission to design the
Oklahoma Institute for Child Advocacy
License Plate in consultation with the
Institute. The Oklahoma Renewable Energy,
Scottish Rite Masons, New State Brand,
University of Oklahoma RUF/NEKS,
National Defense Service Medal, Paramedic,
Oklahoma Golf, Stillwater Public Schools,
Blue Star Mothers, Transportation to
Transportation, Tulsa Community College,
Veterans of the United States Armed Forces,
Navy Chief, Guthrie Street Kings, Epilepsy
Foundation, and America First License
Plates, and Tulsa Flag License Plate are
created by the measure. The Oklahoma Tax
Commission may enter into a licensing
agreement with the Historic Greenwood
District Juneteenth Festival.
HB 1059 (Boles/Garvin) removes a
provision which allowed commercial permit
holders to take the skills examination
without training. The measure allows a
motor license agent to process the voluntary
downgrade of a REAL ID Compliant
Commercial Driver License to any lower-
class license and removes a provision which
prohibits a motor license agent from
performing document recognition and other
requirements needed for approval of an
application for a Class A, B or C
commercial license. A licensee whose
record reflects a notation of the person's
proof of legal presence, verified by the U.S.
Department of Homeland Security, or proof
of U.S. citizenship, may obtain a REAL ID
Compliant Identification Card or a
Noncompliant Identification Card from a
motor license agent or the Department of
Public Safety, regardless of the status of the
license held by the licensee. Additionally,
the Department of Public Safety must
require designated examiner applicants,
driver education instructor applicants, third-
party examiner, and commercial school
driver education instructors to complete an
electronic national criminal history record
check.
HB 1065 (Tommy Hardin/Simpson) waives
all late fees and penalties as it relates to
vehicle registration if the vehicle was
reported and certified as stolen.
HB 1149 (Osburn/Rogers) requires persons
engaged in the activities of a used motor
vehicle sales to obtain a certificate of
registration from the Oklahoma Motor
Vehicle Commission. The measure provides
that the cost of any administrative fine is to
be borne by the employing entity. A
salesperson is deemed to be temporarily
approved and allowed to sell vehicles when
applications and fees are on file with the
Commission. The measure authorizes a
103
person to sell used motor vehicles without
obtaining a separate used motor vehicle
salesperson's certificate of registration if the
person has a certificate of registration from
the Oklahoma Motor Vehicle Commission
to sell new or unused motor vehicles at a
new motor vehicle dealer's licensed
franchise location which also sells used
vehicles. The cost of the registration for
each sales person is $50.00 to be renewed
biennially and may be transferred for a fee
of $25.00.
HB 1153 (Osburn/Garvin) modifies various
terms used in the by the Oklahoma Used
Motor Vehicle and Parts Commission
relating to manufactured homes. The
measure modifies the definition of
“manufactured home dealer” to include a
person who is engaged wholly or in part in
the business of leasing any new and unused,
or used, or both new and used manufactured
homes, that are considered personal
property, with an option to purchase or own
in any form at any time after beginning of
the lease term. The measure provides that a
“manufactured home dealer” does not
include a restricted manufactured home park
dealer. The measure modifies the definition
of “manufactured home salesperson” by
including restricted manufactured home park
dealers. The measure modifies the definition
of “restricted manufactured home park
dealer” to include persons engaged in
leasing manufactured homes with an option
to purchase or own in any form at any time
after the beginning of the lease term. The
measure requires a restricted manufactured
home park dealer to obtain a bond in the
amount of $30,000.00.
HB 1584 (Dollens/Brooks) designates a
section of law relating to approaching
stationary authorized vehicles on the
roadway as Bernardo's Law.
HB 1712 (Hill/Haste) creates the Road User
Charge Task Force. The Task Force is
directed to study methods that may be used
to record and report public road usage as
well as alternatives to the current system of
taxing highway use through motor vehicle
fuel taxes. The Task Force shall submit a
report of its findings to the Legislature no
later than December 31, 2023. The measure
directs the Oklahoma Tax Commission to
administer collection of any charges or fees
associated with the Road User Charge
Program. The expiration date for the task
force is June 30, 2024.
HB 1715 (Hill/Pugh) repeals a section of
law relating to a minor’s reading ability to
obtain driver licenses or permits. The
measure also repeals a section of law
requiring a minor to show that they are
enrolled in a public or private secondary
school to obtain permits and driver licenses.
HB 1788 (Pae/Montgomery) establishes a
definition for video toll collection system
account and requires an owner’s vehicle to
be registered with the Oklahoma Tax
Commission or similar registering agency
that permits access to registration
information with the Oklahoma Turnpike
Authority. The measure requires an owner
or operator of a vehicle to pay a charge to
the Department of Public Safety or other law
enforcement agency for the owner’s failure
to timely pay an invoice for charges
submitted by the Turnpike Authority
through its video toll system. Invoices may
be sent by other methods, not restricted to
certified mail. The measure also prohibits a
person from operating a vehicle on a
turnpike with the knowledge that the
registered owner is liable for outstanding toll
violations.
HB 1795 (Miller/David) provides that the
Department of Public Safety may in its
104
discretion suspend the driving privilege of a
person after receiving a report of a
conviction in another state relating to the
operation of a motor vehicle. Any action
taken by the Department shall not exceed
the penalty imposed by a court or the
Department in this state for a violation
substantially similar to the conviction in the
other jurisdiction which did not result in a
revocation of Oklahoma driving privileges.
Additionally, the measure provides that
suspension of a driver’s license shall be no
earlier than 180 days after providing notice
to the holder. The measure provides that a
person who provides proof of enrollment in
a federal or state government assistance
program may be considered proof of
hardship. The measure provides that a
provisional license may be issued to
suspended license holders allowing them to
drive from 6:00 a.m. to 11:59 p.m. and
12:00 a.m. to 5:59 a.m. in certain
circumstances. Eligibility for a provisional
license shall not take into consideration any
outstanding fines and fees owed.
HB 2182 (Johns/Standridge) authorizes the
removal and towing of a vehicle that is left
unattended upon any street, sidewalk, alley
or thoroughfare, and constitutes a hazard or
obstruction to the normal movement of
public transit along a rail fixed guideway.
HB 2183 (Johns/Standridge) directs the
Department of Public Safety to approve at
least 1 public transit, state, county, or
municipal government agency that maintains
a program instructing students for a Class A,
B, or C license to hire or employ third-party
examiners.
HB 2202 (Wolfley/Dahm) provides that no
citation may be issued by any state, county,
or municipal law enforcement officer during
the 30-day period immediately succeeding
the last day of the month during which a
vehicle registration should have been
renewed and a current license plate decal
obtained and displayed on the license plate
of the vehicle.
HB 2321 (Frix/Pemberton) clarifies that a
truck-tractor carrying cargo on the roadways
must maintain commercial auto, farm and
ranch, inland marine or cargo liability
insurance that applies to the costs of cleanup
of any substance that is spilled or otherwise
deposited on the roadway or right-of-way.
HB 2375 (Davis/Bergstrom) authorizes 2 or
more noncommercial vehicles owned by the
same person which have different
registration months to be registered in the
same month. A convenience fee of $5.00
shall be applied to such registrations. The
convenience fee shall be divided equally
with $2.50 of the fee to be deposited to the
credit of the Oklahoma Tax Commission
and $2.50 to be retained by the motor
license agent. When a noncommercial
vehicle’s registration month is changed,
license and registration fees shall be
prorated to account for the differences
between the previous renewal month and the
new renewal month and those fees are due at
the time of registration. The measure also
allows for the un-staggering of a special or
personalized license plate.
HB 2382 (Sterling/Weaver) defines a street-
legal utility vehicle as well as authorizes a
street-legal utility vehicle to be registered as
a motor vehicle and operated on roadways.
The vehicle may not be operated on the
interstate highway system or U.S. highways.
The vehicle must be issued a certificate of
registration, license plate, and yearly decal
from the Tax Commission and be registered
annually. The measure creates a 5-day
temporary tag for out-of-state owners of
street-legal utility vehicles.
105
HB 2465 (Dick Lowe/Paxton) authorizes the
Department of Public Safety to enter into
agreements with local school districts, the
Oklahoma Department of Career and
Technology Education, or institutions of
higher education to act as approved written
examination proctors for Class A, B, C, or D
driver license tests.
Transportation Funding
SB 298 (Dugger/McDugle) extends the
98.4% and 98.1% remittance rates for
gasoline and diesel respectively from July 1,
2022, to July 1, 2024.
SB 313 (Jech/Ranson) provides the fees for
all special or personalized license plates
issued after January 1, 2022, to be remitted
at the same time and subject to a single
registration period. Upon receipt of a special
license plate, the owner shall surrender the
original plate to the Oklahoma Tax
Commission. The measure also directs the
Oklahoma Tax Commission to determine a
method for making required fee adjustments
when a special or personalized license plate
is obtained during a 12-month period for
which a registration fee has already been
remitted.
SB 1057 (Thompson/Wallace) creates an
option for an 8-year license for commercial
licenses as well as Class-D licenses. Fees for
the 8-year licenses are also established by
the measure. Motor license agents are
authorized to collect a fee for processing
REAL ID and REAL ID Noncompliant ID’s
and Driver License applications as outlined
in the measure. Agents shall also receive
$5.00 for each processed application for a
REAL ID Compliant 4-year Driver License
and $10.00 for each processed application
for a REAL ID Compliant 8-year Driver
License. This measure also marries language
changes that have been enacted during this
legislative session in the statutes affected in
SB1057. The married language includes the
following: The Department of Corrections is
directed by the measure to coordinate with
the Department of Public Safety to provide
REAL ID Noncompliant Identification
Cards to all inmates who do not have a
current state-issued identification card or
driver license upon their release from
custody. Any inmate who is unable to
provide the Department with the required
information may use a Department of
Corrections-issued consolidated record card
to serve as a valid identification document to
obtain a REAL ID Noncompliant
Identification Card. Such cards shall be
valid for a 4-year period. The fee charged
for the issuance or replacement of a REAL
ID Noncompliant Identification Card hall be
deposited in the Department of Public Safety
Revolving Fund. The measure also
authorizes the Department of Public Safety
to enter into agreements with local school
districts, the Oklahoma Department of
Career and Technology Education, or
institutions of higher education to act as
approved written examination proctors for
written examinations relating to driver
licenses. The Department must approve at
least 1 public transit agency that has or
maintains a program instructing students for
a Class A, B or C license to hire or employ
thirdparty examiners. The Oklahoma Tax
Commission is required by the measure to
submit a monthly report of the
apportionment reimbursed out of the
License and ID Apportionment
Reimbursement Revolving Fund to the
Chair of the Senate Appropriations
Committee and Chair of the House of
Representatives Appropriations and Budget
Committee.
HB 2079 (McCall/Quinn) establishes the
Rural Economic Transportation Reliability
and Optimization Fund to be administered
by the Oklahoma Department of
106
Transportation. Monies from the fund shall
be appropriated to assist the Department in
the equitable prioritization of construction,
repair, and maintenance of state highways in
rural areas where robust economic
development has resulted in traffic safety
and circulation difficulties attributed to
significant and unanticipated increases in
traffic volumes and as fully recorded and
documented by the Department. Robust
economic development shall mean those
conditions of the highways of this state in
counties with a population of less than
50,000 where traffic volumes have increased
to become so impaired or hazardous as to
constitute a threat to the safety of persons or
property traveling over or upon such
highways. Once confirmed and documented,
the Department of Transportation may
utilize proceeds from the Rural Economic
Transportation Reliability and Optimization
Fund to incentivize and leverage the
acceleration and prioritization of
improvement projects existing in or to be
incorporated into the Eight-Year
Construction Work Plan.
HB 2234 (Hilbert/Taylor) creates the
Driving on Road Infrastructure with
Vehicles of Electricity (DRIVE) Act of
2021. The measure levies a $0.03 tax per
kilowatt hour or its equivalent on the electric
current used to charge or recharge the
battery or batteries of an electric vehicle
beginning January 1, 2024. This tax shall
not be applicable to electric vehicles charged
at a private residence at which the owner or
occupant of the residence uses electric
power paid for by the owner or occupant of
the residence. A charging station operator
shall make a full and conspicuous disclosure
at the site of the charging station and on the
website maintained by or on behalf of the
owner or operator. Any tax revenue
collected shall be apportioned to the DRIVE
Revolving Fund and counties throughout the
state. The measure provides that 85% of the
monies shall be apportioned to the Fund and
15% shall be apportioned to the counties.
The measure requires charging station
owners to remit the tax monthly, using
forms prescribed by the Tax Commission.
Legacy chargers, and public charging
stations that have never charged a fee for
their use, are exempt from remitting the tax
until 2041. The Tax Commission may
terminate a charging station owner’s
operator license if the owner fails to remit
the tax as required. The Oklahoma
Corporation Commission may inspect the
premises and equipment of the charging
station, and may require periodic third-party
testing, calibration, and inspection reports.
The Commission may set fees necessary to
carry out these duties, and may also assess a
penalty of not more than $500 per day to
charging station operators that fail to comply
with these requirements. Charging stations
constructed after November 1, 2021 shall
use a metering system that is capable of
imposing the cost for the charging service.
The metering system shall include a system
that allows for an audit of the electricity
supplied. The Oklahoma Tax Commission
may inspect the premises and equipment of
any charging station in order to enforce
compliance. The measure allows each motor
license agent to retain $3.56 for each electric
vehicle registered. Agents may also retain
$3.25% of the vehicle excise tax collected.
HB 2892 (Wallace/Thompson) hanges the
counties’ allocation of revenue from the
Oklahoma Vehicle License and Registration
Act. Beginning July 2021, 25% of the
monthly allocation that would otherwise be
credited to the County Improvements for
Roads and Bridges Fund would be
distributed directly to the counties: 1/3 of
the funds distributed in proportion by area,
1/3 by proportional share of county road
miles, and 1/3 by proportion based on

107
bridges in a county (For FY 2021-2026,
based upon yearly ODOT Bridge Summary
Reports for obsolete or deficient bridges;
beginning in 2026, based on the number of
bridges in each county according to the
ODOT 2020 Bridge Summary Report).
HB 2895 (Wallace/Thompson) updates the
funding mechanism for the Rebuilding
Oklahoma Access and Driver Safety
(ROADS) Fund. The measure apportions
$80 Million to the fund for the purpose of
making required payments for principal,
interest or other costs of borrowing, and
further authorizes apportionment of an
amount necessary to bring the amount in the
fund up to $575 Million for FY 2021 and
$590 Million for FY 2022 and every year
after.
HB 2896 (Wallace/Thompson) authorizes
the Oklahoma Capitol Improvement
Authority to issue bonds or other obligations
in an amount necessary to raise $200
million.
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Oklahoma
Department of
Transportation
$765,000,000
$761,893,663
-0.41%
Veteran Measures
SB 86 (Simpson/Miller) modifies the
membership criteria of the Oklahoma
Veterans Commission. The measure
decreases the number of veterans from the
Vietnam conflict from 3 to 1 and increases
the number of Persian Gulf Wars members
from 1 to 2 members. The measure requires
appointments to the Commission to be
broadly representative of the veterans of this
state in terms of age, gender, and ethnicity.
Additionally, the measure prohibits the
appointment of any member to the
Commission if he or she is related by
affinity or consanguinity within the third
degree to any person employed by the
Oklahoma Department of Veterans Affairs.
SB 114 (Simpson/ Tommy Hardin) repeals
the requirement for the War Veterans
Commission to prioritize applicants
currently confined in state institution as well
as provisions of law creating the Agent
Orange Outreach Commission and the Gulf
War Syndrome Outreach Commission.
SB 285 (Simpson/Tommy Hardin) directs
the Oklahoma Department of Veterans
Affairs to evaluate the Union Soldiers Home
and determine the measures and the amount
of funds necessary to meet all standards
required by the United States Department of
Veterans Affairs. The Department must
submit a report of its findings no later than
November 1, 2021, to the President Pro
Tempore of the Senate and Speaker of the
House.
SB 860 (J.J. Dossett/Burns) renames the
45th Infantry Division Museum as the
Oklahoma National Guard Museum and
authorizes the Museum to sell military
artifacts, books, and maps and to use the
proceeds to fund artifact purchases and
museum upgrades. The measure also
updates references to the museum as it
relates to the Armed Forces Veterans
Motorcycle License Plate.
$0
$200,000,000
$400,000,000
$600,000,000
$800,000,000
$1,000,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Department of
Transportation
108
HB 2271 (Cornwell/Simpson) authorizes
persons with a Purple Heart License Plate to
park in handicapped parking spaces.
HB 2374 (Davis/Bullard) directs the state to
develop a program to provide up to
$10,000.00 in financial assistance for
funeral expenses for eligible members of
state military forces who die in the line of
duty while serving on state active-duty
orders. The measure directs the Director of
the Oklahoma Department of Emergency
Management or their designee of the
Oklahoma Department of Emergency
Management to determine whether the
deceased member is eligible for the program
and to disburse funds from the Oklahoma
Homeland Security Revolving Fund to such
members.
HB 2508 (Kannady/Simpson) modifies the
eligibility criteria for Adjutant General to
require an individual to be eligible for a
Certificate of Eligibility if not already a
general officer. The measure also authorizes
the Governor to appoint multiple Assistant
Adjutants General after considering the
number of such positions recommended by
the National Guard Bureau. The Adjutant
General may, in writing, delegate specific
command or supervisory authority to the
Assistant Adjutants General or to general
staff officers. The measure directs the
Adjutant General to develop, publish and
maintain an enlisted and officer rating
scheme for all billets assigned to joint forces
headquarters and an organizational chart, to
be updated annually, showing the chain of
command between the Adjutant General and
the major commands of the Oklahoma
National Guard. The measure allows the
Governor to order the National Guard on
state active duty in the event of an imminent
or existing epidemic or pandemic. The
measure also adopts civil law protections
established in the federal Servicemembers
Civil Relief Act as state law and applies
them to state military forces on state active
duty or Title 32 active duty. Any officer or
employee of the state or political subdivision
who is not a member of the state military
force is entitled to military judicial leave
from their regular employment when serving
as a military trial judge or an appellate
military judge. The employing state agency
or political subdivision is required to pay
full regular pay for the first 30 regular
business days the employee is absent. For
any time after this, the employer must pay a
difference prescribed in the measure. The
bill modifies personal liability for military
forces to include only forces acting in the
line of duty. The measure directs the
Adjutant General to designate a State Judge
Advocate from the judge advocates duly
commissioned in the state military forces.
The senior force component judge advocate
of each force component shall oversee
certain duties. These senior force component
judge advocates shall also determine the
place of duty and frequency of reassignment
among the major commands for each judge
advocate and paralegal in their respective
force components. The State Judge
Advocate shall provide legal counsel to the
Adjutant General and, as requested, to the
other senior leaders of the state military
forces. The measure allows any officer
setting a punishment to mitigate that
punishment at any time, so long as the
mitigated punishment isn’t for a greater
period than the original punishment. Any
nonjudicial punishment may be appealed to
a senior officer designated by the Adjutant
General. The measure prohibits certain
military trial judges from reviewing certain
trial records if the judge served as an
assistant attorney general, district attorney,
assistant district attorney, or municipal
prosecutor who determined whether to
prosecute certain nonmilitary offenses. The
measure also provides for the calculation of
109
compensation for military trial judges. The
measure requires military magistrates to be a
member of the bar of a federal court or the
highest court of a state and certified to be
qualified for duty as a military magistrate by
the State Judge Advocate. No military
magistrate may issue warrants or court
orders for contents or records of wire or
electronic communications. The measure
modifies the definition of a judicial officer
to include a military magistrate. The
measure prohibits current state employees of
the Oklahoma Military Department and
federal technicians from being nominated to
serve on the Military Court of Appeals.
Statutory language establishing criminal
procedure in district courts shall not apply to
court-martial proceedings and where
statutory language conflicts within any
appellate provisions in the Oklahoma
Uniform Code of Military Justice, the
conflicting statutory language shall not
apply to appellate proceedings arising from
court-martial proceedings. State employees
serving as military trial judges or appellate
military judges are exempt from the
statutory language prohibiting someone
from holding an office under the laws of the
state or being a deputy of someone holding
office and also holding any other office or
being a deputy of another office. The
measure classifies members of the state
military forces on state active duty or Title
32 active duty as state employees regardless
of where their duties as employees are being
performed. The measure also clarifies that
the state is not liable for losses or claims
resulting from the activities of state military
forces on state active duty or Title 32 active
duty. The measure modifies leave of
absence procedures to include members of
state military forces on state active duty. If
the leave of absence exceeds the 30
regularly scheduled work days for which
state employees should receive their full
regular pay, the employing state agency is
required to pay the difference between their
full salary pay and their military base pay,
and this calculation shall exclude untaxed
military allowances and entitlements.
HB 2545 (Burns/Simpson) creates the
Oklahoma Uniformed Services Employment
and Reemployment Rights Act. The measure
prohibits employers from discriminating
against employees or prospective employees
based on their membership or service in
state military forces. Employers are further
prohibiting from discriminating against any
employee or prospective employee who has
enforced a protection, testified, assisted an
investigation, or exercised a right in regards
to the Oklahoma Uniformed Services
Employment and Reemployment Rights
Act. The measure also provides that any
person whose absence from employment is
necessitated by reason of service in state
military forces, provided that the person has
given advance notice to their employer, is
not absent for a cumulative length of more
than 5 years, and reports or submits a
reemployment application to their employer
shall be entitled to reemployment. The
measure further provides for exceptions to
these provisions, requirements regarding
application for reemployment, and order of
priority when reemploying members of the
same position. The measure requires the
administrator of each state agency or
political subdivision to submit a report to the
House and Senate Veterans and Military
Affairs committees by December 31 of each
year that contains the number of persons
whose reemployment with such state agency
or political subdivision was determined to be
impossible or unreasonable, with the reason
for that determination. The measure also
requires the Commissioner of Labor to assist
such persons and investigate any complaints.
The measure provides for complaint and
judicial process. Finally, the measure
requires each state agency and political

110
subdivision to provide training for their
human resources personnel about the rights,
benefits and obligations provided in the Act
and the application of its requirements.
Veterans Funding
HB 2944 (Wallace/Thompson) authorizes
the Oklahoma Capitol Improvement
Authority to issue obligations to acquire
property to develop and provide funding for
a new Oklahoma National Guard Museum in
a total amount necessary to generate $45
million in project funds. Upon final
redemption or defeasance of the obligations,
the title to the property and improvements
shall be transferred to the Oklahoma
Military Department.
Agency
FY21
Appropriation
FY22
Appropriation
Change
from
Original
Department of
Veteran Affairs
$33,316,393
$34,316,393
3.00%
Senate & House Joint Resolutions
SJR 23 (Standridge/Echols) is a continuing
application for an Article V Constitutional
Convention. The resolution calls for an
Article V Constitutional Convention in order
to pass a Constitutional Amendment to limit
federal appropriations made by the Congress
in a fiscal year to the amount of all
estimated federal revenues for that fiscal
year. The joint resolution also calls for
another Article V Constitutional Convention
that shall propose and consider amendments
that impose fiscal restraints on the federal
government, limit the power and jurisdiction
of the federal government, and limit the
terms of office for its officials and for
members of Congress.
HJR 1046 (Gann/Daniels) is the annual
omnibus administrative rule
approval/disapproval measure.
Vetoed Measures
SB 222 (Standridge/Pae) modifies the
definition of “bullying” within the School
Safety and Bullying Prevention Act to
include behavior that is repeated or highly
likely to be repeated. The measure requires a
school district board of education to update
its discipline and bullying policy annually.
The measure allows a student, school
employee, school volunteer or the parent or
legal guardian of a student to report an act of
bullying and requires anonymous reports to
be investigated in the same manner as other
reports. The measure provides immunity
from a cause of action to school employees,
school volunteers, students and parents or
legal guardians of students who promptly
report incidents of bullying in good faith. It
requires notification to be provided to the
parents or legal guardians of a reported
victim and reported perpetrator of bullying
within 24 hours of receiving a report of
bullying. The measure requires immediate
notification of the parents or legal guardians
of a student who expresses suicidal thoughts
or intentions or who encourages another
student to commit suicide. The bill requires
a bullying policy to contain a statement
prohibiting retaliation against a school
employee who notifies the district board of
education or the State Department of
Education of noncompliance with the
discipline and bullying policy. The measure
directs a district board of education to hold
at least one public hearing prior to adopting
$30,000,000
$31,000,000
$32,000,000
$33,000,000
$34,000,000
$35,000,000
$36,000,000
FY19…
FY20…
FY21…
FY 22…
Department of Veteran
Affairs
111
or amending the bullying policy and to
submit the approved policy to the State
Department of Education within 30 days of
adoption. The bill also requires a district
superintendent to provide a report on
bullying prevention activities and reported
incidents of bullying to the district board of
education at least once each semester at a
public meeting. It requires district boards of
education to provide each employee and
newly hired employee with a copy of the
bullying policy and an explanation of his/her
responsibilities.
SB 419 (J.J. Dossett/Waldron) allows a
teacher to use the highest-achieved score on
the U.S. history assessment administered in
high school to calculate the final grade for
the applicable social studies, history or
citizenship skills unit taken the same school
year the assessment is administered.
SB 500 (Boren/Dick Lowe) requires the
governing body of any city, town, or county
to prepare a disclosure report for any tax
incentives financing or tax increment district
established by the governing body if the
district has been in operation for at least 12
months. The disclosure report shall be
published on or before 60 business days
following the end of each fiscal year on the
website of the city, town, or county if such a
website exists beginning January 1, 2022,
and each year thereafter.
SB 821 (McCortney/McEntire) defines
“pharmacy benefits management” as it
relates to the Patient’s Right to Pharmacy
Choice Act and broadens pharmacy benefits
manager (PBM) to include any entity
performing pharmacy benefits management
activities. The measure broadens the
prohibition on PBM’s forcing customers to
use pharmacies that are directly or indirectly
owned by the PBM to include affiliates of
the PBM whether in-network, preferred, or
otherwise. Additionally, contracts between a
PBM and pharmacist shall not prevent the
disclosure of the total costs for pharmacist
services for a prescription drug or from
selling a more affordable alternative to the
covered person if such alternative is
available nor shall such contract fall below a
certain price point outlined in the measure.
PBM’s are also prohibited from
incentivizing or requiring customers to
differentiate between in-network
pharmacies, whether that pharmacy is in a
preferred or nonpreferred network, a retail
pharmacy, mail order pharmacy, or any
other type of pharmacy.
HB 1090 (Kendrix/Howard) clarifies the
authority of the Governor to request the
State Auditor and Inspector to examine the
books and accounts of public officers and
other governmental entities as well as the
authority of the State Auditor and the
Performance Audit Division to examine
books and accounts independently of a
request.
HB 1598 (Provenzano/Quinn) allows
personnel approved by the State Department
of Education to conduct vision screenings of
first and third graders. It authorizes the
Department of Education to approve the
vision screeners.
HB 1849 (Fugate/Brooks) creates a sales tax
exemption for parent-teacher associations
that are sanctioned by a school district and
school support organizations, defined as
sanctioned nonprofit organizations that
collect funds in support of a school
organization, club, or activity of a school.
HB 2088 (McCall/Thompson) exempts the
legislative and judicial branches of state
government from fees and costs from
services rendered by an executive agency.
112
HB 2090 (McCall/Leewright) expands the
membership of the Rural Broadband
Expansion Council from 14 to 16 members.
The measure directs the council to develop a
set of broadband incentive award guidelines
and make recommendations to the
Legislature. The guidelines would consider a
an area’s need for services, existing
broadband assets, whether existing resources
have been allocated to broadband in the
area, a preference for partnerships with other
governmental or private entities, and the
capacity of the provider to maintain assets
for an extended period.
HB 2313 (Lawson/Haste) modifies duties of
the Office of Juvenile System Oversight
(OJSO). The measure requires the OJSO to
conduct inspections of privately operated
children’s facilities not less than annually or
as needed. OJSO will have access to all
children and youth facilities to conduct site
visits and speak with residents.
HB 2500 (Culver/David) specifies that a
person serving on the Oklahoma Abstractors
Board must be a licensed abstractor and who
has held the Oklahoma abstract license for
not less than 5 years in a county in the
district from which the member is appointed
prior to appointment.
HB 2510 (Kannady/Thompson) modifies
“approved purpose” as it relates to the
Political Subdivisions Opioid Abatement
Grants Act to include addressing the needs
of parents and caregivers caring for babies
with neonatal abstinence syndrome. The
measure also provides for law enforcement
and emergency responders to receive
reimbursements for mental health response
training. Additionally, the measure
authorizes reimbursements of attorney fees
and expenses directly related to opioid
litigation incurred as part of legal services
agreements entered into before May 21,
2020. Eligible participants in the program
are expanded to include any political
subdivision or first responder organization
negatively impacted by the opioid crisis.
The measure provides for the Oklahoma
Opioid Abatement Board to award grants
based on criteria approved by the Board.
Such awards must be listed on a distribution
table.
